Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) is an alternative to prostatic adenomectomy for the surgical treatment of benign prostatic hypertrophy. We analyzed our learning curve for this technique, and we compared it in a secondary manner with prostatic adenomectomy.
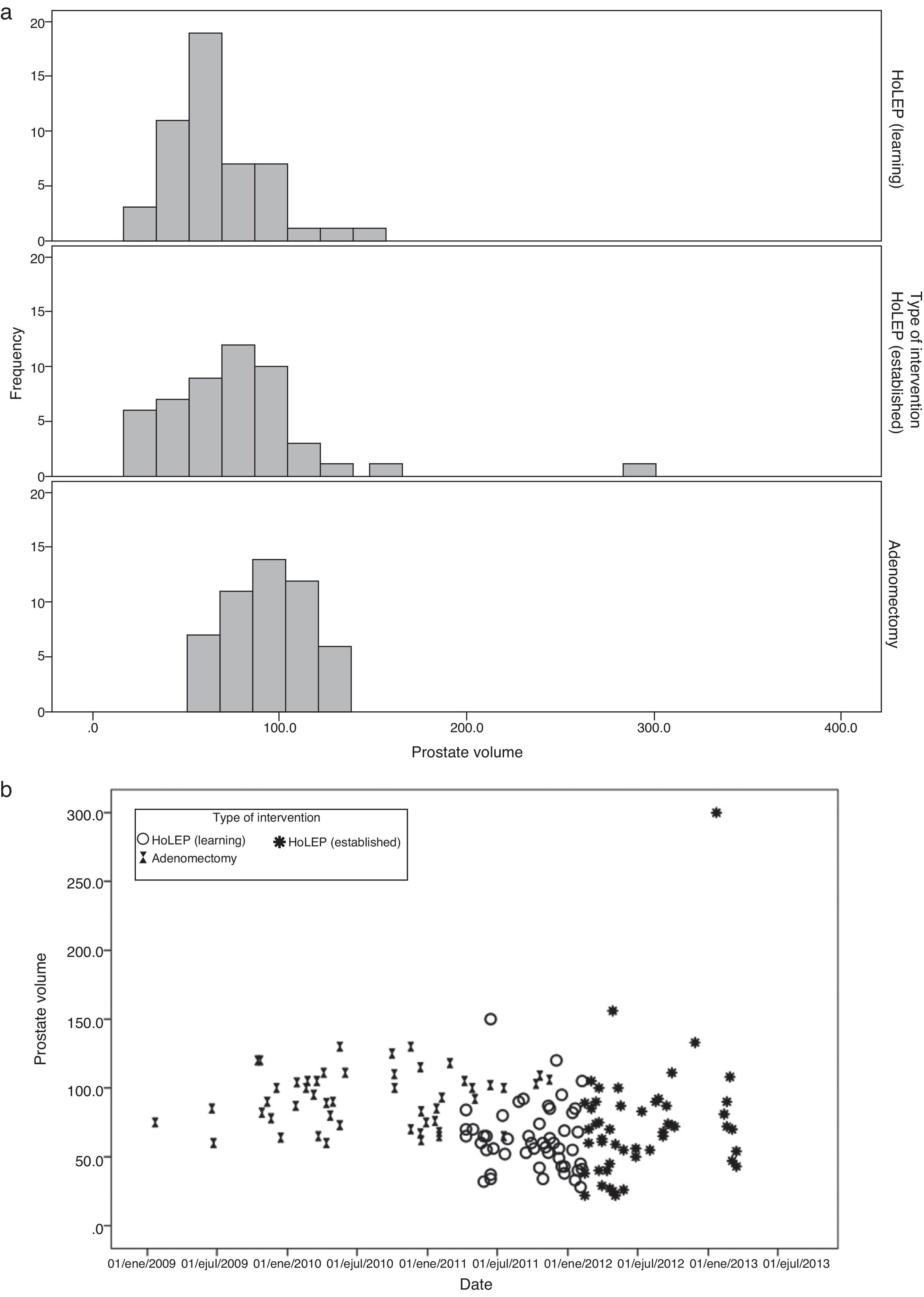
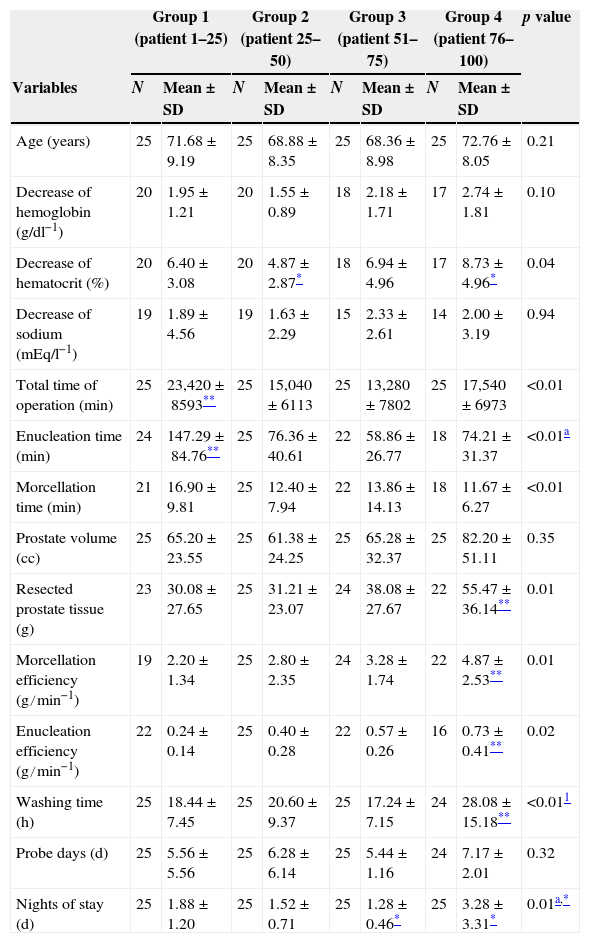
Materials and methodsA retrospective comparative study was conducted that included the first 100 cases of HoLEP performed in our center and the latest 50 cases of retropubic adenomectomy. We collected data on the patients, the surgery, the anesthesia, the perioperative variables, the anesthesia complications and the postoperative variables, with a 6-month follow-up. We analyzed the learning curve without mentors for HoLEP and compared the characteristics of HoLEP in 2 separate phases (learning and stabilization phases) with the latest retropubic prostatic adenomectomies performed.
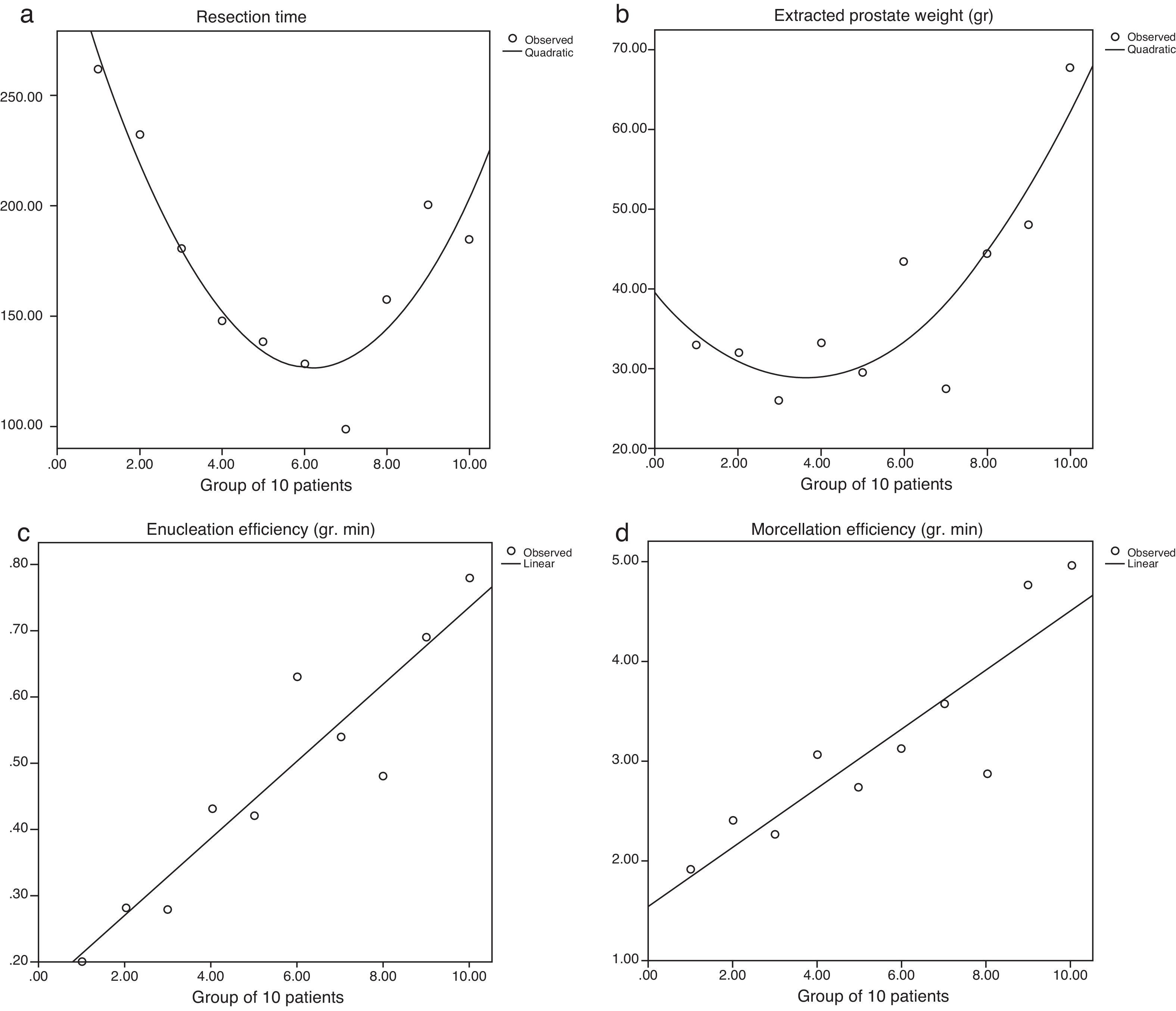
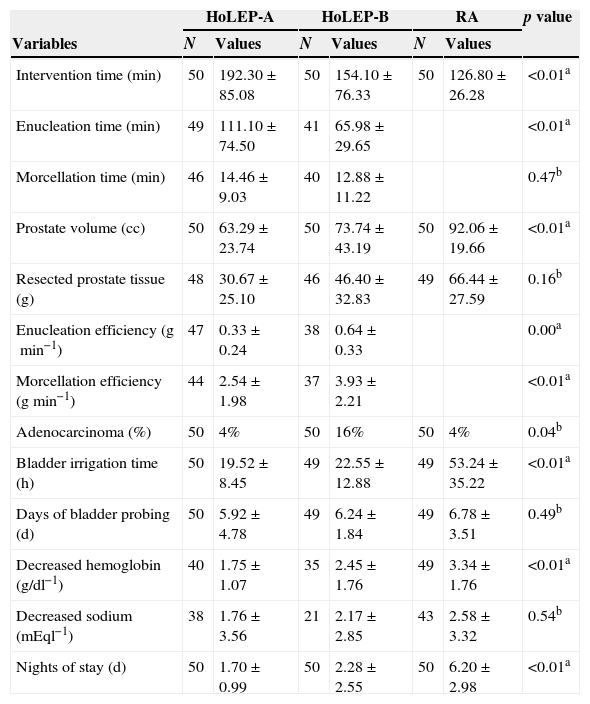
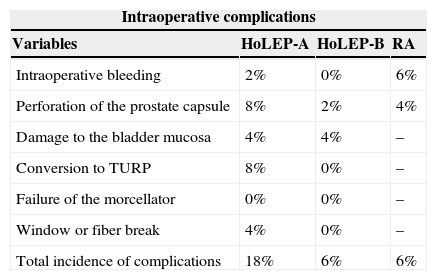
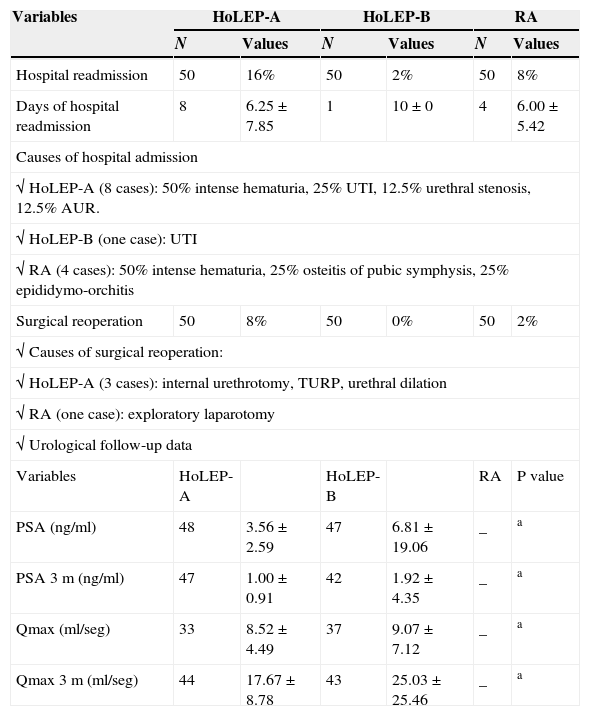
ResultsIntradural anesthesia was the most common technique. The transfusion needs, length of stay (P<.01) and postoperative morbidity were lower for HoLEP than for adenomectomy. However, the retropubic adenomectomy group had larger initial prostate volumes (P<.001) and shorter surgical times (P<.001). Better surgical performance (P<.001) and a lower incidence of complications were observed in the HoLEP-B group (once the learning curve had been overcome) compared with the HoLEP-A group.
ConclusionIn our center, HoLEP was introduced as a valid alternative to open retropubic adenomectomy, with excellent results in terms of morbidity and reduced hospital stay. In terms of the learning curve, we consider that approximately 50 patients (without mentor) is an appropriate cutoff. Local anesthesia is a good choice for the anesthesia technique.
La enucleación prostática mediante láser de holmio (HoLEP) es una alternativa a la adenomectomía prostática para el tratamiento quirúrgico de la hipertrofia benigna de próstata. Analizamos nuestra curva de aprendizaje de dicha técnica y la comparamos de forma secundaria con las adenomectomías de próstata.
Materiales y métodosEstudio retrospectivo y comparativo donde se incluyeron los 100 primeros casos de HoLEP realizados en nuestro centro y los últimos 50 casos de adenomectomías retropúbicas. Se recogen los datos del paciente, de la intervención, del acto anestésico, de las variables perioperatorias, de las complicaciones anestésicas y de las variables postoperatorias con un seguimiento durante 6 meses. Se analizó la curva de aprendizaje sin mentor del HoLEP y se compararon las características del HoLEP en 2 fases diferenciadas (fase de aprendizaje y fase de estabilización) con las últimas adenomectomías retropúbicas de próstata realizadas.
ResultadosLa anestesia intradural fue la técnica más frecuente. Las necesidades de transfusión, el tiempo de estancia (p<0,01) y la morbilidad postoperatoria fueron menores en los HoLEP que en las adenomectomías. Sin embargo, el grupo de las adenomectomías retropúbicas tenía un mayor volumen prostático inicial (p<0,001) y un menor tiempo quirúrgico (p<0,001). Se observó un mejor rendimiento quirúrgico (p<0,001) y una menor incidencia de complicaciones en el Grupo HoLEP-B (superada ya la curva de aprendizaje) frente al grupo HoLEP-A.
ConclusiónEn nuestro centro el HoLEP se ha introducido como una opción válida frente a las adenomectomías retropúbicas abiertas, con muy buenos resultados en términos de morbilidad y reducción de estancia hospitalaria. Respecto a la curva de aprendizaje consideramos en torno a los 50 pacientes (sin mentor) como un punto de corte adecuado. La anestesia regional es una buena elección como técnica anestésica.