Prosthetic surgery to treat erectile dysfunction has a risk of infection of up to 3%, but this risk can increase to 18% when the surgery involves replacement. This increased risk of infection is attributed to the bacterial colonization of the prosthesis during the initial surgery.
ObjectiveTo analyze the presence of germs in the prosthesis that is withdrawn due to mechanical failure (not infection), as well as the surgical results and its progression.
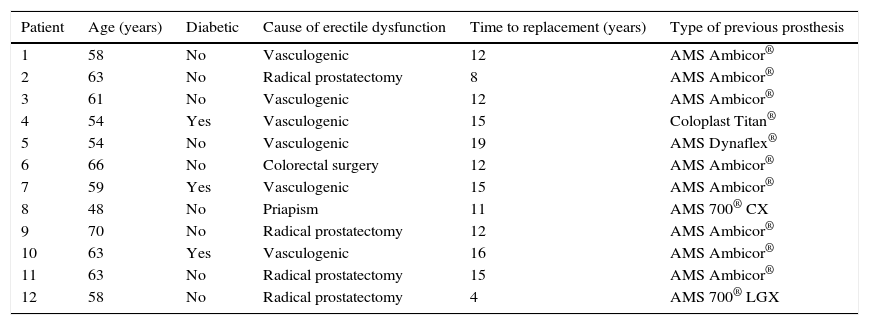
Materials and methodA retrospective study was conducted of all replacements performed between 2013 and 2016 at a single center. We analyzed demographic data, prior type of prosthesis, surgical procedure, microbiological study and follow-up.
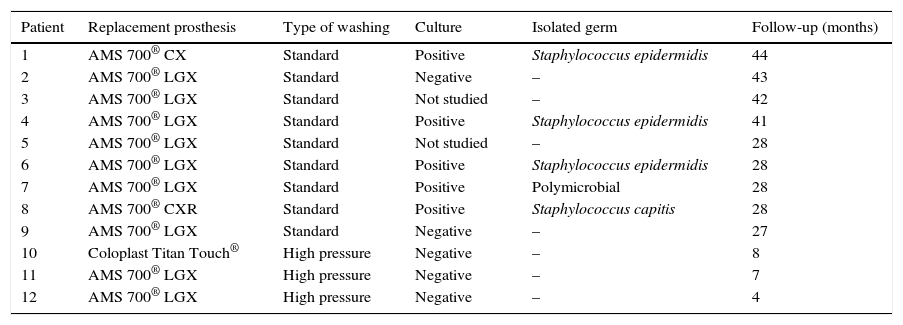
ResultsOf the 12 replacement procedures, a microbiological study of the extracted prosthesis was performed in a total of 10 cases. Of the 10 replacements, the cultures were positive in 5 cases (50%). Staphylococcus epidermidis was the most prevalent germ. All patients underwent a flushing procedure, and an antibiotic-coated prosthesis was implanted. We recorded no infections with the new implanted device after a mean follow-up of 27.33 months (SD 4.13; 95% CI 18.22–36.43).
ConclusionIn our study population, we observed a high rate of bacterial colonization of the prostheses that were replaced due to mechanical failure. When a flushing procedure was performed during the replacement surgery, there were no more infections than those reported in treatment-naive cases.
La cirugía protésica para el tratamiento de la disfunción eréctil tiene un riesgo de infección de hasta un 3%, pero este riesgo puede aumentar hasta un 18% cuando se trata de una cirugía de recambio. Este aumento del riesgo de infección se atribuye a la colonización bacteriana de las prótesis durante la primera cirugía.
ObjetivoAnalizar la presencia de gérmenes en las prótesis que se retiran por fallo mecánico (no infección), así como los resultados quirúrgicos y su evolución.
Materiales y métodoEstudio retrospectivo de todos los recambios realizados entre el año 2013 y el 2016 en un solo centro. Se analizan datos demográficos, tipo de prótesis previa, procedimiento quirúrgico, estudio microbiológico y evolución.
ResultadosDe 12 procedimientos de recambio se realizó un estudio microbiológico de la prótesis extraída en un total de 10 casos. De los 10 recambios, los cultivos resultaron positivos en 5 casos (50%). Staphylococcus epidermidis fue el germen mayoritario. Todos los pacientes se sometieron a un procedimiento de lavado y se implantó una prótesis recubierta de antibiótico. No registramos infecciones del nuevo dispositivo implantado tras un seguimiento medio de 27,33 meses (DE 4,13; IC 95% 18,22–36,43).
ConclusiónEn nuestra población a estudio objetivamos un alto índice de colonización bacteriana de las prótesis que se recambian por fallo mecánico. Tras realizar un procedimiento de lavado en el momento del recambio no objetivamos un mayor número de infecciones que lo descrito en casos vírgenes.