To demonstrate the presence of mineral metabolism disorders and lithogenic factors in the urine of patients with osteoporotic fracture without previously known stones.
Material and methods67 patients with osteoporotic fractures surgically treated in trauma service are included. The area of the fracture site, fracture mechanism and the presence of osteoporosis were the factors taken into account to diagnose osteoporotic fracture. Mineral metabolism, calciuria, oxaluria, uricosuria and citraturia in 24-h urine were analyzed. The presence of abnormal calcium and phosphorus metabolism was proved comparing hypercalciuria patients with normocalciuria ones.
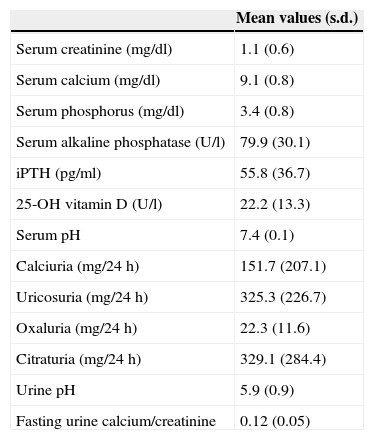
Results12 men and 55 women with mean age 68.8±14.5 years old were included. Mean body mass index (BMI) was 27.4±4.1kg/m2. 42% of patients showed hypercalciuria, 34% hyperoxaluria, 34% hypocitraturia and 7% hyperuricosuria. Statistically significant differences were observed only in fasting calcium/creatinine ratio (0.17 versus 0.08; p<0.0001) when comparing patients with hypercalciuria with those with normocalciuria.
ConclusionsPatients with osteoporotic fractures show different lithogenic factors in urine, mainly hypercalciuria, always in fasting conditions.
Demostrar la presencia de alteraciones del metabolismo del fósforo y calcio y la presencia de factores litogénicos en orina de pacientes con fractura osteoporótica sin litiasis previamente conocida.
Material y métodosSe incluyen 67 pacientes con fractura osteoporótica tratados quirúrgicamente en un servicio de traumatología. Se incluyen pacientes con fractura osteoporótica demostrada por la zona de la fractura, mecanismo de fractura y presencia de osteoporosis en la densitometría ósea. Se analiza el metabolismo fosfocálcico, el estudio de calciuria, la oxaluria, la citraturia y la uricosuria de 24h. Se compara entre los pacientes con hipercalciuria versus normocalciuria la presencia de alteraciones del metabolismo fosfocálcico.
ResultadosDoce hombres y 55 mujeres incluidos con edad media de 68,8±14,5 años. El IMC medio fue de 27,4±4,1kg/m2. Presentan hipercalciuria el 42% de los pacientes, hiperoxaluria el 34% de los pacientes, hipocitraturia el 34% de los pacientes e hiperuricosuria el 7% de los pacientes. Al comparar los pacientes con hipercalciuria versus normocalciuria únicamente hay diferencias estadísticamente significativas en el calcio/creatinina en ayunas (0,17 versus 0,08; p<0,0001).
ConclusiónLos pacientes con fractura osteoporótica presentan diversos factores litogénicos en la orina, fundamentalmente hipercalciuria, siendo siempre de ayunas.