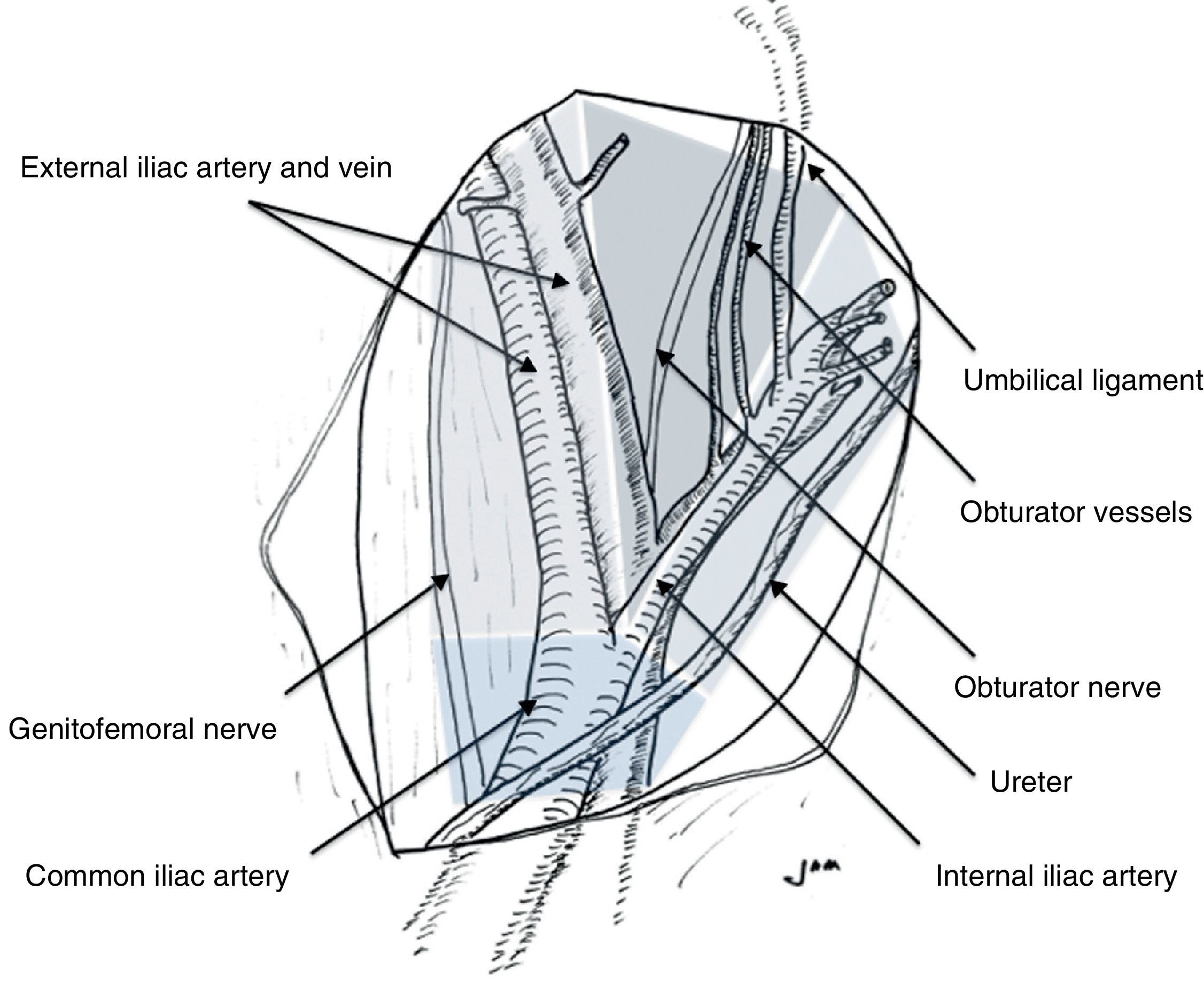
Lymphadenectomy for prostate cancer (PC) is the most reliable procedure for detecting lymphatic metastases. The optimal extension of this procedure is still a topic of debate.
ObjectiveTo analyze the diagnostic performance and complications of extended lymphadenectomy (ELD) and limited lymphadenectomy (LLD) in a series of patients with high-risk PC who underwent radical prostatectomy (RP).
Material and methodsA retrospective study was conducted on patients with high d’Amico risk who underwent RP with lymphadenectomy between 1999 and 2014.
A comparative analysis was performed of the diagnostic capacity of lymphatic metastases of ELD and LLD and of postoperative complications at 90 days.
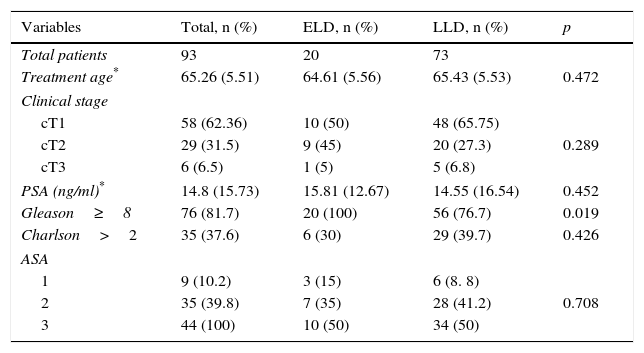
ResultsNinety-three patients were analyzed, 20 (21.5%) and 73 (78.5%) of whom underwent ELD and LLD, respectively. The mean age of the series was 65.26 years (SD, 5.51). The median follow-up was 1.51 (0.61–2.29) years in the ELD group and 5.94 (3.61–9.10) in the LLD group.
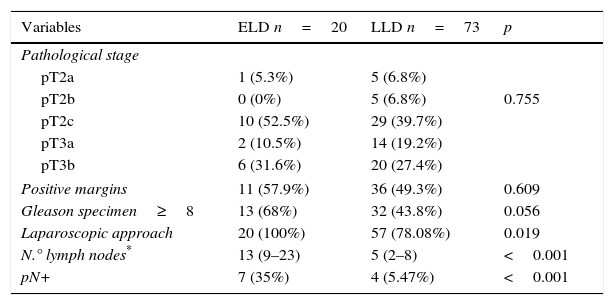
The median number of nodes obtained was 13 (9–23) in the ELD group compared with 5 (2–8) in the LLD group (p<.001). The percentages of patients with positive nodes in the ELD and LLD groups were 35% and 5.47%, respectively (p<.001).
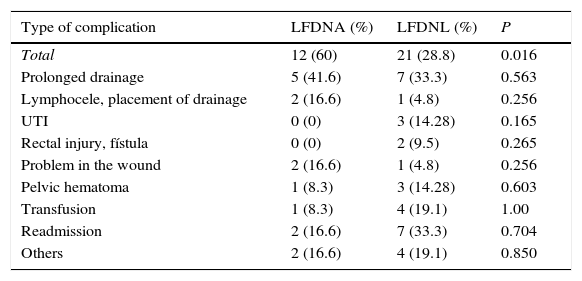
The overall complication rate at 90 days was 35.5% (33 patients). In the ELD group, 12 patients (60%) had complications, compared with 21 patients (28.8%) in the LLD group (p=.016), with no significant differences in severity according to the Clavien scale (p=.73).
ConclusionsIn our series, the detection of metastatic nodes was significantly greater with ELD. ELD increases the number of complications, with no differences compared with LLD in severity according to the modified Clavien scale.
La linfadenectomía en el cáncer de próstata (CP) es el procedimiento más fiable para la detección de metástasis linfáticas. La extensión óptima de la misma aún es un tema en debate.
ObjetivoAnalizar el rendimiento diagnóstico y las complicaciones de la linfadenectomía ampliada (LFDNA) y limitada (LFDNL) en una serie de pacientes con CP de alto riesgo sometidos a prostatectomía radical (PR).
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de pacientes con CP de alto riesgo de D’Amico sometidos a PR con linfadenectomía entre 1999-2014.
Análisis comparativo de la capacidad de diagnóstico de metástasis linfáticas de la LFDNA y LFDNL y de las complicaciones postoperatorias a 90 días.
ResultadosSe analizaron 93 pacientes, 20 (21,5%) sometidos a LFDNA y 73 (78,5%) a LFDNL. La edad media de la serie fue de 65,26 años (DE 5,51). La mediana de seguimiento fue de 1,51 (0,61-2,29) años en el grupo de LFDNA y 5,94 (3,61-9,10) en LFDNL.
La mediana de ganglios obtenidos fue de 13 (9-23) en las LFNDA vs. 5 (2-8) en las limitadas (p<0,001) y el porcentaje de pacientes con ganglios positivos obtenidos fue de 35 y 5,47% respectivamente (p<0,001).
El porcentaje global de complicaciones a 90 días fue 35,5% (33 pacientes). Del grupo de LFDNA 12 pacientes (60%) presentaron complicaciones, frente a 21 (28,8%) en LFDNL (p=0,016), sin encontrar diferencias significativas en la gravedad según la escala de Clavien (p=0,73).
ConclusionesEn nuestra serie, la detección de ganglios metastásicos ha sido significativamente superior en la LFDNA. La LFDNA aumenta el número de complicaciones, sin encontrar diferencias con la LFDNL en la gravedad según la escala de Clavien modificada.