To design and assess a novel penile fracture simulation model for teaching penile fracture repair.
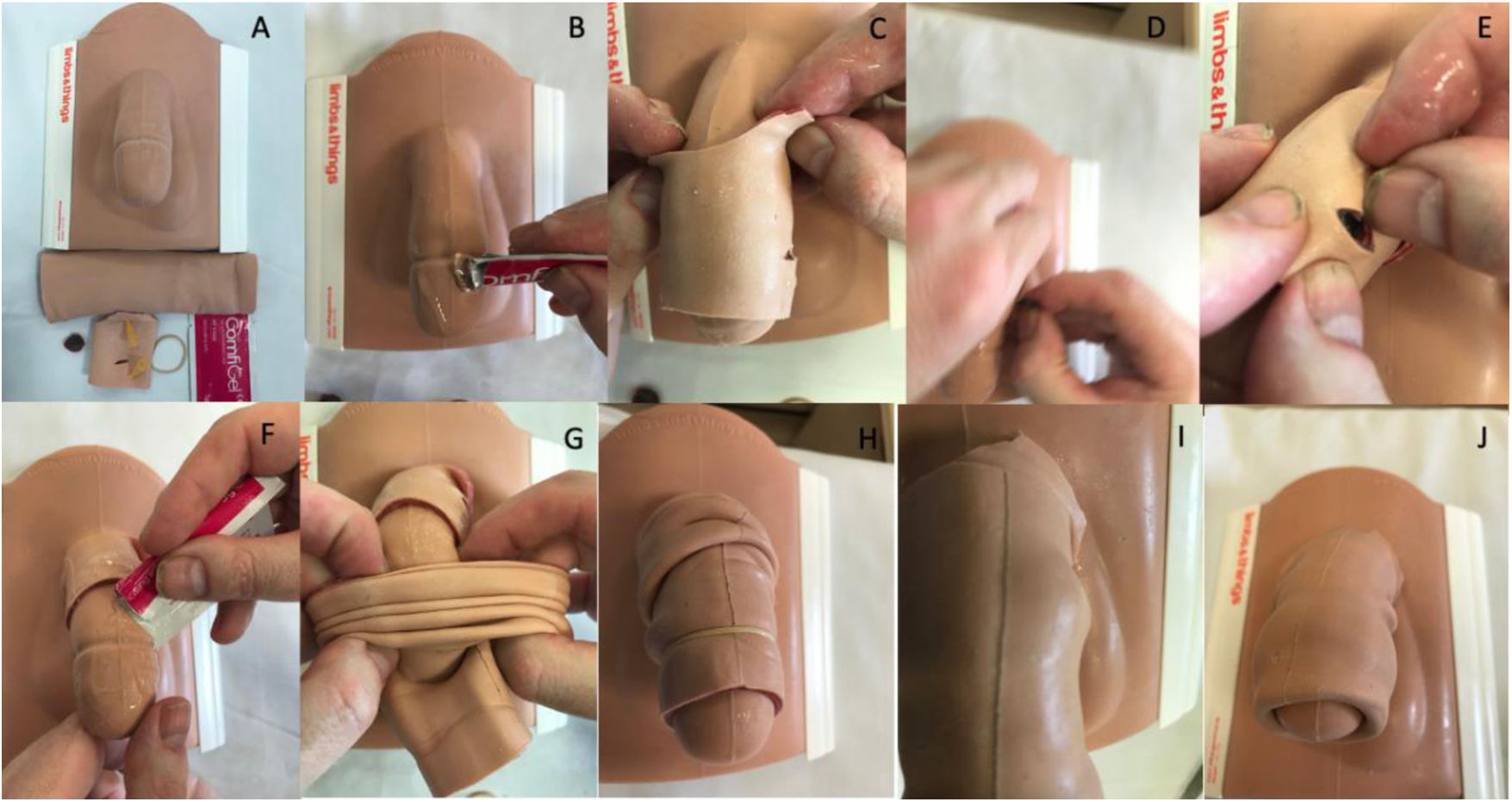
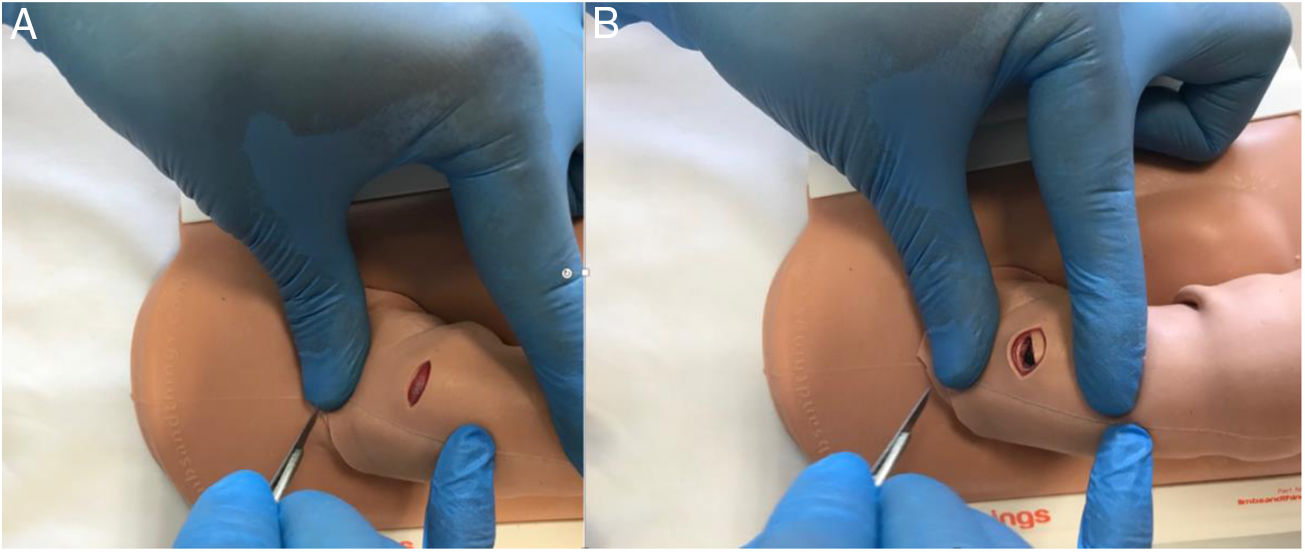
MethodsWe used a validated circumcision simulator to create a model. Foreskin for a circumcision was divided into two halves. A transverse slit (“simulated fracture”) was created on one part of the first half of the foreskin (mimicking “tunica”) and was applied over the penile model. A red jelly tablet (“clot”) was placed underneath the cut. A second full-length of foreskin was applied over it to cover the defect. The model was assessed by participants and expert faculty at the Urology Simulation Boot Camp. Evaluation was performed using a 5-point Likert Scale questionnaire. Data was analysed using Microsoft Excel and IBM SPSS Statistics V25. The intra-class correlation was calculated using a “One-way random model”.
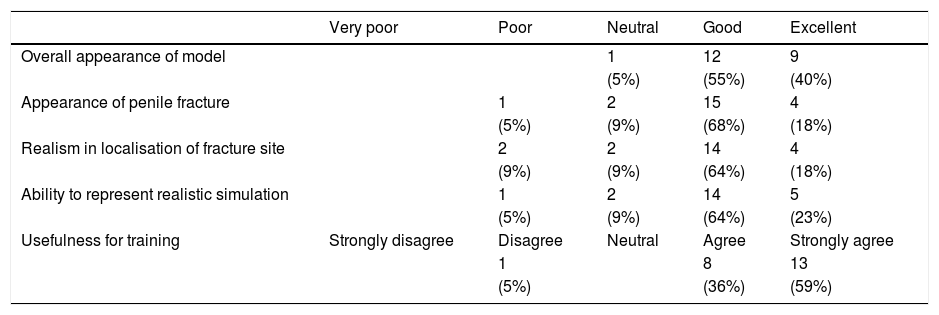
ResultsTwenty-two urology trainees and four experts participated in the evaluation. The majority of trainees strongly agreed (59%, n = 13) the model is useful for training with experts similarly agreeing in 75% of cases. The appearance of penile fracture was considered good by both trainees (68%, n = 14) and faculty (75%). Overall, the ability of the model to represent a realistic simulation of the task was considered excellent by 23% of participants and good by 64%. Personal confidence after simulation in managing a similar situation was considered high among trainees. The main difficulties reported were related to fascial planes and urethra.
ConclusionThis is the first simulation model for penile fracture repair and has demonstrated face validity at a national urology bootcamp.
Diseñar y evaluar un nuevo modelo de simulación de fractura de pene para la enseñanza de su reparación.
MétodosHemos utilizado un simulador de circuncisión validado para crear un nuevo modelo. El prepucio para circuncisión se dividió en 2 mitades. Se creó un corte transversal («simulación de fractura») en una parte de la primera mitad del prepucio (imitando la «túnica») y se colocó sobre el modelo de pene. Se colocó una pastilla de gelatina roja («coágulo») debajo del corte. Se aplicó un segundo trozo para completar el prepucio por encima y cubrir el defecto. El modelo fue evaluado por los participantes y docentes expertos del boot camp de simulación de urología. La evaluación se realizó mediante un cuestionario con escala de Likert de 5 puntos. Los datos se analizaron mediante Microsoft Excel e IBM SPSS Statistics V25. La correlación intraclase se calculó mediante «un modelo aleatorio unidireccional».
ResultadosVeintidós estudiantes de urología y 4 expertos participaron en la evaluación. La mayoría de los aprendices estuvieron muy de acuerdo (59%, n = 13) en la utilidad del modelo para la formación, y los expertos también estuvieron de acuerdo en el 75% de los casos. Tanto alumnos (68%, n = 14) como docentes (75%) consideraron correcta la apariencia de la fractura del pene. En general, la capacidad del modelo para representar una simulación realista de la tarea fue considerada excelente por el 23% de los participantes y buena por el 64%. Tras la simulación los alumnos afirmaron tener una mayor confianza en el manejo de este tipo de casos. Las principales dificultades señaladas estaban relacionadas con los planos fasciales y la uretra.
ConclusiónEste es el primer modelo de simulación para la reparación de fracturas de pene y ha demostrado su validez en un boot camp de urología nacional.