Despite early diagnosis of prostate cancer, seminal vesicle invasion is still a common clinical scenario nowadays. The objective of this study is to evaluate clinical and pathological prognostic factors in that subgroup of patients.
Material and methodsAfter approval of our Ethical Committee, we selected all pT3b prostate cancer patients operated between 1987 and 2010. Neoadjuvant treatment patients were excluded. The biochemical free survival periods BFS and the period free of complementary treatment were calculated with the Kaplan Meier method. Cox regression model was used to select those variables associated with biochemical failure and the need for complementary treatment. We considered complementary treatment when radiotherapy or hormone therapy in an adjuvant or salvage scheme was required.
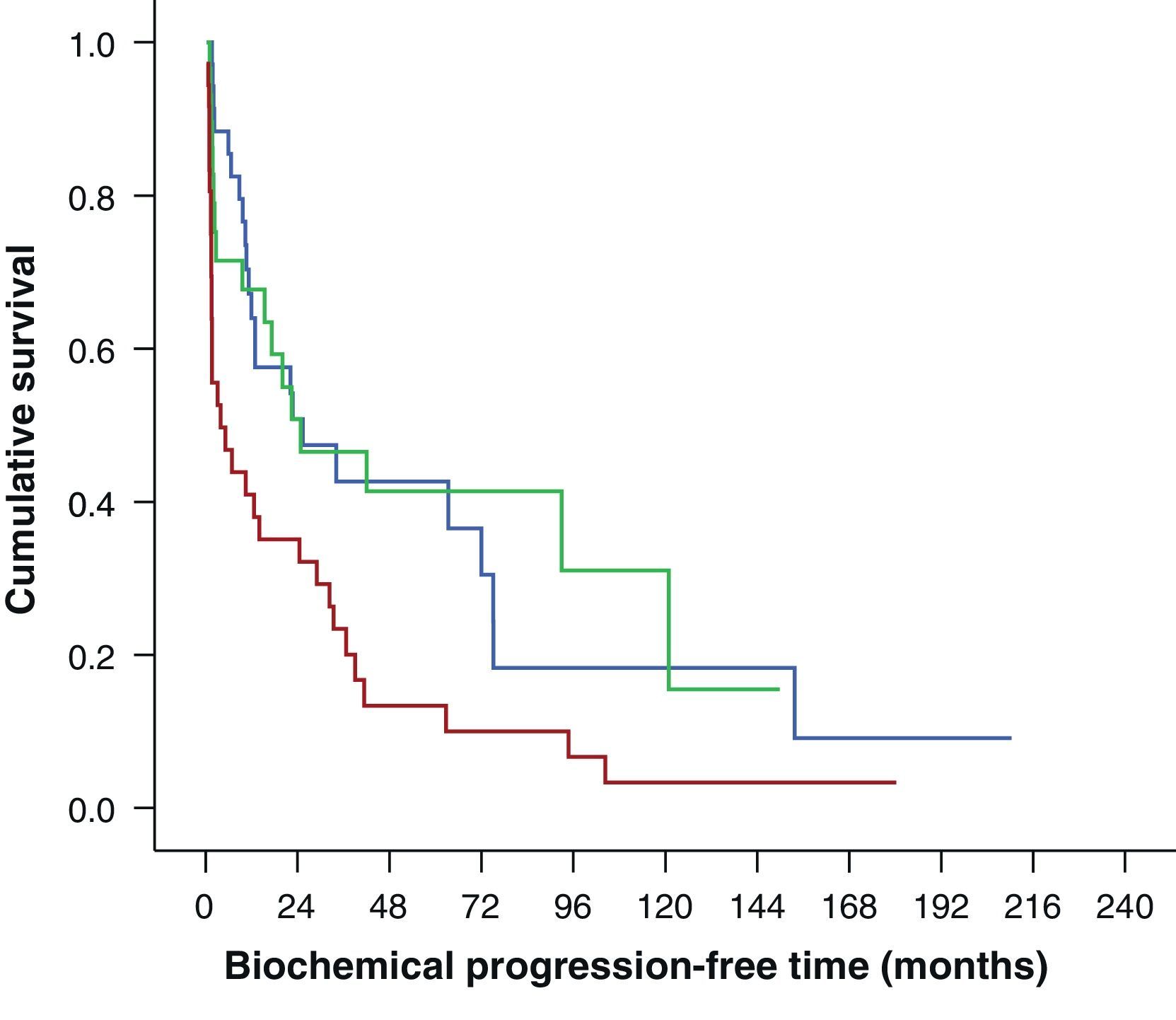
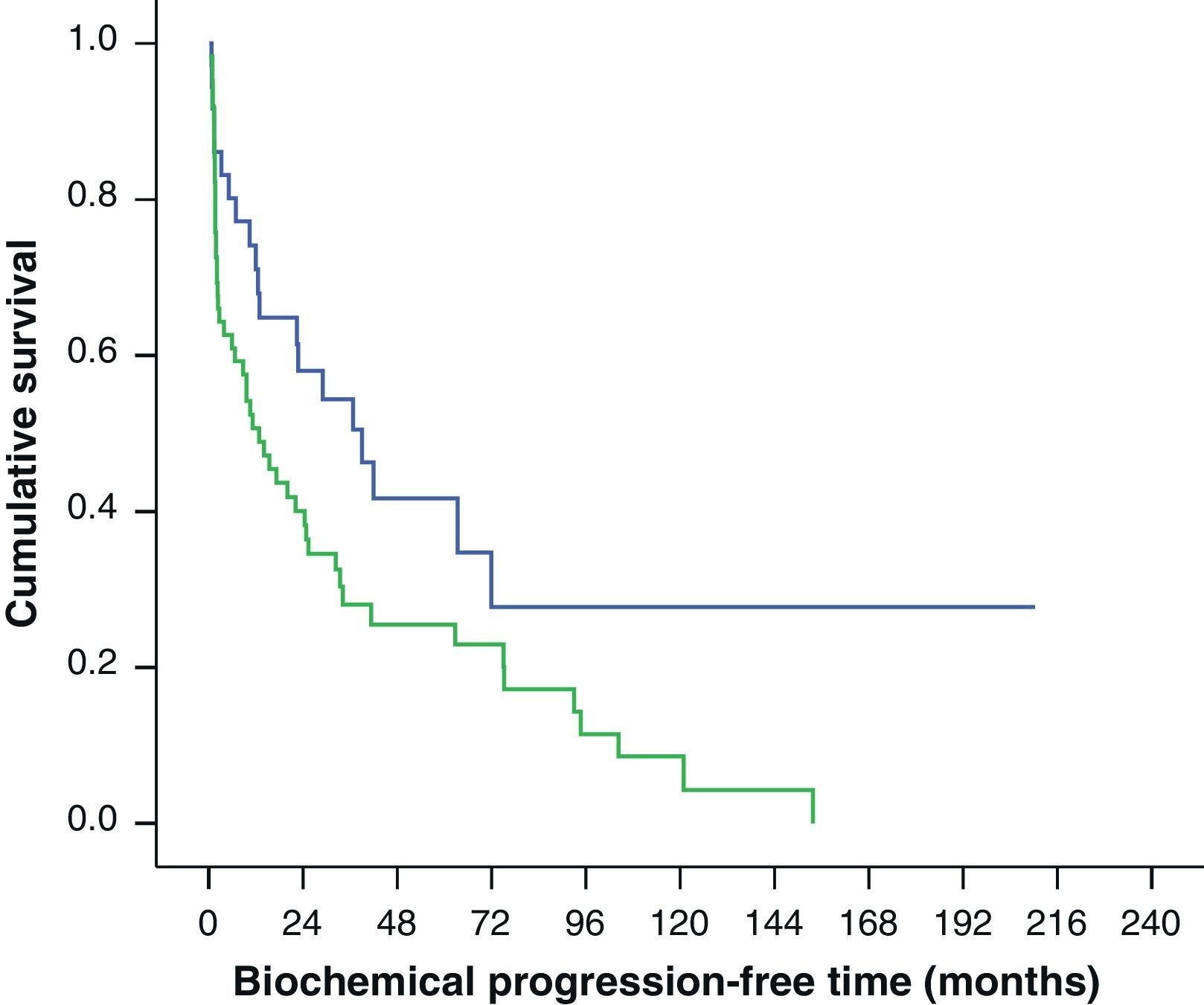
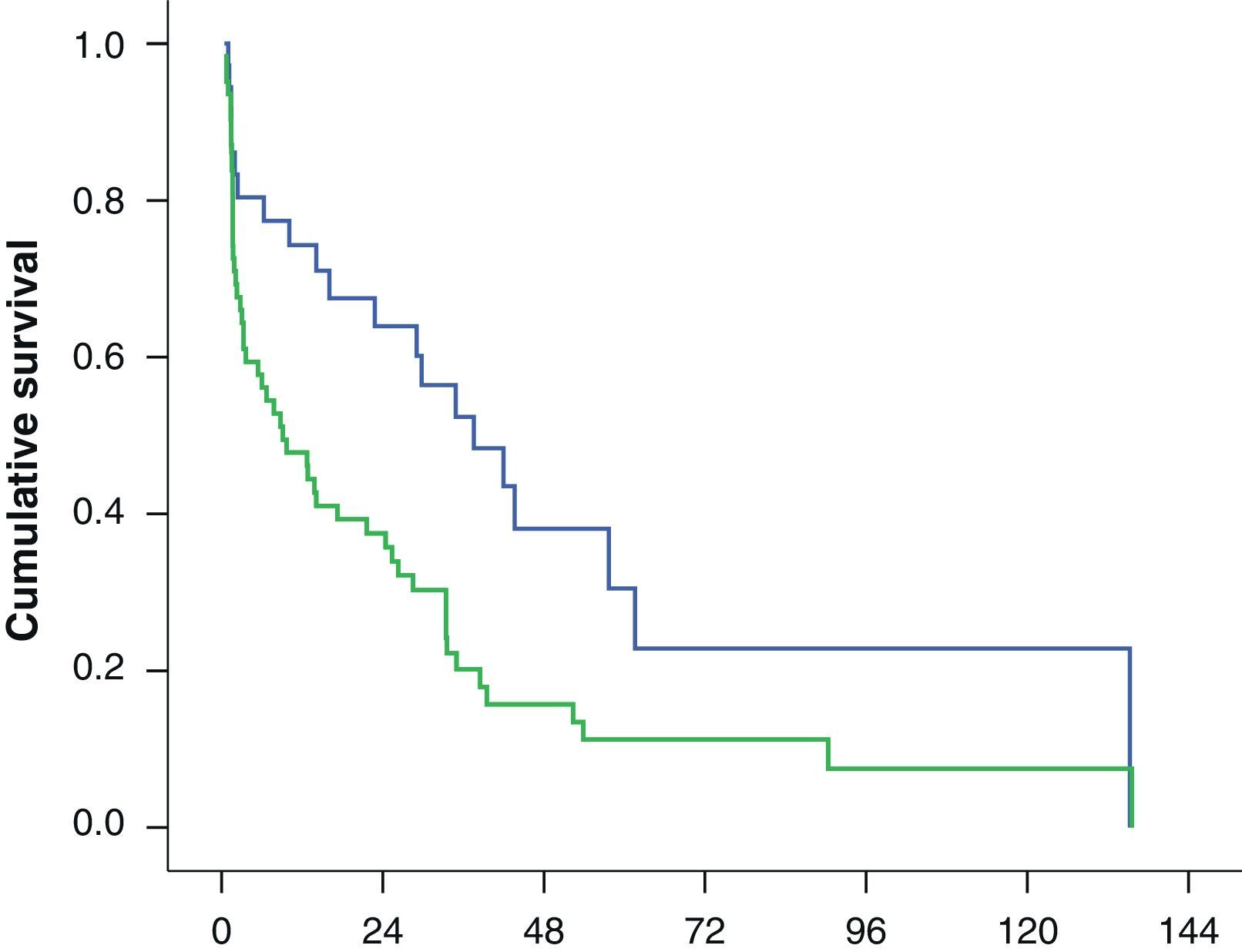
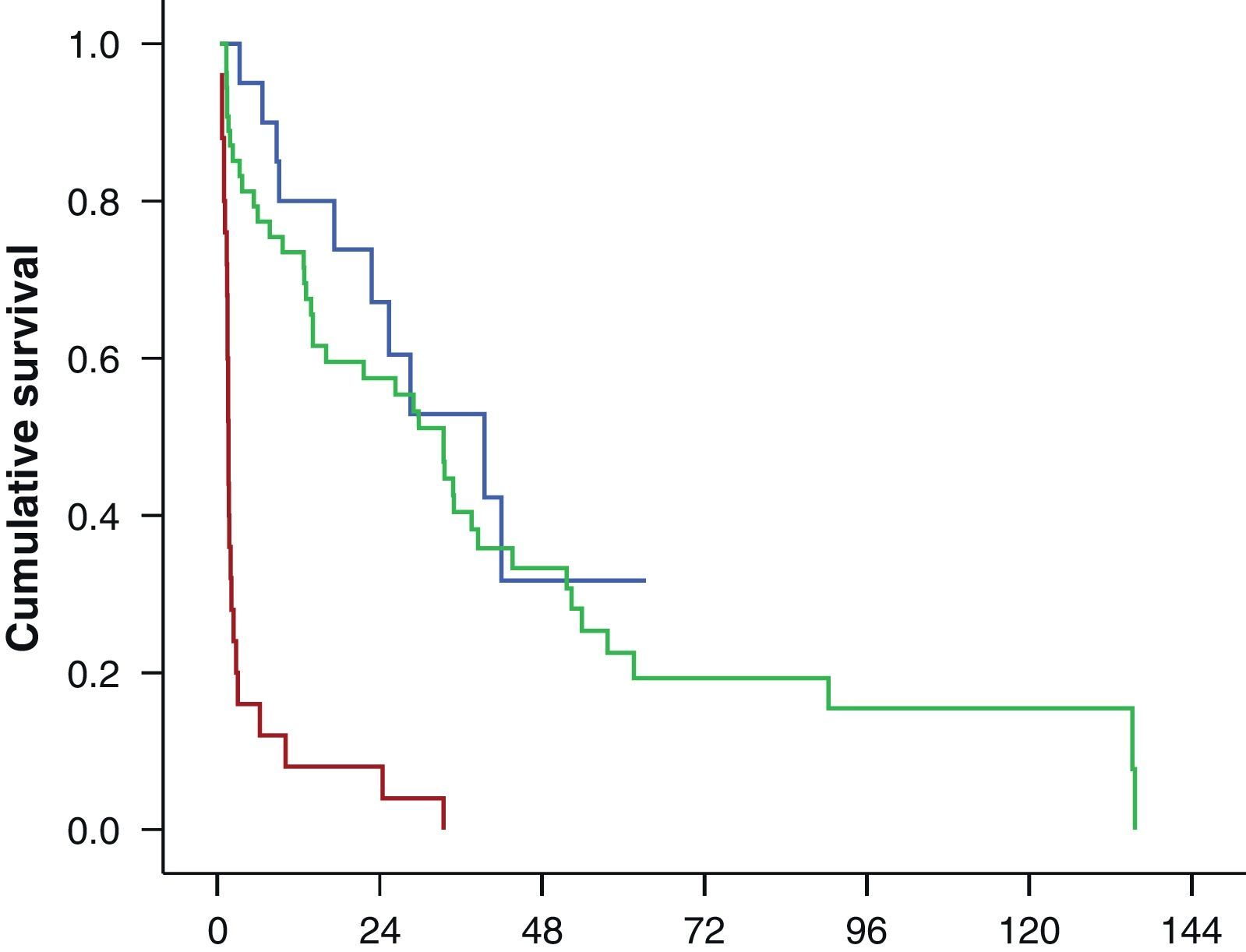
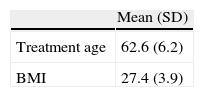
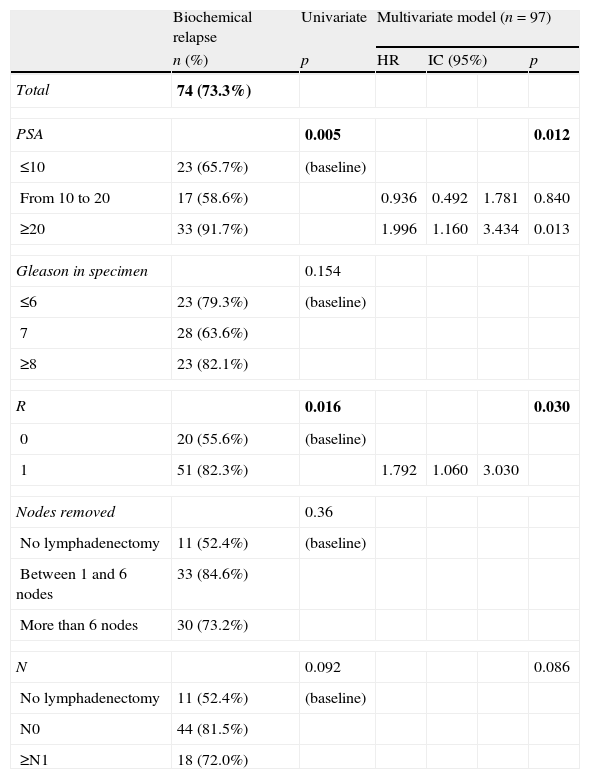
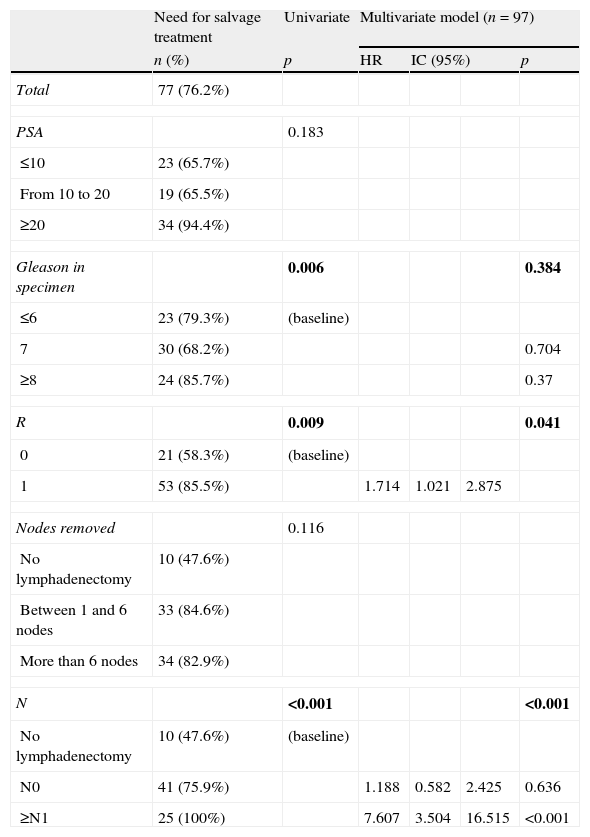
Results101 patients were selected from 1470 procedures. Among these, 28 patients died (27.7%), 18 due to tumor, and 74 showed biochemical relapse (73.3%). The median follow up was of 4 years and 4 months. The five years BFS was 30.2% (IC 95%: 20.2–40.1), whereas the 5-year period free of complementary treatment was 16.9% (IC 95%: 8.1–25.8%).
In the multivariate analysis, margin status (R) was independently and significantly associated with biochemical relapse and the need for complementary treatment. Likewise, the preoperative PSA was associated to biochemical relapse and N1 tumors were clearly associated to complementary treatment.
ConclusionpT3b prostate cancer patients with R1 disease have a worse biochemical prognosis and higher probability of complementary treatment.
Pese al diagnóstico precoz del cáncer de próstata, la invasión de las vesículas seminales por este tumor es un escenario patológico, todavía presente en nuestra práctica clínica. El objetivo del presente trabajo es evaluar los factores pronósticos clínicos y patológicos en la evolución de este subgrupo de pacientes.
Material y métodoPrevia autorización por el comité de investigación clínica de nuestro centro, procedimos a la selección en nuestra base de datos de los pacientes con estadio pT3b intervenidos durante el periodo comprendido entre los años 1987-2010. Excluimos los pacientes con tratamientos neoadyuvantes. Mediante el método de Kaplan-Meier se evaluó el periodo libre de recidiva bioquímica (SLRB) y el periodo libre de necesidad de tratamientos complementarios (SLTC) (adyuvante o rescate). El modelo de regresión de Cox se utilizó para determinar las variables clínicas y patológicas que se asociaban a las anteriores circunstancias.
ResultadosDe 1.470 procedimientos 101 pacientes fueron incluidos en el estudio. Con una mediana de seguimiento de 4 años y 4 meses, 28 pacientes (27,7%) fallecieron, 18 por el tumor y 74 (73,3%) presentaron progresión bioquímica. La SLRB a los 5 años fue del 30,2% (IC 95%: 20,2-40,1) mientras que la SLTC fue del 16,9% (IC 95%: 8,1-25,8%).
En el estudio multivariante el estado de los márgenes quirúrgicos (R1) fue la variable que se asoció de manera independiente y significativa a la recidiva bioquímica y a la necesidad de rescate. El PSA preoperatorio se asoció a la recidiva bioquímica, y la presencia de adenopatías patológicas a la necesidad de tratamiento. El número de ganglios extraídos y la puntuación Gleason no alcanzaron la significación estadística.
ConclusiónEn el grupo de pacientes con infiltración de las vesículas seminales R1 es un factor de mal pronóstico común, tanto para la recidiva bioquímica como para la necesidad de rescate.