Following current European guidelines, lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) are produced by several causes and, thus, thorough clinical assessment should be undertaken for a correct therapeutic management. This study was conducted in order to assess the symptoms profile and their impact on health-related quality of life (HRQL) of male patients attending urology outpatient clinics.
Materials and methodsEpidemiological, cross-sectional study including adult male patients (n=826) presenting with at least one de novo previously untreated LUTS. Socio-demographic and clinical variables were collected. Patients completed IPSS, Bladder Control Self-Assessment Questionnaire (B-SAQ) and SF-12 questionnaires.
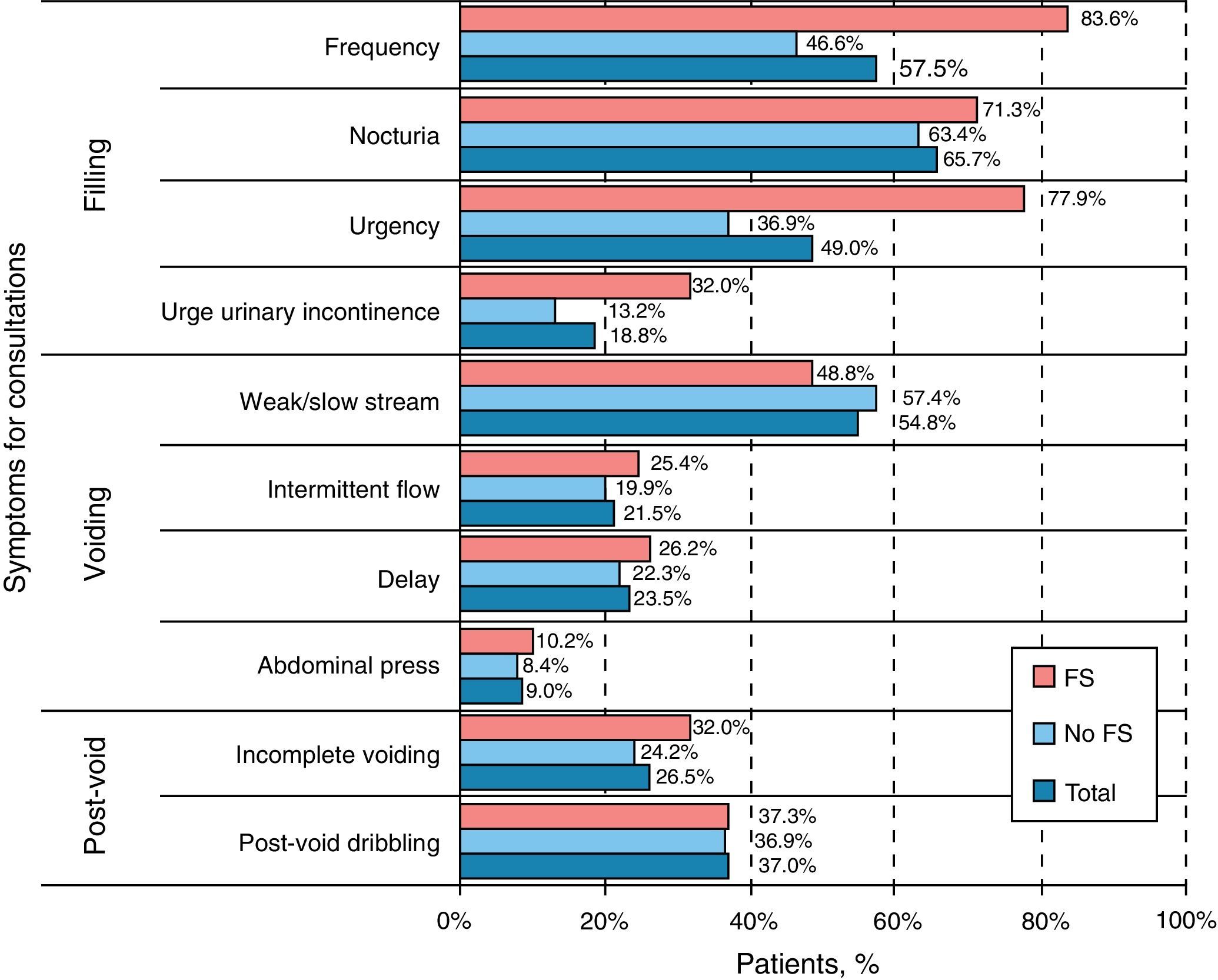
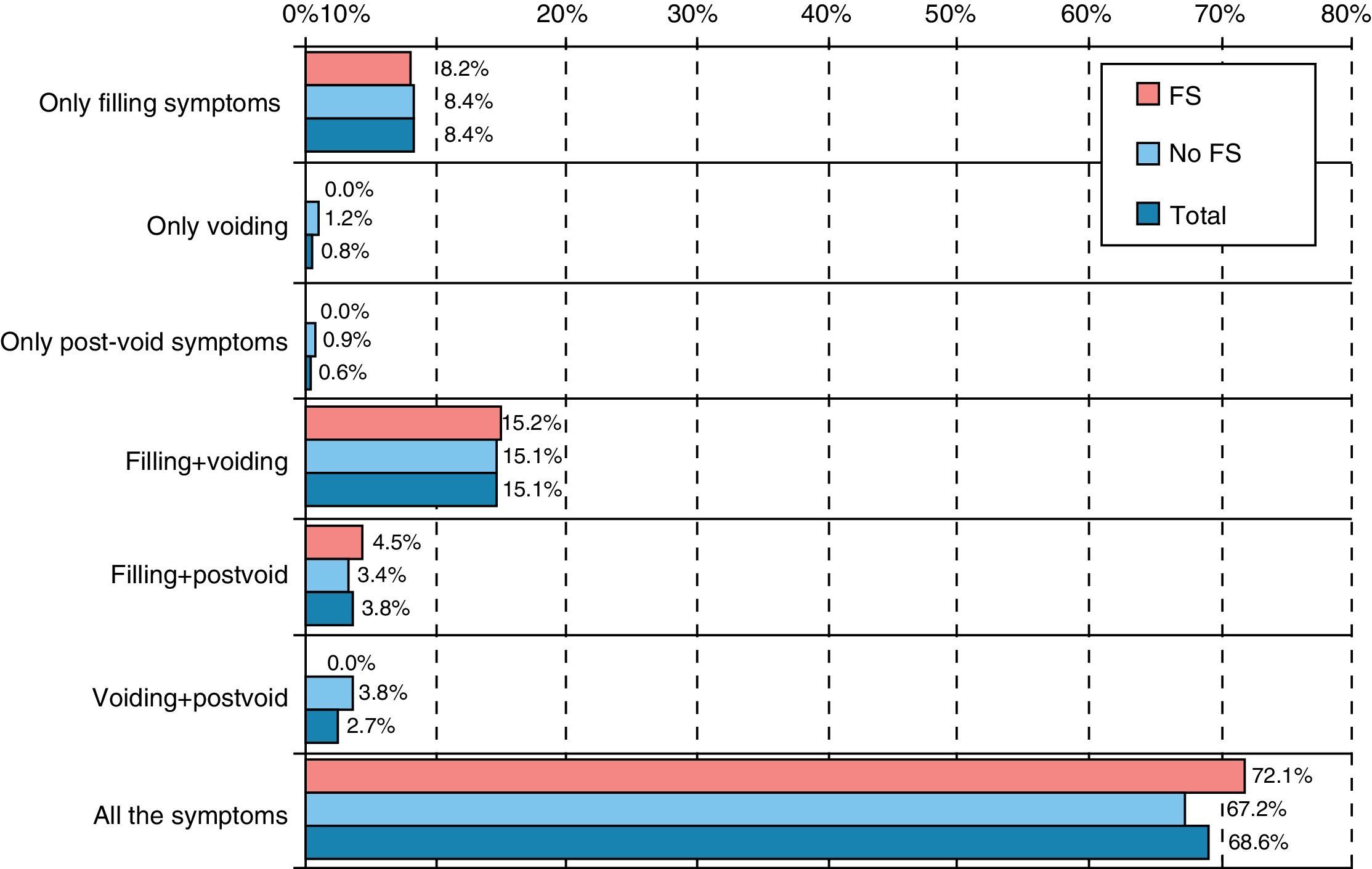
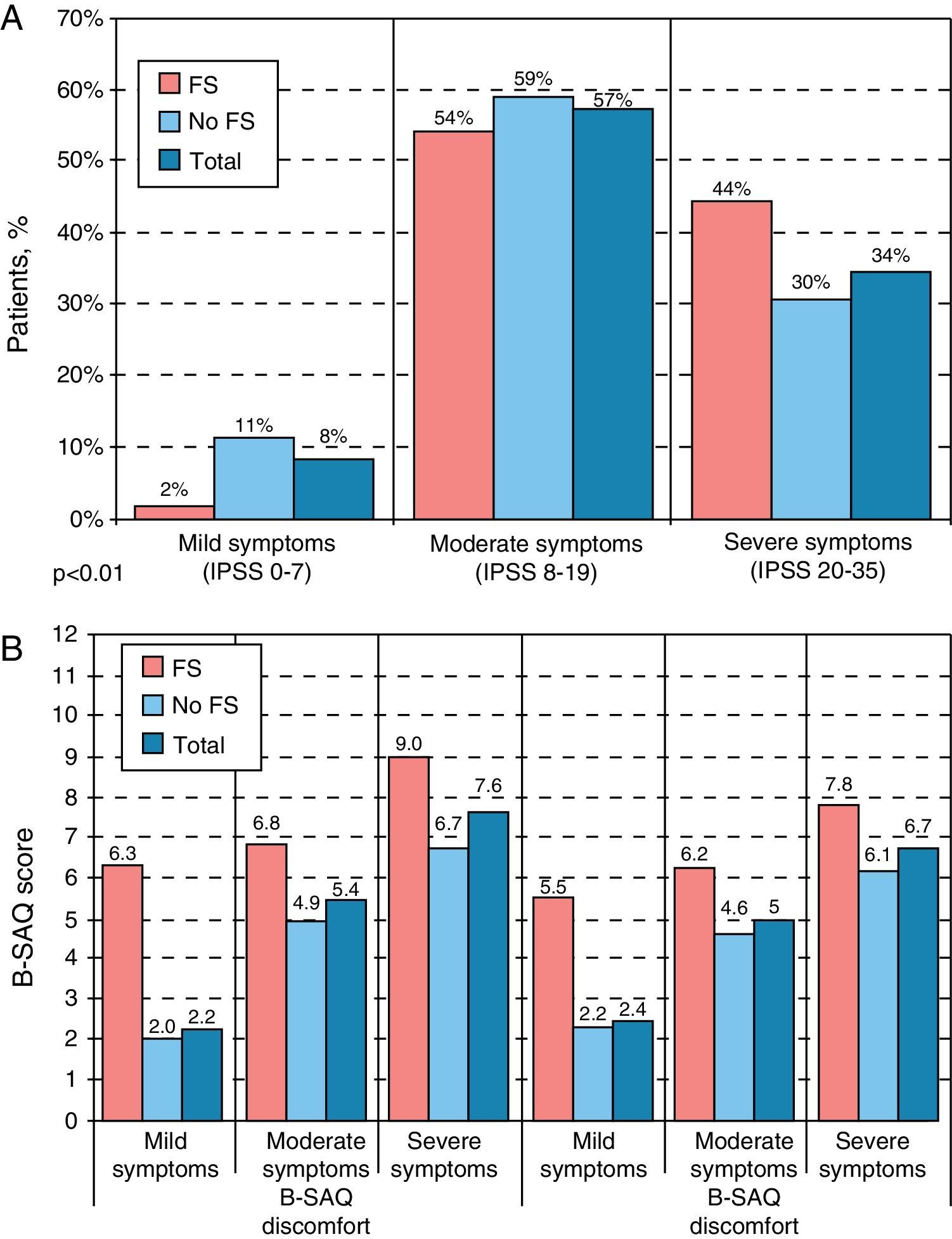
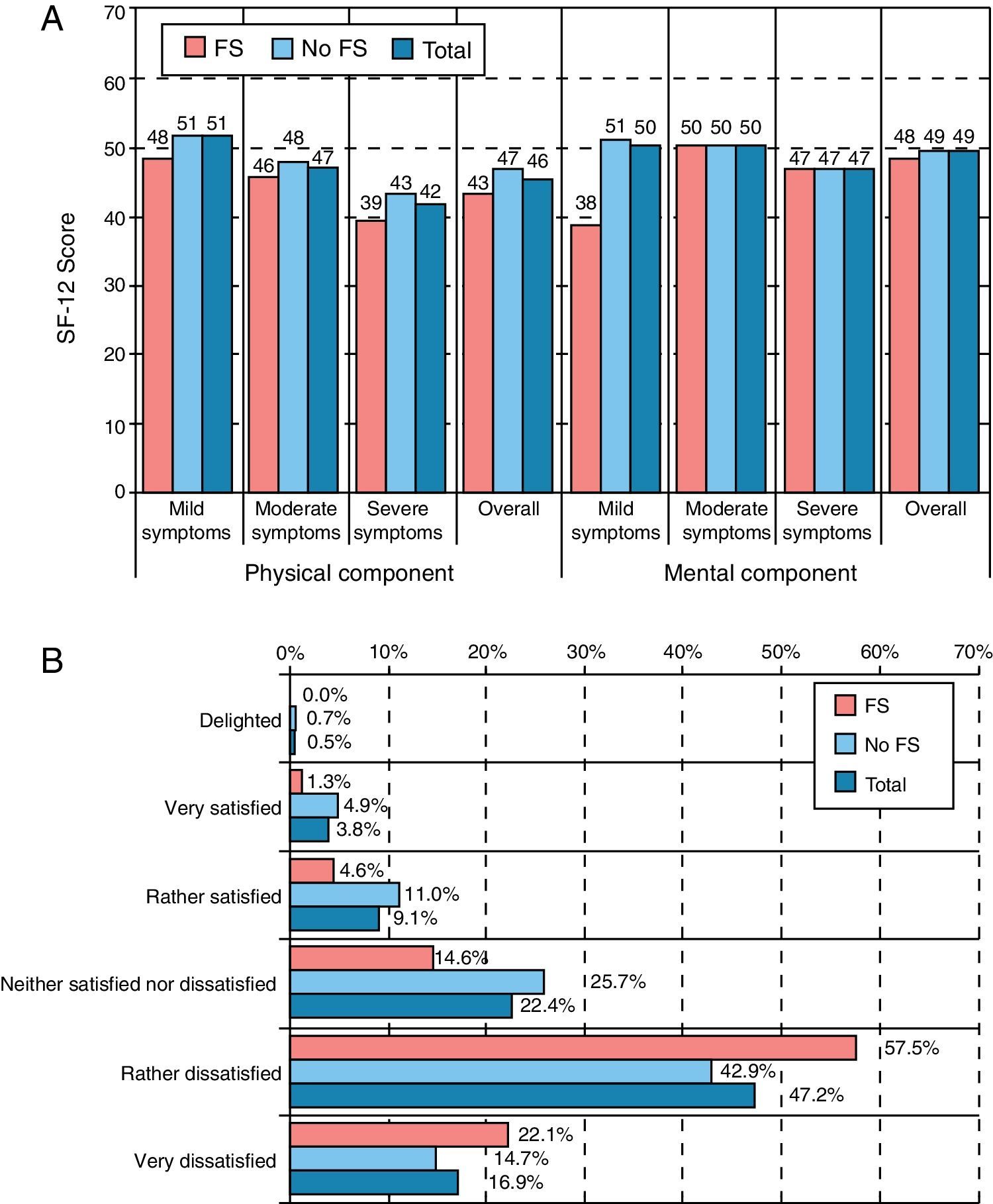
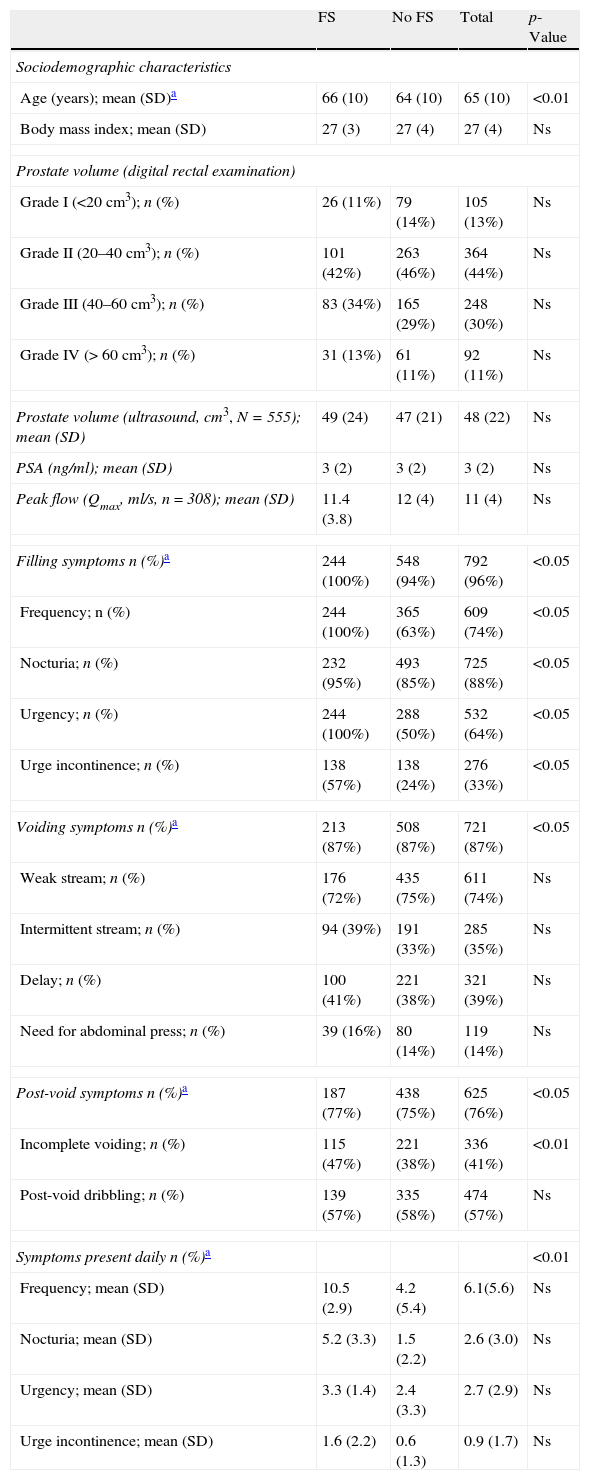
ResultsMean age (SD) was 65 (10) years. A combination of storage, voiding and post-micturition symptoms were present in 69% of subjects and 30% showed ≥2 urgency episodes and ≥6 micturitions daily (storage symptoms – SS – sub-population). Storage symptoms were the reason for consultation in 86%. Mean peak urinary flow (Qmax) was 11.4mL/s, in 44% of patients, prostate volume was 20–40mL and 91% showed moderate or severe symptoms on IPSS with an overall mean (SD) score of 17 (7). SS sub-population had higher B-SAQ scores (6.9 versus 4.8 for symptoms; 7.8 versus 5.1 for bother), and worse HRQL (IPSS item 8).
ConclusionsThese findings support the importance of addressing treatment adequately according to patient profile, bothersomeness and impact on HRQL.
La etiología multifactorial de los síntomas del tracto urinario inferior (STUI) justifica su evaluación detallada para un adecuado abordaje terapéutico según las guías europeas actuales. Para conocer el perfil sintomático e impacto en la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud (CVRS) de pacientes varones que acuden a consulta de urología se desarrolló el siguiente estudio.
Material y métodosEstudio epidemiológico, transversal en 826 varones adultos con ≥1 STUI de novo no tratados previamente. Se recogieron variables sociodemográficas y clínicas. Los pacientes cumplimentaron la Puntuación internacional de síntomas prostáticos (IPSS), Cuestionario de autoevaluación del control vesical (CACV) y cuestionario SF-12.
ResultadosLa edad media (DE) fue de 65 (10) años. El 69% presentaba una combinación de síntomas de llenado, vaciado y posmiccionales. El 30% tenía ≥2 episodios de urgencia y ≥8 micciones al día (subpoblación con síntomas de llenado [SLL]). Los SLL fueron el motivo de consulta en el 86% de los casos. El flujo urinario máximo medio fue 11,4ml/s y el 44% tenía volumen prostático entre 20–40cc y el 91% síntomas moderados o graves (IPSS) con puntuación media (DE) de 17 (7). La subpoblación con SLL tenía puntuaciones mayores del CACV (síntomas 6,9 vs 4,8; molestias 7,8 vs 5,1). La subpoblación con SLL presentaba peor CVRS (IPSS ítem 8).
ConclusionesEstos hallazgos evidencian que es importante conocer el perfil de síntomas de cada paciente y el grado de molestia e impacto en la calidad de vida para orientar adecuadamente el tratamiento.