Although in the recent years, laparoscopy and Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) protocols have improved postoperative recovery in radical cystectomy (RC), the clinical efficacy of their association remains unclear. Our objective is to analyze the possible benefits obtained from laparoscopic RC (LRC) and its subsequent combination with an ERAS (ERAS-LRC) protocol compared to open RC (ORC).
Material and methodsWe analyzed 187 consecutive RCs with ileal conduit performed in our center, of which 139 met the inclusion criteria: 47 ORC, 39 LRC (both with conventional protocol) and 52 ERAS-LRCs.
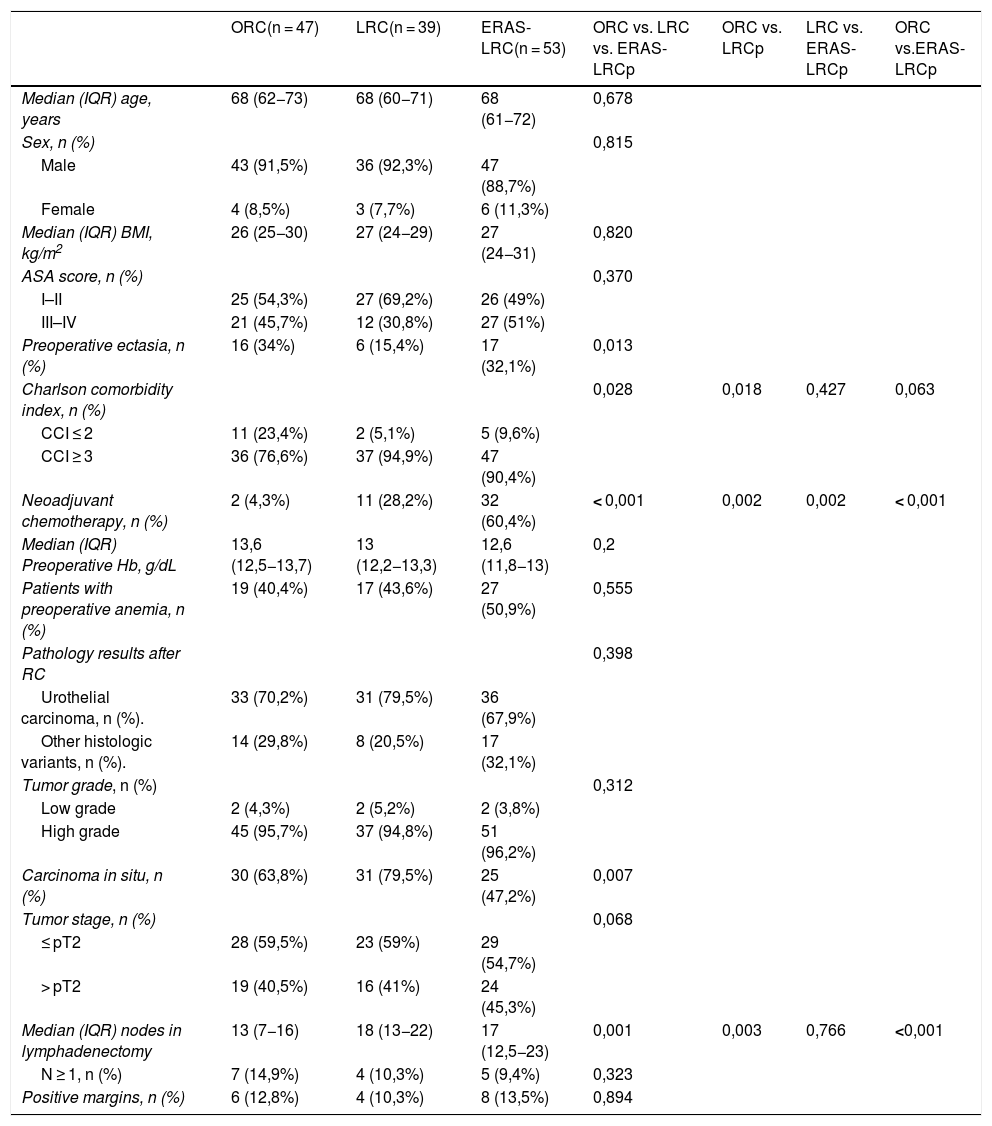
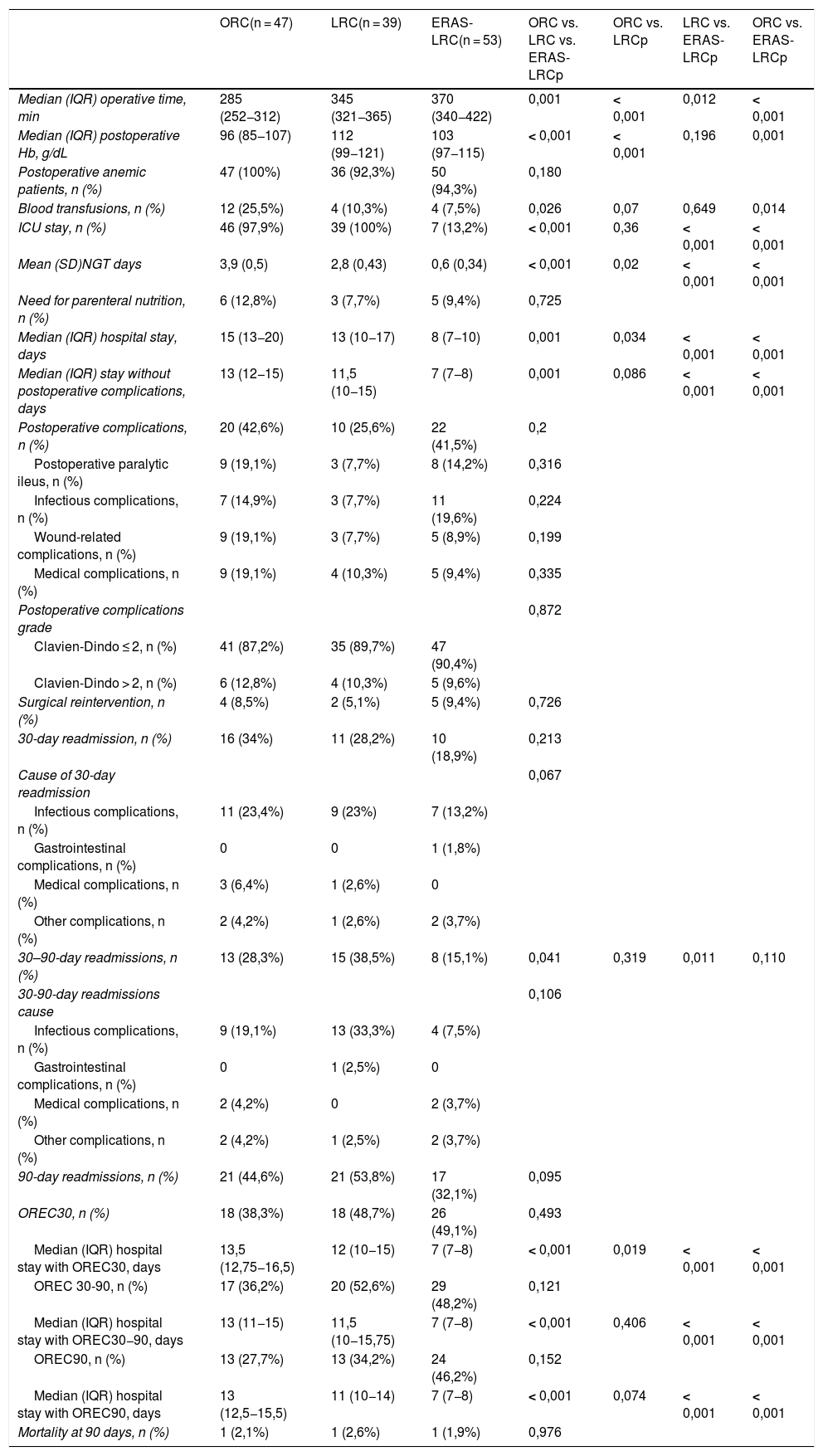
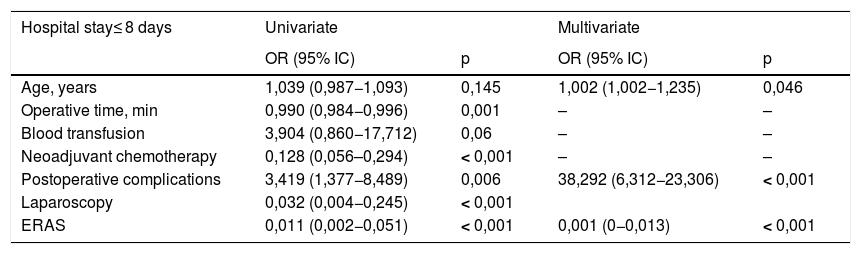
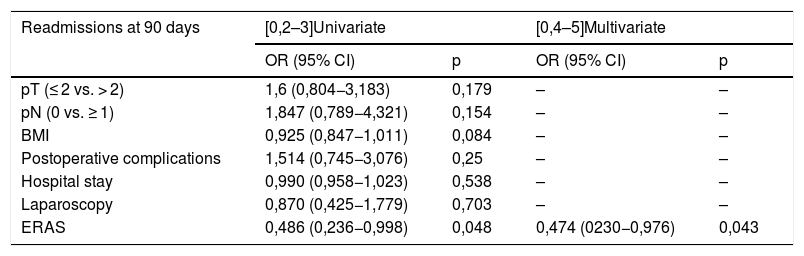
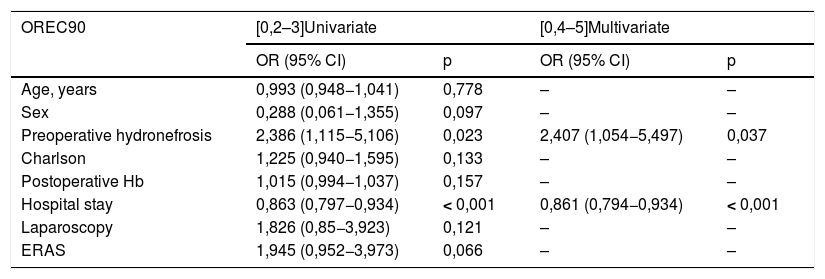
ResultsNo significant differences were found regarding age, sex, BMI and ASA score between groups. ERAS-LRC obtained a shorter length of stay than LRC and ORC (median 8 [7–10]) vs. 13 [10–17] vs. 15 [13–19.5] days, respectively; P < .001). ERAS-LRC had a shorter stay in the ICU and less days of nasogastric tube (P < .001). Postoperative complications and readmission rates were similar among groups. Multivariate logistic regression showed that absence of complications, younger age and ERAS behaved as independent factors for shorter hospital stay, while ERAS was the only independent factor of lower readmission rate at 90 days.
ConclusionsAlthough LRC presented perioperative benefits compared to ORC, the results were better after the implementation of an ERAS protocol. ERAS protocol had stronger impact on recovery than the surgical approach of the procedure.
Aunque en los últimos años la laparoscopia y los protocolos de rehabilitación multimodal Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) han demostrado mejorar la recuperación postoperatoria en la cistectomía radical (CR), la eficacia clínica de su asociación aún sigue en estudio. Nuestro objetivo es analizar los posibles beneficios obtenidos de la CR laparoscópica (CRL) y su posterior combinación con ERAS (ERAS-CRL) frente a la CR abierta (CRA).
Material y métodosAnalizamos 187 CR consecutivas con derivación urinaria heterotópica realizadas en nuestro centro, de las cuales 139 cumplieron los criterios de inclusión: 47 CRA, 39 CRL (ambas con protocolo convencional) y 52 ERAS-CRL.
ResultadosNo se encontraron diferencias significativas en cuanto a edad, sexo, IMC y ASA entre los 3 grupos. ERAS-CRL obtuvo una estancia hospitalaria más corta que CRL y CRA (mediana 8 [7–10]) vs. 13 [10–17] vs. 15 [13–19,5] días, respectivamente; p < 0,001). ERAS-CRL también tuvo una estancia más corta en la UCI y menos días de sonda nasogástrica (p < 0,001). Las complicaciones postoperatorias y los reingresos fueron similares en los 3 grupos. La ausencia de complicaciones, una edad más joven y ERAS fueron factores independientes relacionados con una menor estancia hospitalaria, mientras que ERAS fue el único factor independiente asociado con un menor reingreso a los 90 días.
ConclusionesAunque la CRL presentó beneficios perioperatorios respecto a la CRA, los resultados fueron mejores tras la implementación de un programa ERAS, siendo el impacto de este último más importante que la técnica quirúrgica utilizada.