Umbilical laparoendoscopic single-site (LESS) surgery is an increasingly used modality for treating renal masses. We present a prospective comparison between LESS renal surgery and conventional laparoscopy.
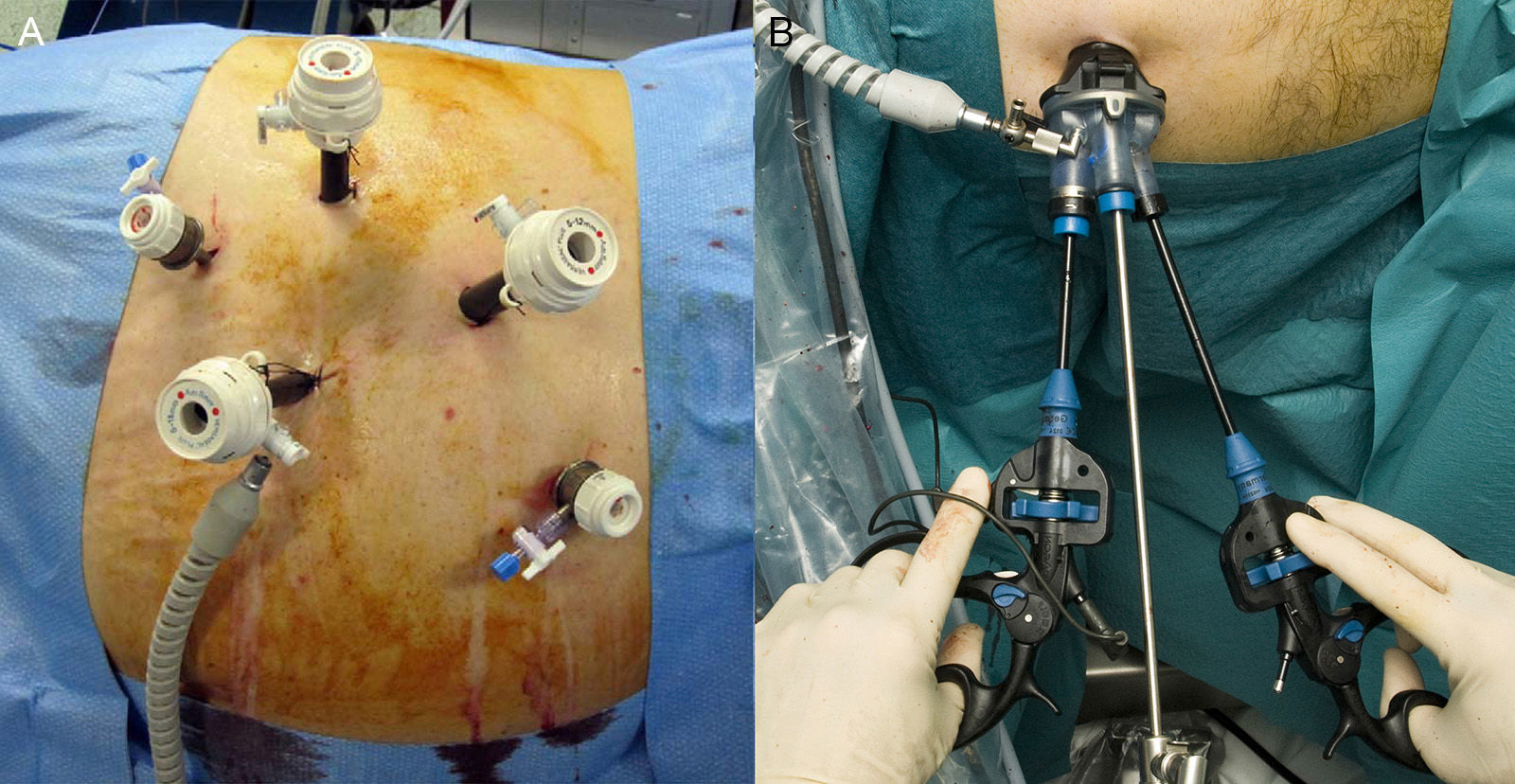
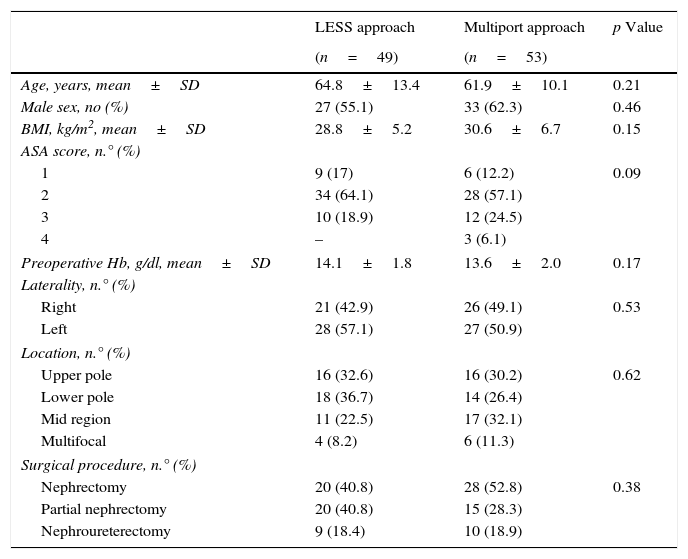
Material and methodA comparative paired study was conducted that evaluated the surgical results and complications of patients with renal neoplasia treated with LESS surgery (n=49) or multiport laparoscopy (n=53). The LESS approach was performed with reusable material placed in the navel and double-rotation curved instruments. An additional 3.5-mm port was employed in 69.4% of the cases. We assessed demographic data, the type of technique (nephrectomy, partial nephrectomy and nephroureterectomy), surgical time, blood loss, hemoglobin, need for transfusion, number and severity of complications (Clavien-Dindo), hospital stay, histological data and prognosis.
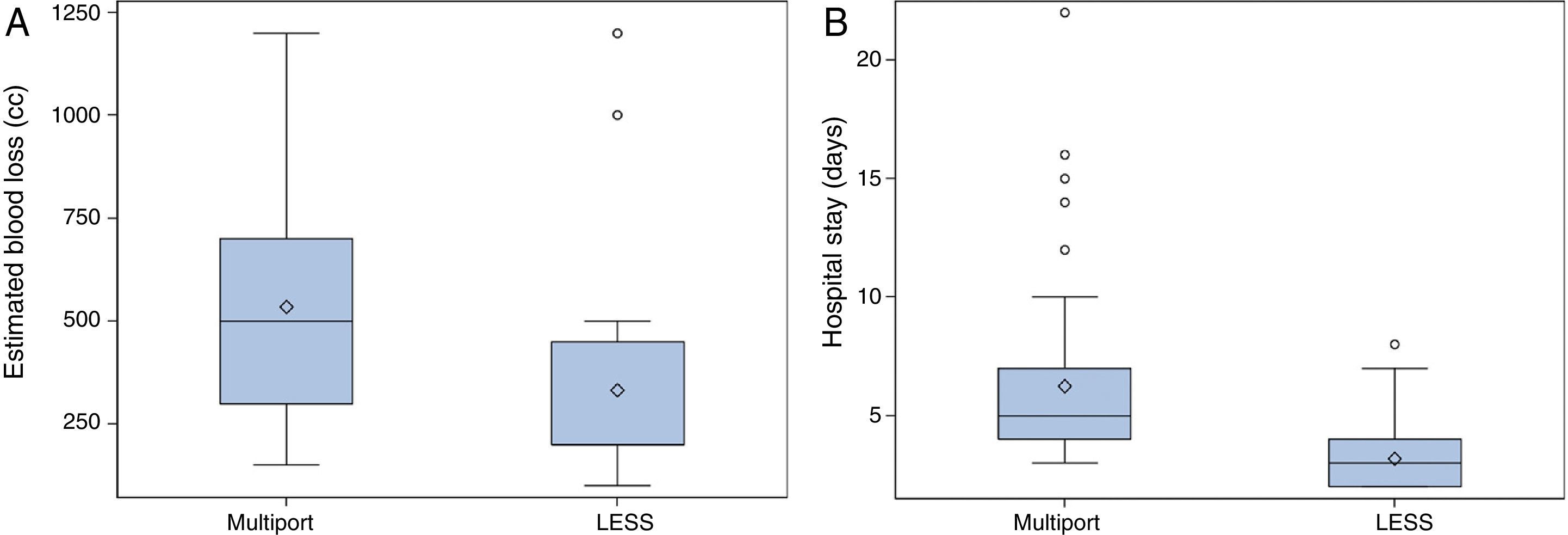
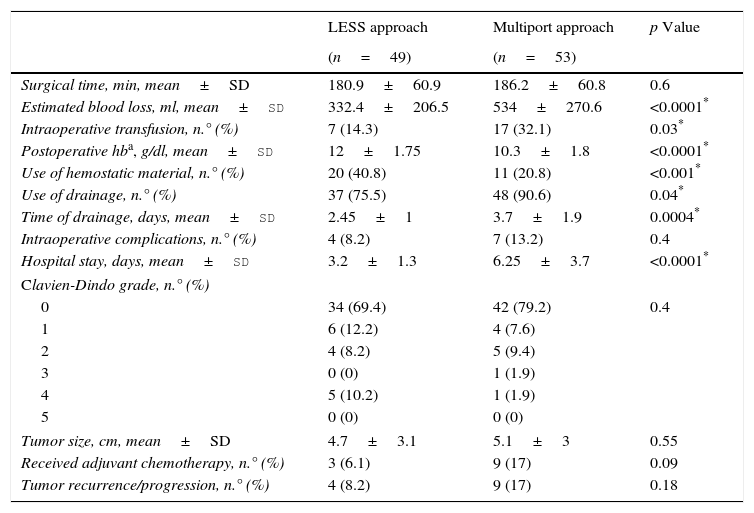
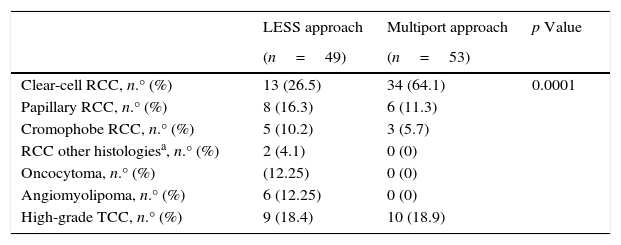
ResultsThere were no differences in follow-up, age, sex, body mass index, preoperative hemoglobin levels or type of surgery. Conversion occurred in 2 cases (1 in each group). The surgical time was equivalent (p=0.6). Intraoperative transfusion (p=0.03) and blood loss (p<0.0001) was lower with LESS, postoperative hemoglobin levels were higher (p<0.0001) and haemostatic agents were used more frequently (p<0.0001). There were no differences in the number (p=0.6) or severity (p=0.47) of complications. The length of stay (p<0.0001), the proportion of patients with drainage (p=0.04) and the number of days with drainage (p=0.0004) were lower in LESS. Twenty-five percent of the lesions operated on with LESS were benign, but the mean size was similar in the 2 groups (p=0.5). Tumor recurrence and/or progression were more frequent in multiport laparoscopy (p=0.0013).
ConclusionsUmbilical LESS surgery with reusable platform enables various surgical techniques to be performed when treating renal masses, with time consumption and safety comparable to conventional laparoscopy. The LESS approach is advantageous in terms of blood loss and hospital stay.
La cirugía umbilical laparoendoscópica por puerto único (LESS) es una modalidad de uso creciente en el tratamiento de las masas renales. Se presenta una comparación prospectiva entre cirugía renal LESS y laparoscopia convencional.
Material y métodoEstudio pareado comparativo que evalúa resultados operatorios y complicaciones en pacientes con neoplasia renal tratada con cirugía LESS (n=49) o laparoscopia multipuerto (n=53). El abordaje LESS se realizó con material reutilizable colocado en el ombligo e instrumentos curvos de doble rotación, y en el 69,4% se empleó un puerto adicional de 3,5mm. Se evalúan datos demográficos, tipo de técnica (nefrectomía, nefrectomía parcial o nefroureterectomía), tiempo operatorio, pérdida hemática, hemoglobina, necesidad de transfusión, número y gravedad de complicaciones (Clavien-Dindo), estancia hospitalaria, datos histológicos y pronóstico.
ResultadosNo hubo diferencias en seguimiento, edad, sexo, IMC, hemoglobina preoperatoria o tipo de cirugía. Hubo conversión en 2 casos (uno en cada grupo). El tiempo operatorio fue equivalente (p=0,6). Transfusión intraoperatoria (p=0,03) y pérdida hemática (p<0,0001) fue menor en LESS, la hemoglobina postoperatoria mayor (p<0,0001) y se emplearon también agentes hemostáticos más frecuentemente (p<0,0001). No hubo diferencias en número (p=0,6) ni gravedad (p=0,47) de complicaciones. La estancia (p<0,0001), la proporción de pacientes con drenaje (p=0,04) y el número de días con drenaje (p=0,0004) fueron menores en LESS. Un 25% de las lesiones intervenidas con LESS fueron benignas, pero el tamaño medio fue similar en ambos grupos (p=0,5). La recurrencia y/o progresión tumoral fue más frecuente en laparoscopia multipuerto (p=0,0013).
ConclusionesLa cirugía LESS umbilical con plataforma reutilizable permite realizar diferentes técnicas quirúrgicas para el tratamiento de masas renales con consumo de tiempo y seguridad equiparable a laparoscopia convencional. El abordaje LESS resulta ventajoso en términos de pérdida hemática y estancia hospitalaria.