Introducing a consensus on pharmacological treatment of male LUTs to be applied to Urology Primary Care.
Evidence compilationThe consensus has been created by an expert committee based on the latest recommendations by the European and American Guides for male LUTs treatment. Also, a bibliographic review of the latest advances in the therapeutical approach to these patients has been carried out.
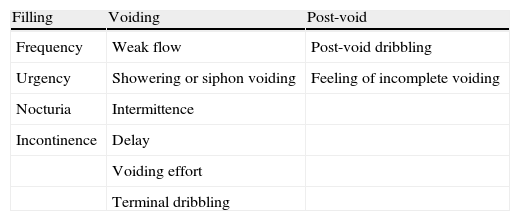
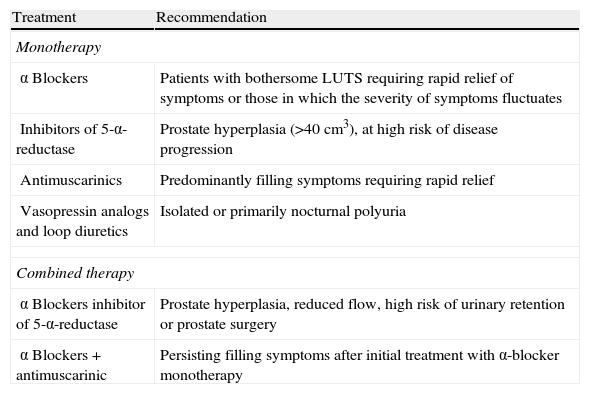
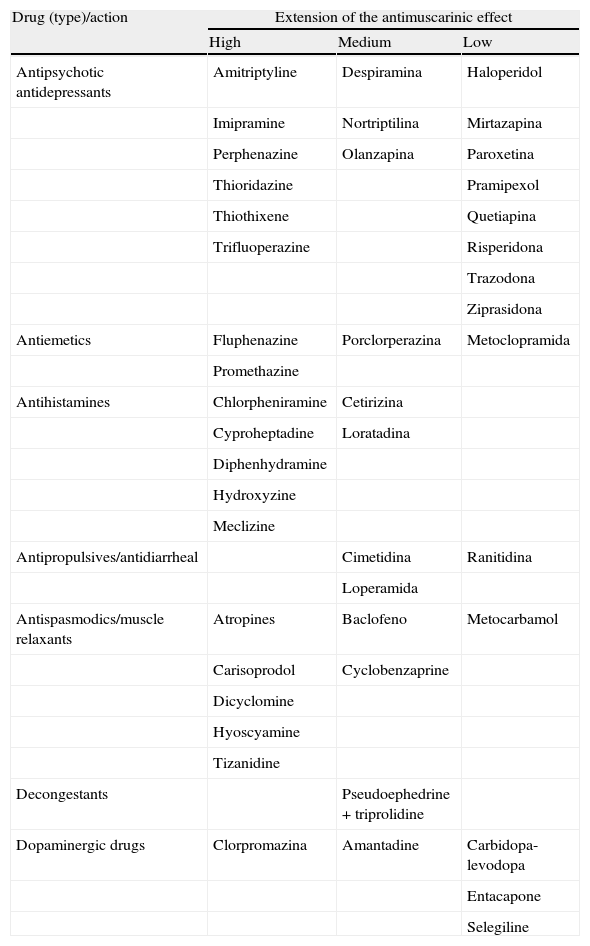
Evidence synthesisAlthough the prevalence of both LUTs and overactive bladder is high, and its impact on the quality of life and social cost has been widely described, the number of patients treated is low. On the other hand, current clinical practice does not necessarily match the Guides and for this reason false perceptions of the available treatments circulate. For instance, men with storage LUTS are often treated inadequately with α-blockers or 5-α-reductase inhibitors due to underlying obstructive disorders. However, it is known that the incidence of real obstruction tends to be low. Current evidence, though limited, shows that antimuscarinic drugs may be used safely by men with LUTs, and are not associated with an increase in the prevalence of high urinary retention.
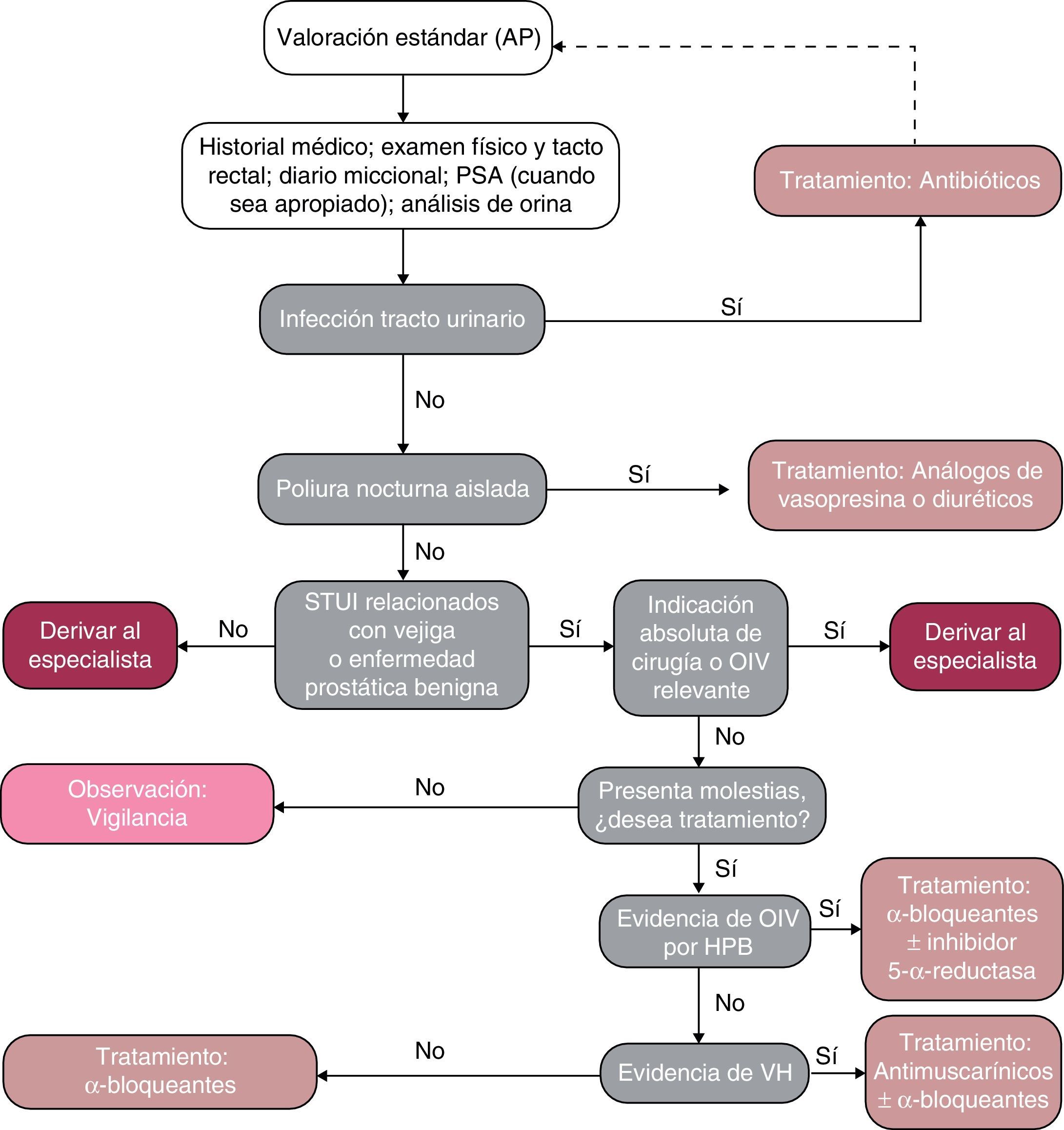
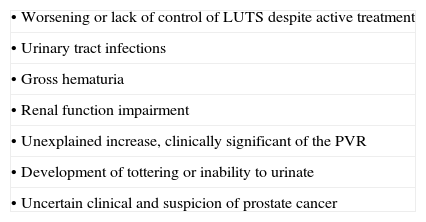
ConclusionWe propose an algorithm for the management of male LUTs in which various levels of clinical evaluation are shown for a specific diagnose, as well as for choosing the most appropriate treatment.
Presentar un documento de consenso sobre el tratamiento farmacológico de los síntomas del tracto urinario inferior (STUI) en el hombre para su aplicación en el ámbito de la urología en atención primaria.
Adquisición de evidenciaEste documento de consenso se ha elaborado y consensuado por un comité de expertos en base a las últimas recomendaciones dadas en las Guías Europeas y Americanas, para el tratamiento de STUI en hombres. Además, se ha realizado una revisión bibliográfica de los últimos avances en el abordaje terapéutico de estos pacientes.
Síntesis de evidenciaAunque la prevalencia de STUI y vejiga hiperactiva es alta, y su impacto sobre la calidad de vida y los costes para la sociedad han sido bien documentados, el número de pacientes que reciben tratamiento es bajo. Por otro lado, la práctica clínica actual no concuerda con las Guías y por este motivo se generan ideas equivocadas sobre los tratamientos disponibles. Por ejemplo, los hombres con STUI de llenado son frecuentemente tratados de forma inadecuada con α-bloqueantes o inhibidores de la 5-α-reductasa, debido a la sospecha de trastornos obstructivos subyacentes. Sin embargo, hoy es sabido que la incidencia real de obstrucción es más bien baja. Las evidencias actuales, aunque limitadas, demuestran que los fármacos antimuscarínicos pueden ser empleados con seguridad clínica en hombres con STUI, no asociándose a incremento de la prevalencia de retención aguda de orina.
ConclusiónSe propone un esquema para el manejo de los STUI en hombres en el que se muestran varios niveles de evaluación clínica requeridos para un diagnóstico específico y, también, para la determinación de un tratamiento con los medicamentos más adecuados.