Burnout syndrome has increased dramatically in urology within recent years. A healthy lifestyle has been described as a protective factor. However, data on lifestyle is lacking among residents and urologists and remains to be elucidated. We aim to assess lifestyle among urology residents and young urologists across Europe.
Materials and MethodsMembers of the European Society of Residents in Urology (ESRU) designed a 34-item online survey via surveymonkey.com. The survey was designed in accordance with Checklist for Reporting Results of Internet E-Surveys (CHERRIES) guidelines and was distributed via e-mail and social media in 23 European countries to urology residents and young urologists. The primary endpoint was reported as self-perceived health status. Secondary endpoints included questions on sleeping disorders, exercise and dietary habits. Data was analyzed SPSS software.
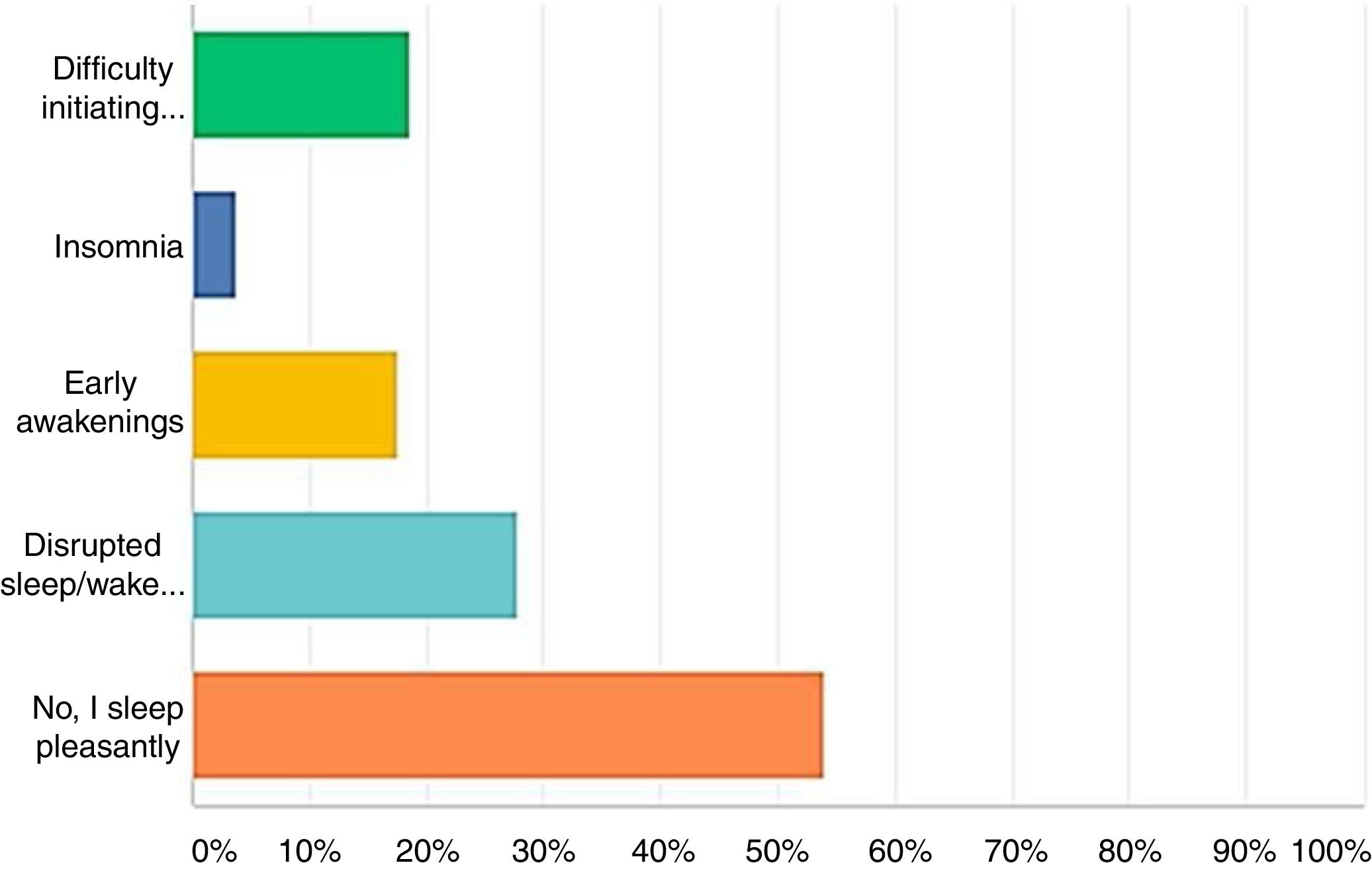
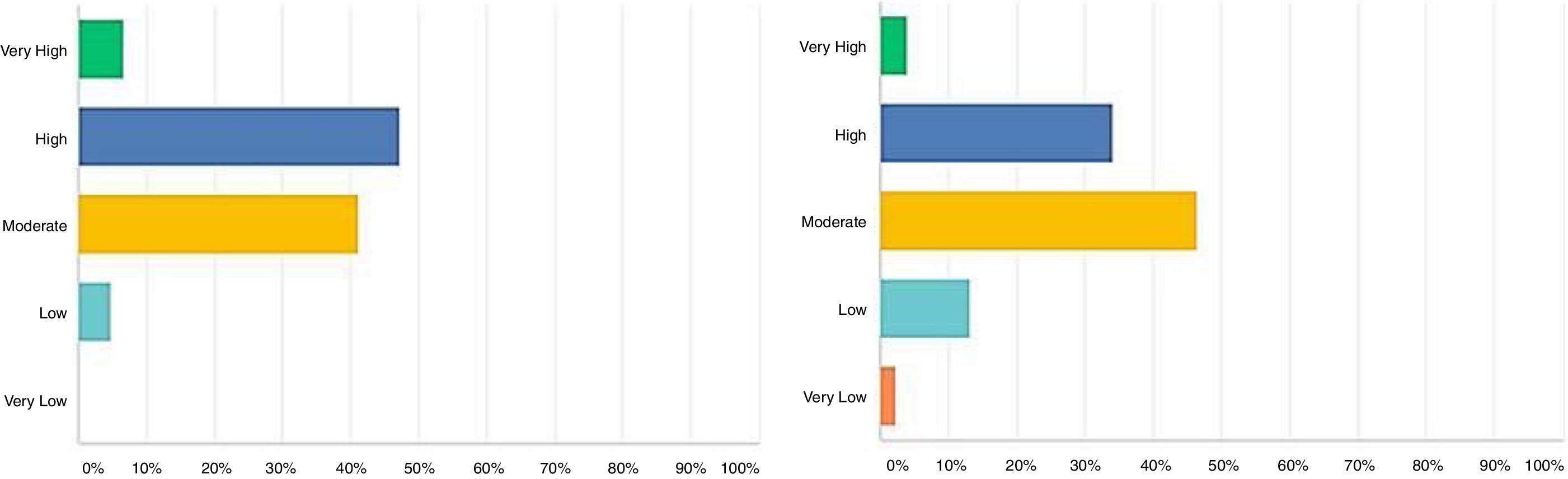
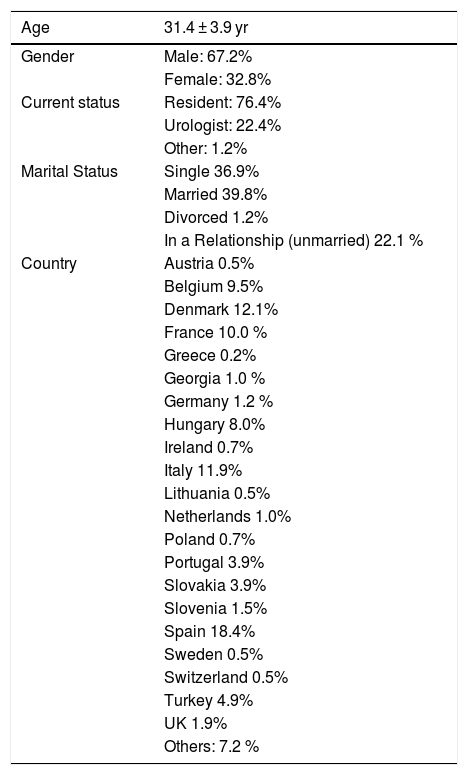
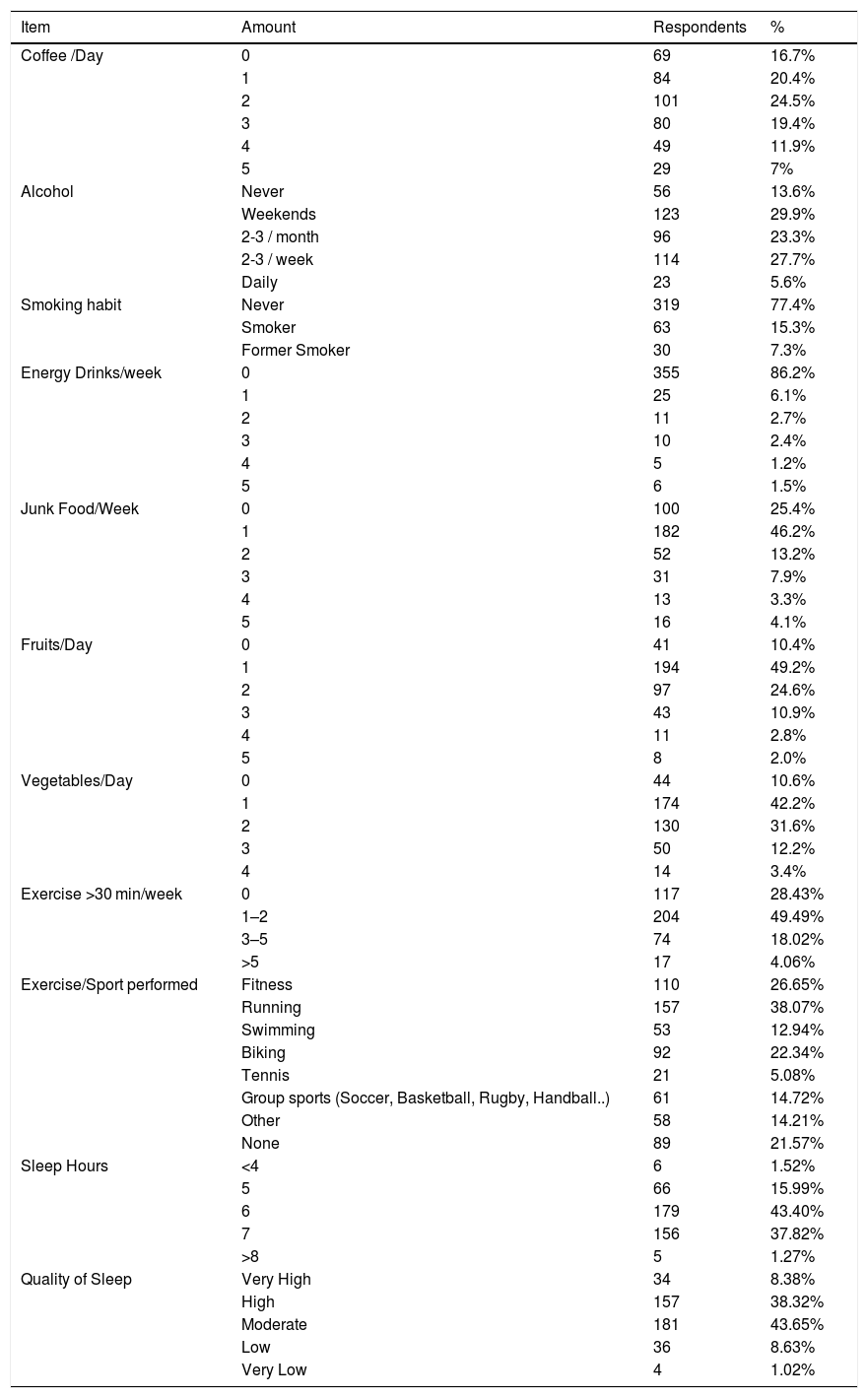
ResultsA total of 412 residents and young urologists responded to the survey. The mean age of the respondents was 31.4 ± 3.9 yr. The data on dietary intake demonstrate a mean of 2 or more cups/day of coffee and alcohol consumption 2-3 times/week. The intake of fruits and vegetables is very low, almost 60% of responders consume <1 portions of fruit/day and more than half (52%) eat <1 portion of vegetable/day. Overall, the majority of respondents reported to have a moderate to low satisfaction with lifestyle (59.65%) and low to moderate self-perceived health status (45.94%). Moreover, 46% of respondents reported to have some kind of sleep disturbance and 60% only slept 6 h/night or less with 53% reporting a moderate to very low quality of Sleep. Regular exercise of at least 30 min twice weekly was only performed by 33% of the respondents.
ConclusionsResidents and young urologists have unbalanced diet, tend to exercise too little and often suffer from sleep disturbances all of which increases the risk of burnout. Physicians, organizations and institutions should strive to promote healthy lifestyle, resiliency and support programs.
El síndrome de burnout ha aumentado espectacularmente en el ámbito de laurología en los últimos años. Un estilo de vida saludable se ha descrito como un factor protector.Sin embargo, aún no han sido evaluados los datos relacionados con el estilo de vida de residentesy urólogos. Nuestro objetivo es evaluar el estilo de vida entre los residentes y urólogos jóvenesde toda Europa.
Materiales y métodosLos miembros de la Sociedad Europea de Residentes de Urología (ESRU,por sus siglas en inglés) diseñaron una encuesta online de 34 ítems, a través de sur-veyymonkey.com. La encuesta fue diseñada de acuerdo con la lista de verificación parareportar resultados de encuestas online (Checklist for Reporting Results of Internet E-Surveys[CHERRIES]), y se distribuyó por correo electrónico y redes sociales en 23 países europeos, aresidentes de urología y urólogos jóvenes. La variable principal del estudio ha sido la autovalo-ración del estado de salud. Para las variables secundarias había preguntas sobre los trastornosdel sueño, el deporte y los hábitos alimentarios. Se analizaron los datos con el software SPSS.
ResultadosUn total de 412 residentes y urólogos jóvenes respondieron la encuesta. La media de edad de los encuestados fue de 31,4±3,9 años. Los datos sobre la ingesta alimentaria delatan una media de consumo de 2 o más tazas/día de café y 2-3 veces/ semana de alcohol. La ingesta de fruta y verdura es muy baja, casi el 60% de los encuestados consumen < 1 ración de fruta al día y más de la mitad (52%) toman < 1 ración de verdura por día. En general, la mayoría de los encuestados reportaron estar baja/medianamente satisfechos con su estilo de vida (59,65%) y en la autovaloración del estado de salud los resultados están entre bajo y moderado (45,94%). Además, el 46% de los encuestados informó tener algún tipo de trastorno del sueño: el 60% solo duerme 6 h/noche o menos, y el 53% afirmó tener una calidad del sueño de moderada a muy baja. Solo un 30% de los encuestados practica al menos 30 min de deporte, 2 veces por semana.
ConclusionesLos residentes y urólogos jóvenes tienen una dieta desequilibrada, tienden a hacer poco ejercicio y, a menudo, sufren trastornos del sueño, lo que aumenta el riesgo de desgaste y agotamiento. Los médicos, las organizaciones y las instituciones deben esforzarse por promover programas de estilo de vida saludable, resiliencia y apoyo.