The inflammatory pseudotumor is a rare lesion, having benign behavior and some histological heterogeneity that appears in the genitourinary tract. A series of urogenital inflammatory pseudotumors are reviewed with emphasis on their clinicopathological and immunohistochemical characteristics.
Materials and methodsA retrospective study on the causistics treated between January 1981 and December 2010 was performed. It identified the cases of inflammatory pseudotumor with urogenital localization. The variables age, gender, symptoms, topography, treatment and anatomopathological and immunohistochemical characteristics of each case were analyzed.
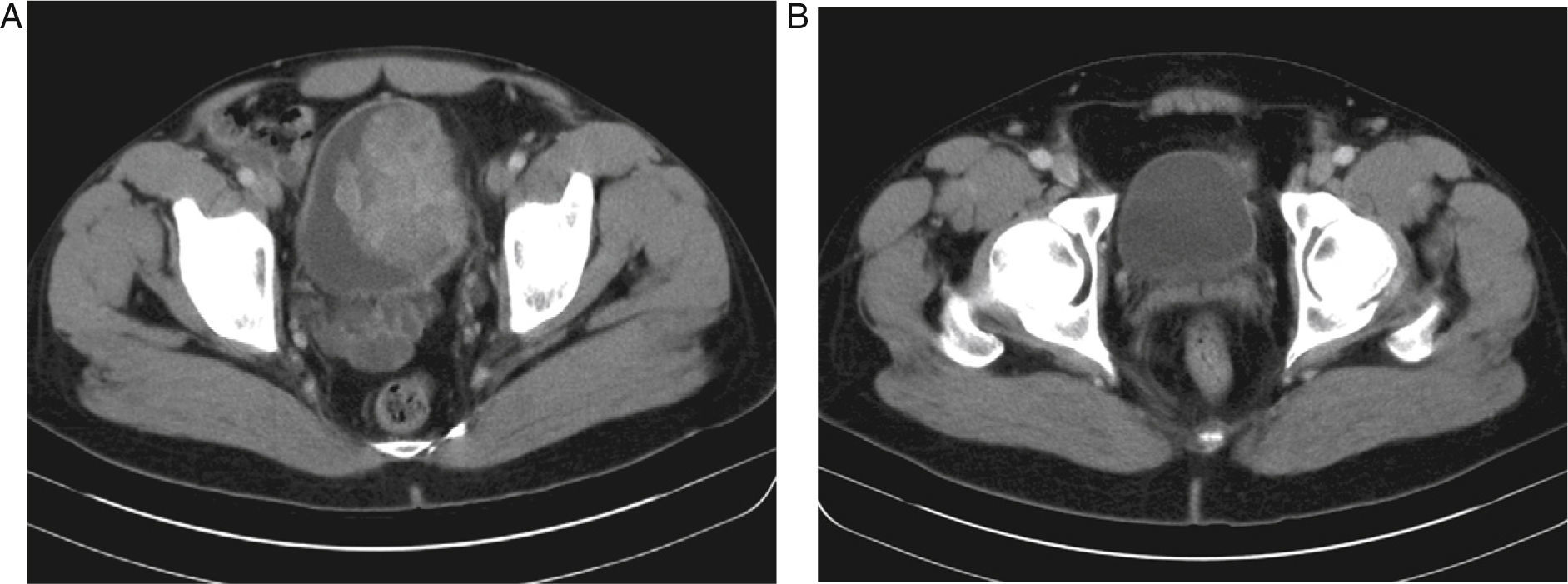
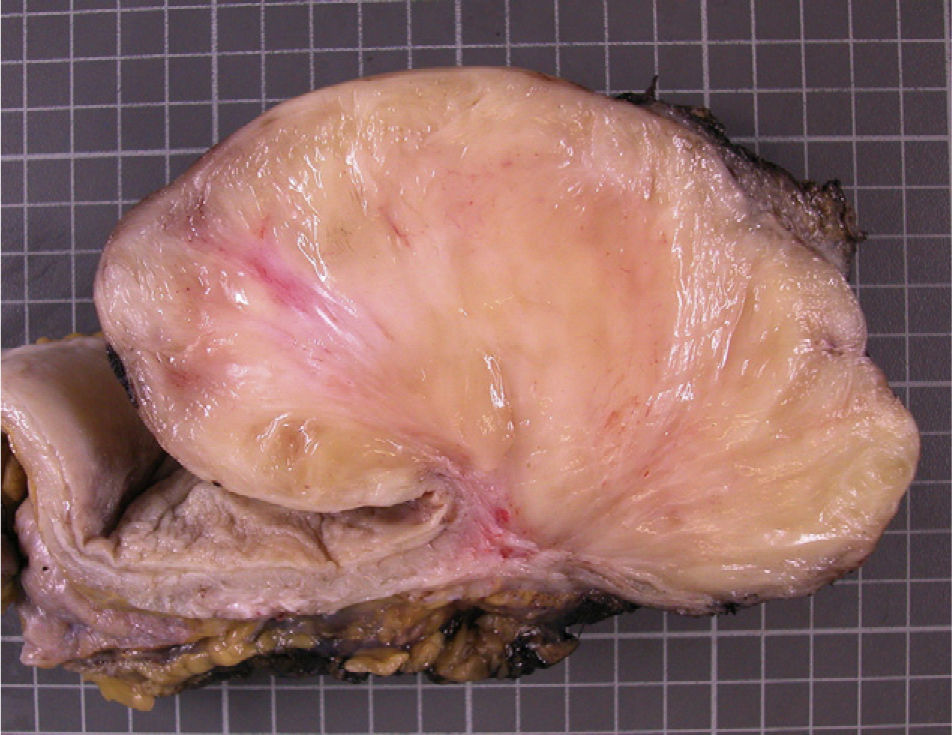
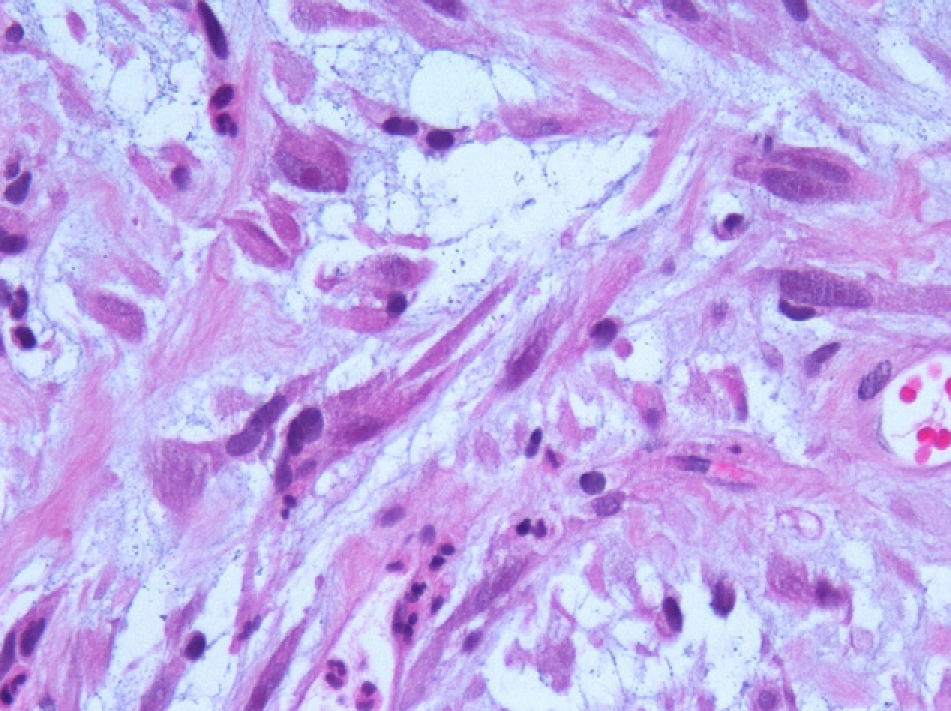
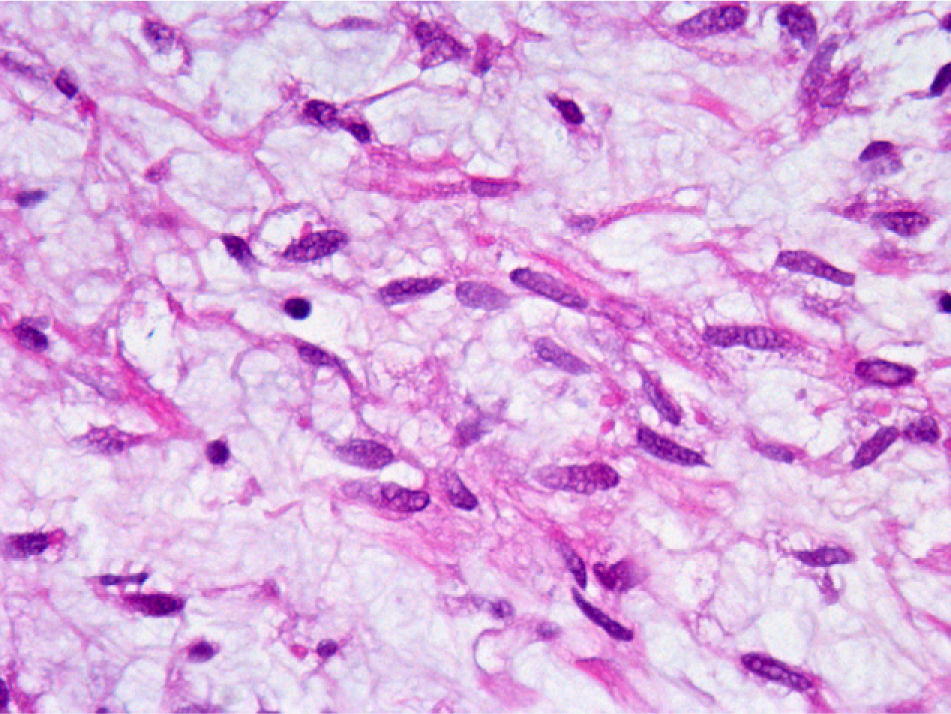
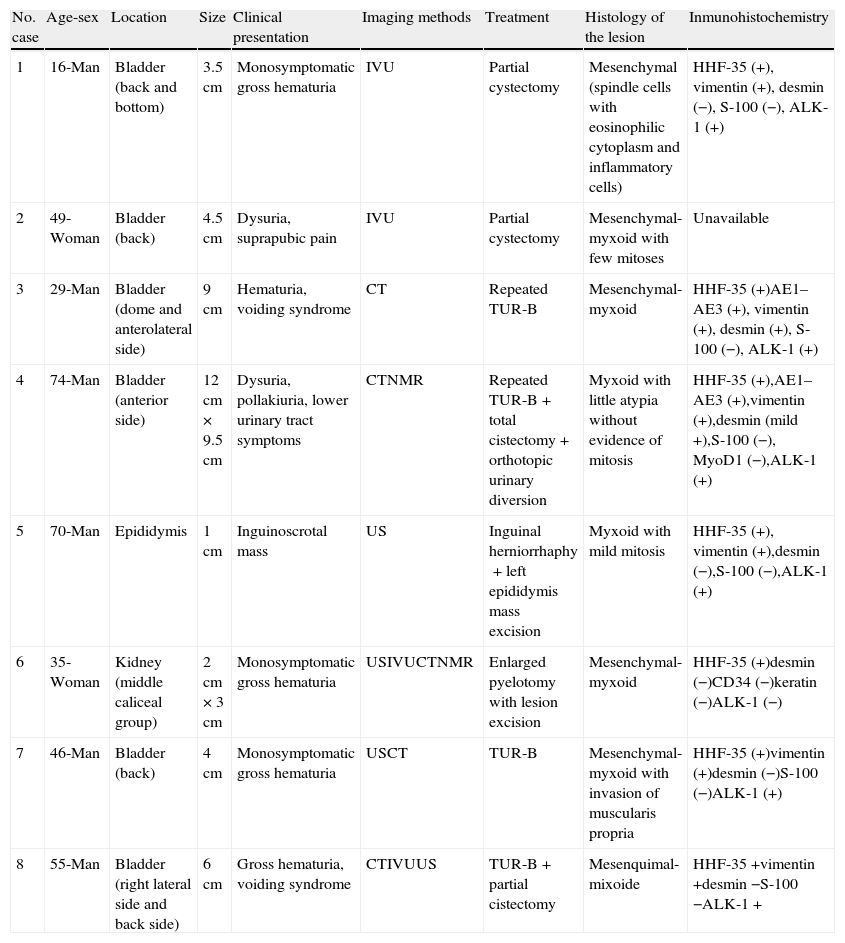
ResultsA total of 8 cases of the urogenital-located inflammatory pseudotumor are described. Of these, 6 were located in the bladder, one in the kidney and one in the epididymis. Mean age of the patients was 46.75 (±19.84) years. Tumor presentation symptoms were macroscopic hematuria, single symptom or accompanied by symptoms of the lower urinary tract and inguinoscrotal mass. With regard to treatment in the cases of bladder localization, transuretheral±cystectomy were performed. In the case of kidney localization, treatment was made by means of pyelotomy and exeresis, and in the case of epididymis localization, simple exeresis was performed. The anatomopathological study showed inflammatory pseudotumor in every case, having a mesenchymal and myxoid appearance, with fusiform cells of eosinophil cytoplasm, with presence of frequent inflammatory cells. The most common immunohistochemical pattern shows positivity for the muscle-specific actin (HHF-35), vimentin and negativity for protein S-100. ALK-1 was positive in 87.5% of the cases.
ConclusionThe inflammatory pseudotumor is a condition having good prognosis which, when there is a good histopathological and immunohistochemical diagnosis, every urologist should recognize and distinguish in order to carry out as conservative a surgical treatment as possible.
El pseudotumor inflamatorio es una lesión rara, de comportamiento benigno y cierta heterogeneidad histológica que aparece en el tracto genitourinario. Se revisan una serie de pseudotumores inflamatorios urogenitales poniendo especial énfasis en sus características clínico-patológicas e inmunohistoquímicas.
Material y métodosAnálisis retrospectivo de la casuística tratada entre enero de 1981 y diciembre de 2010 que identifica los casos de pseudotumor inflamatorio de localización urogenital. Se analizan las variables edad, sexo, clínica, topografía y tratamiento, y las características anatomopatológicas e inmunohistoquímicas de cada caso.
ResultadosSe describen un total de 8 casos de pseudotumor inflamatorio de localización urogenital, de los cuales 6 se localizaron en la vejiga, uno en el riñón y uno en el epidídimo. La edad media de los pacientes fue 46,75 (±19,84) años. Los síntomas de presentación tumoral fueron hematuria macroscópica, monosintomática o acompañada de sintomatología del tracto urinario inferior y masa inguino-escrotal. En cuanto al tratamiento en los casos de localización vesical se realizó resección transuretral±cistectomía; el caso de localización renal se trató mediante pielotomía y exéresis y el de localización epididimaria mediante exéresis simple. El estudio anatomopatológico evidenció pseudotumor inflamatorio en todos los casos, de aspecto mesenquimal y mixoide con células fusiformes de citoplasma eosinófilo, con presencia de frecuentescélulasinflamatorias. Elpatróninmunohistoquímicomáscomúnmostrópositividadpara actina músculo-específica (HHF-35), vimentina y negatividad para proteína S-100. ALK-1 resultó positivo en el 87,5% de los casos.
ConclusiónEl pseudotumor inflamatorio es una entidad de buen pronóstico que, con un buen diagnóstico histopatológico e inmunohistoquímico, todo urólogo debe conocer y distinguir para realizar un tratamiento quirúrgico tan conservador como sea posible.