To determine the percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) effects on the tissues using the quantification of inflammatory mediators, and to assess their impact on the development of postoperative complications.
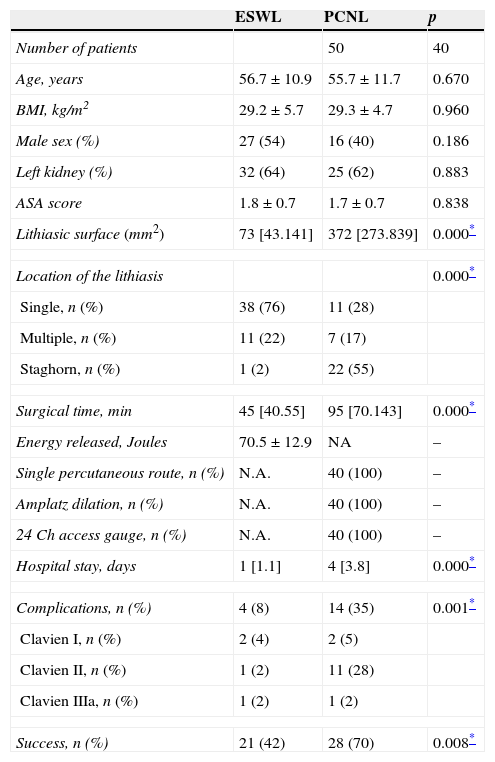
Patients and methodsProspective observational non-randomized study on 40 patients who underwent to PCNL. 50 patients with kidney stone who were treated by extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) were used as control group. Interleukin-1beta (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and C-reactive protein (CRP) were determined at baseline (T0: before treatment), and after 2, 6 and 24h (T1, T2 and T3).
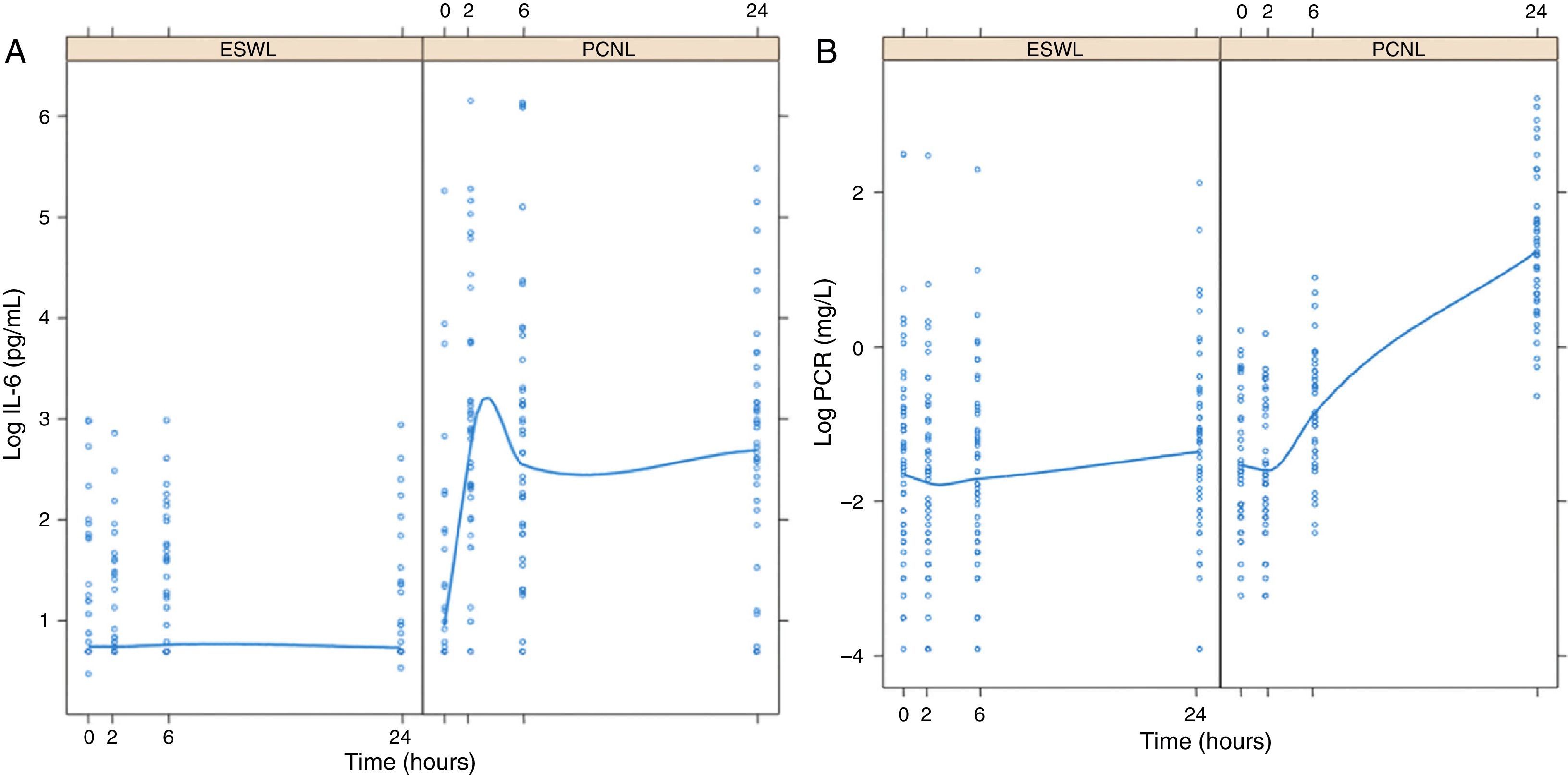
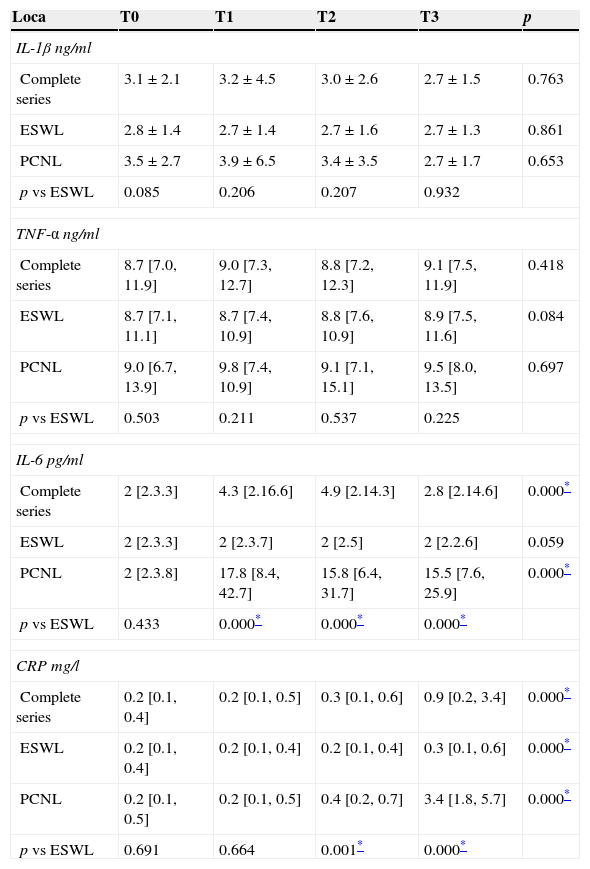
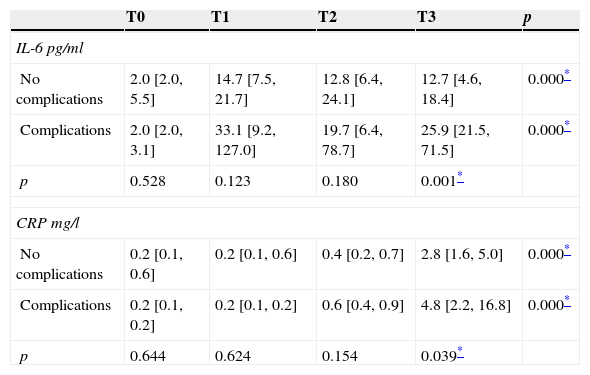
ResultsNo relevant changes on IL-1β and TNF-α were found. IL-6 showed two peaks at 2 and 6h post-PCNL (median 17.8 and 15.8pg/mL, respectively). At 24h CRP had reached its peak value (3.4mg/L). The group treated with ESWL showed no significant changes in any of the markers.
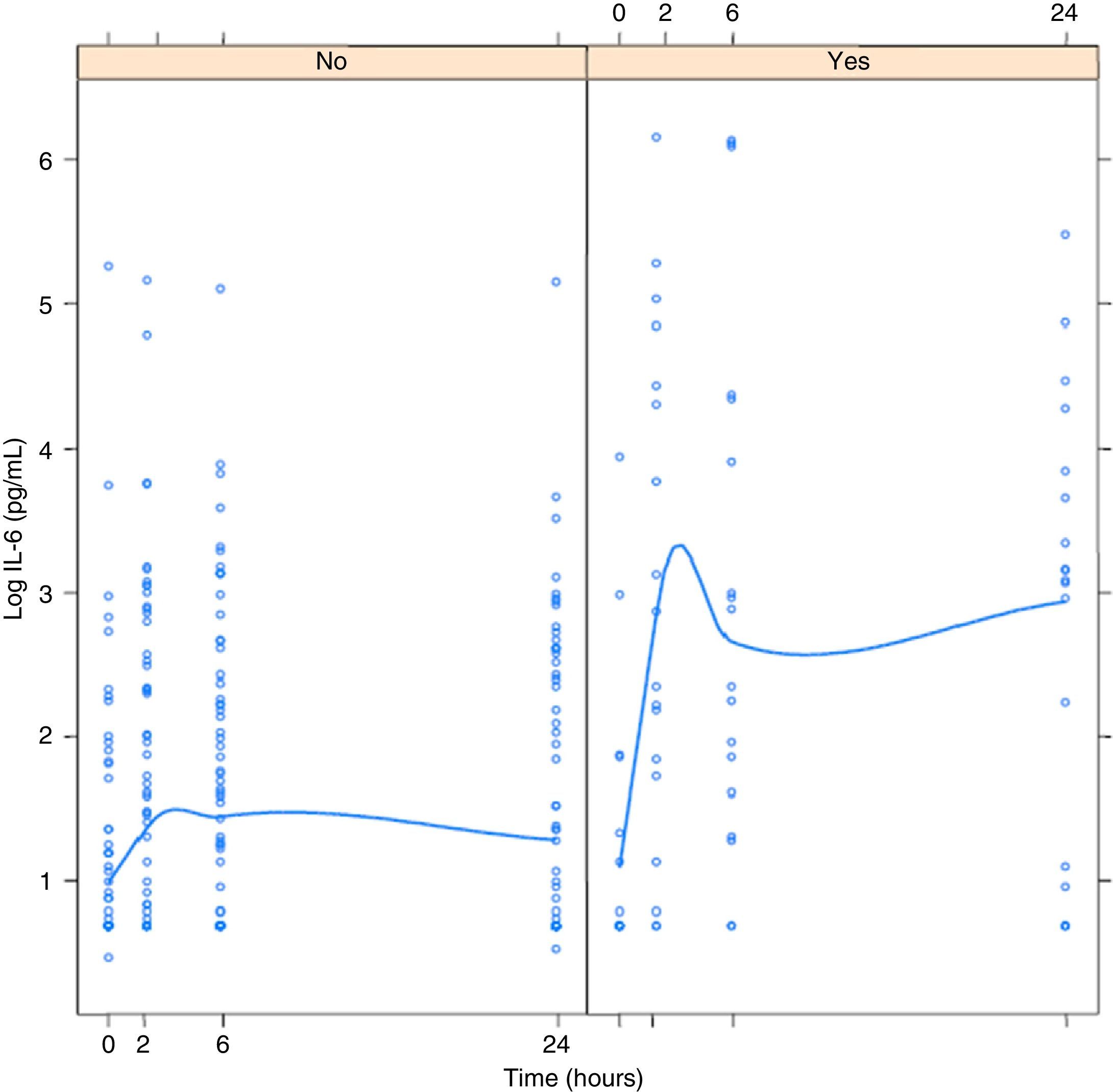
The serum concentration of IL-6 and CRP at 24-h post-NLP is different depending on the occurrence of complications (p=0.001 and p=0.039, respectively). IL-6 showed a good predictive power for the development of complications (AUC .801).
ConclusionsTissue damage caused by the PCNL is low. This damage increases significantly in those cases showing postoperative complications. IL-6 at 24h has been shown to be a good predictive tool for the development of complications.
Determinar los efectos producidos por la nefrolitotomía percutánea (NLP) sobre los tejidos mediante la cuantificación de mediadores de respuesta inflamatoria, así como la influencia del desarrollo de complicaciones postoperatorias en el daño tisular.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio observacional, prospectivo, no aleatorizado en 40 pacientes intervenidos mediante NLP. Como grupo control se empleó una cohorte de 50 pacientes con litiasis renal tratada con litotricia extracorpórea por ondas de choque. Determinación previa al tratamiento (T0) y a las 2, 6 y 24h (T1, T2 y T3) de interleuquina-1beta (IL-1β), factor de necrosis tumoral-alfa (TNF-α), interleuquina-6 (IL-6) y proteína C-reactiva (PCR).
ResultadosNo se observaron cambios en los niveles de IL-1β y TNF-α. IL-6 presentó un pico sérico entre las 2 y 6h de la NLP (mediana de 17,8 y 15,8pg/ml, respectivamente), mientras que el valor pico de PCR fue de 3,4mg/l a las 24h. En el grupo tratado con litotricia expracorpórea por ondas de choque no se apreciaron variaciones significativas en ninguno de los marcadores.
La concentración sérica de IL-6 y PCR a las 24horas post-NLP es diferente en función de la aparición de complicaciones (p=0,001 y p=0,039, respectivamente). IL-6 presentó una buena capacidad predictiva para el desarrollo de complicaciones (AUC de 0,801).
ConclusionesEl daño tisular producido por la NLP es de baja intensidad. Este daño aumenta significativamente en aquellos casos que desarrollan complicaciones en el postoperatorio. La determinación de IL-6 a las 24h post-NLP parece ser un buen marcador predictivo para el desarrollo de complicaciones.