Clinical practice guidelines recommend measuring serum testosterone (ST) during androgenic suppression (AS) to assess its efficacy and define castration resistance (CR). The objectives of this systematic review were to assess the level of scientific evidence that justify checking ST levels during AS, when to perform it and for what purpose.
Material and methodsWe performed a search in PubMed with the following mesh terms: androgen suppression, testosterone, and prostate cancer. The search was narrowed to original articles published in English.
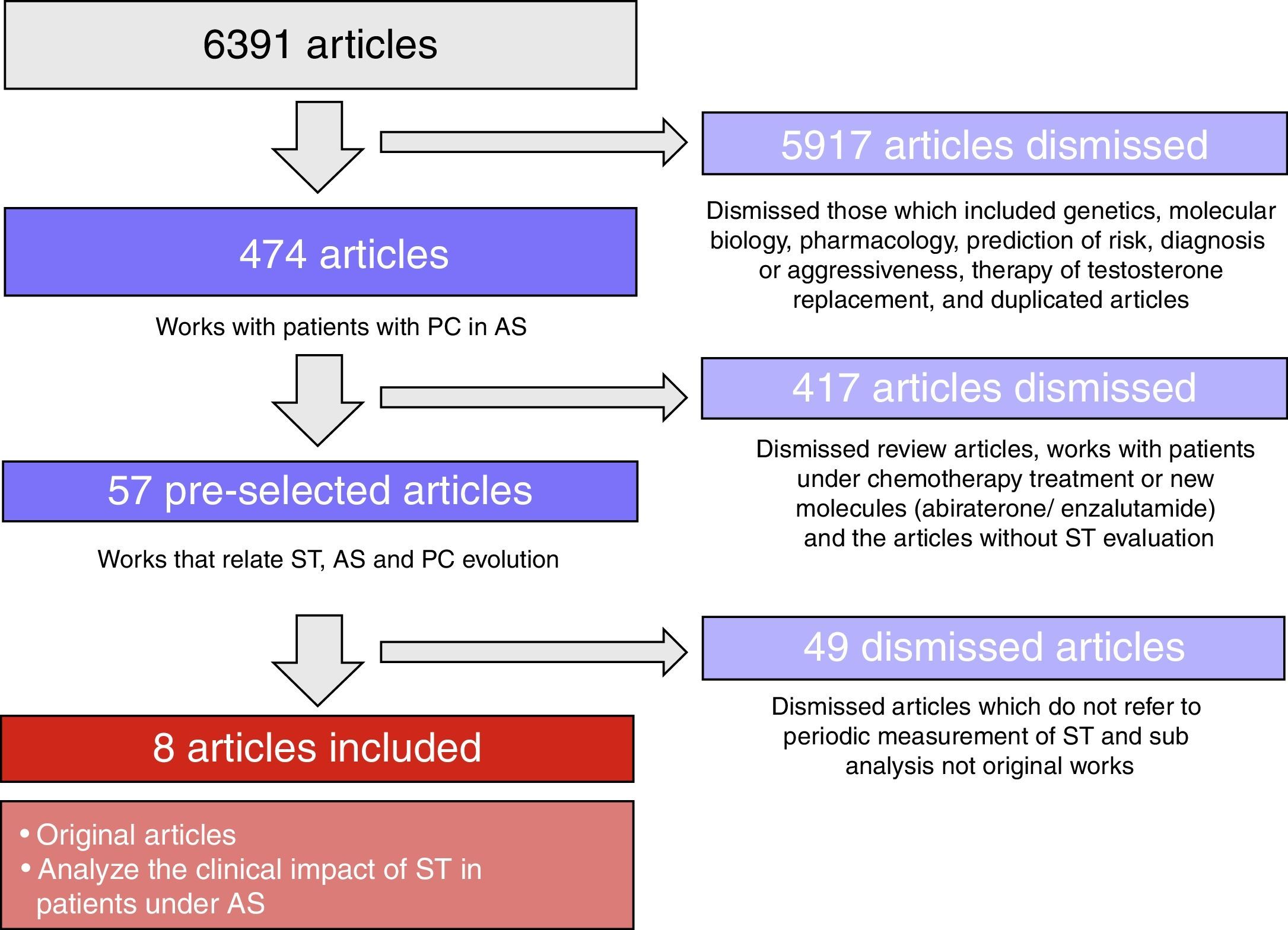
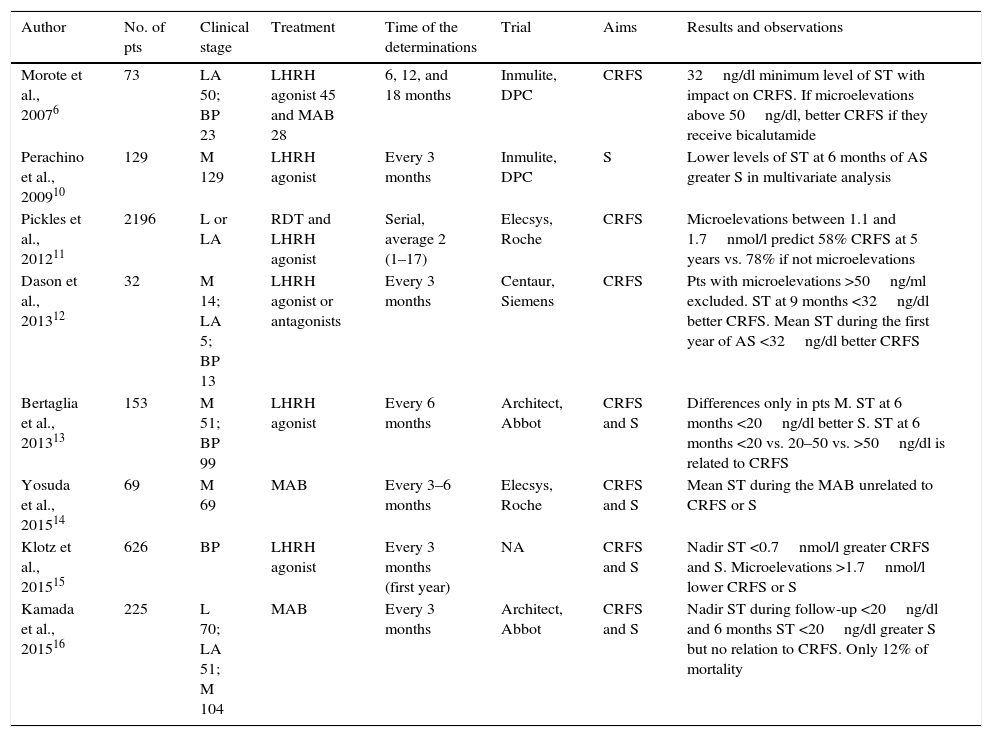
ResultsWe found 8 publications that analyzed the clinical impact of ST concentrations during AS. In all of the series, ST was measured using chemiluminescent assays. However, only indirect methods based on liquid or gas chromatography for its extraction and subsequent quantification using mass spectrometry are recommended, especially for measuring low levels. The endpoints were specific survival and CR-free survival. Six studies were retrospective. The series were not uniform in terms of clinical stage, types of AS and ST assessment methods. In general, low ST levels (<20ng/dl or <32ng/dl) were related to longer CR-free survival. The measurements were performed every 3 or 6 months. Four studies confirmed the beneficial effect of adding bicalutamide when detecting microelevations above 50ng/dl.
ConclusionsThe level of scientific evidence justifying the measurement of ST during AS is low, and the methods employed for quantifying ST levels are inadequate. However, we consider it useful to check ST levels during AS, and there appears to be an association between low ST levels and better disease outcomes. In the event of microelevations above 50ng/dl, we recommend the administration of bicalutamide.
Las guías de práctica clínica recomiendan determinar testosterona sérica (TS) durante la supresión androgénica (SA) para evaluar su eficacia y definir la resistencia a la castración (RC). Los objetivos de esta revisión sistemática han sido evaluar la evidencia científica que puede justificar su control durante la SA, cuándo hacerlo y para qué.
Material y métodosSe realizó un búsqueda en PubMed con los términos MeSH: androgen suppression, testosterone, and prostate cancer. Se acotó la búsqueda a artículos originales publicados en inglés.
ResultadosSe encontraron 8 publicaciones que analizaron el impacto clínico de la concentración de TS durante la SA. En todas las series se determinó la TS mediante ensayos quimioluminiscentes. Sin embargo, solamente métodos indirectos basados en cromatografía líquida o gaseosa para su extracción y posterior cuantificación mediante espectrometría de masas son recomendados, especialmente para determinar niveles bajos. Los objetivos fueron supervivencia específica y libre de RC. Seis estudios fueron retrospectivos. Las series no fueron uniformes respecto al estadio clínico, tipos de SA y forma de valorar la TS. En general, niveles de bajos de TS (<20ng/dl o <32ng/dl) se relacionaron con mayor supervivencia libre de RC. Las determinaciones se realizaron cada 3 o 6 meses. En 4 estudios se confirmó el efecto beneficioso de añadir bicalutamida cuando se detectaron microelevaciones por encima de 50ng/dl.
ConclusionesEl nivel de evidencia científica que justifica la determinación de TS durante la SA es bajo, y los métodos utilizados para su cuantificación inapropiados. A pesar de ello, se considera útil controlar nos niveles de TS durante la SA, y parece existir una asociación entre niveles bajos y mejor evolución de la enfermedad. En caso de microelevaciones por encima de 50ng/dl se recomienda la administración de bicalutamida.