To put forth new findings in urologic oncology with impact in the clinical practice, presented in the principal annual meetings (EAU, ESTRO, AUA, ASCO and ASTRO).
MethodsThe reporters of the OncoUrology Forum select and classify the summaries on genitourinary cancer based on the impact on present or future practice. This document includes the summaries having the highest scores.
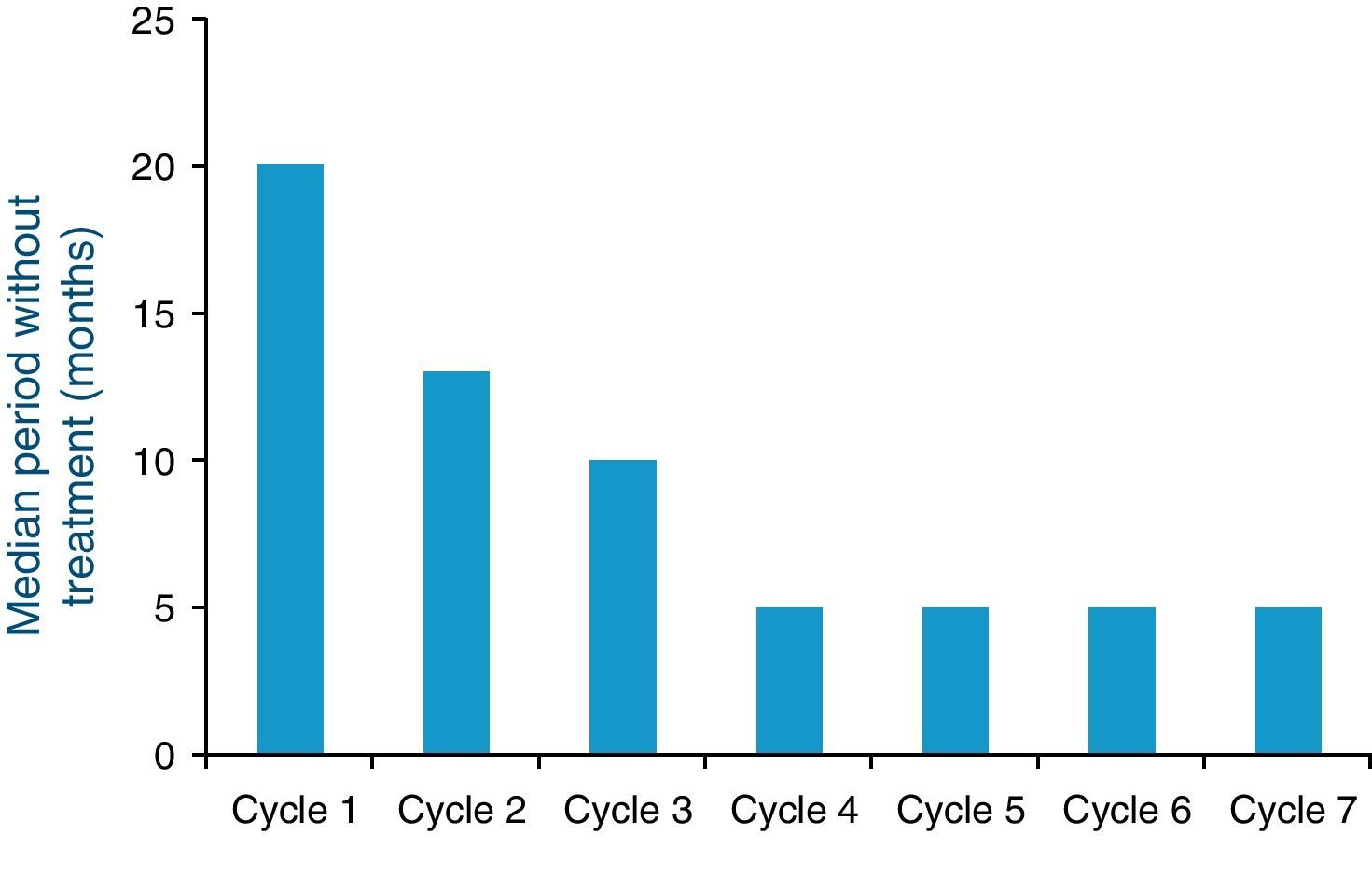
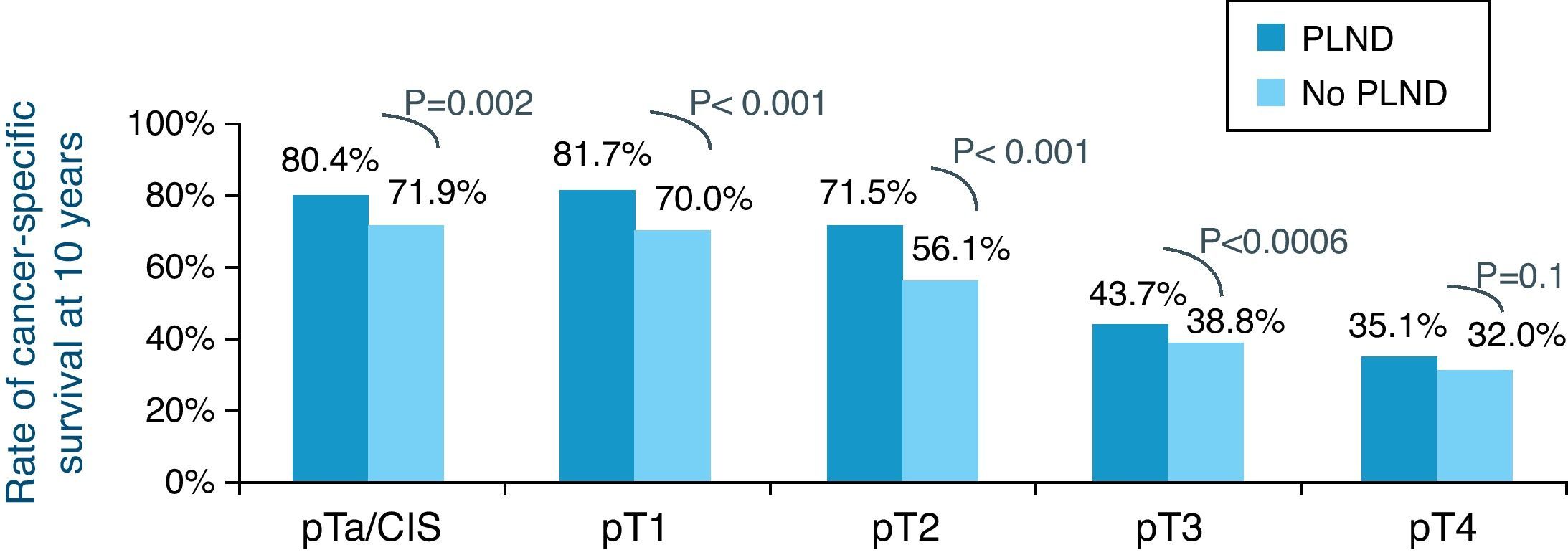
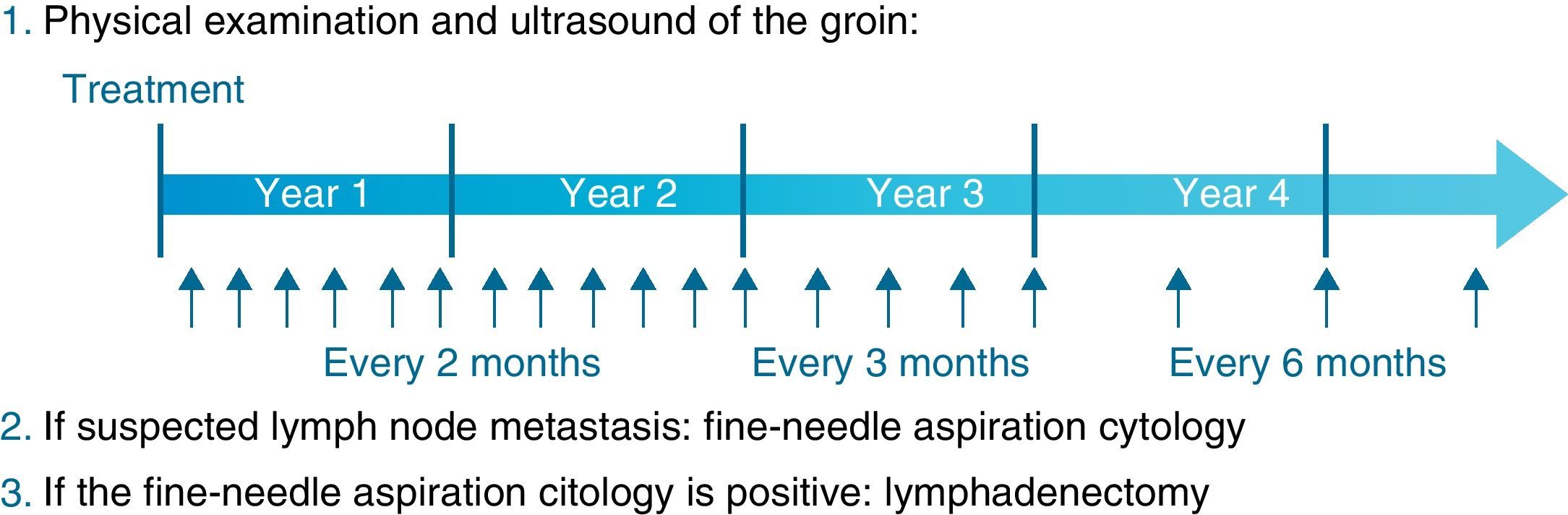
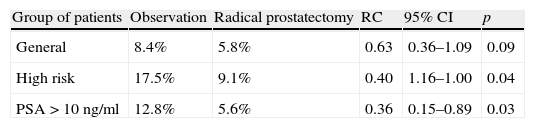
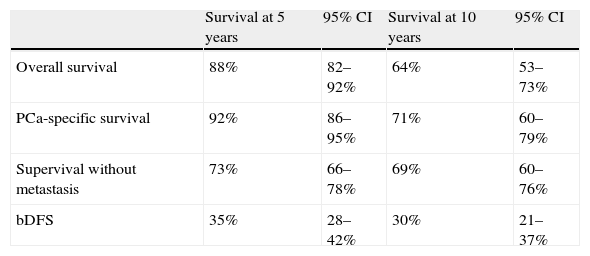
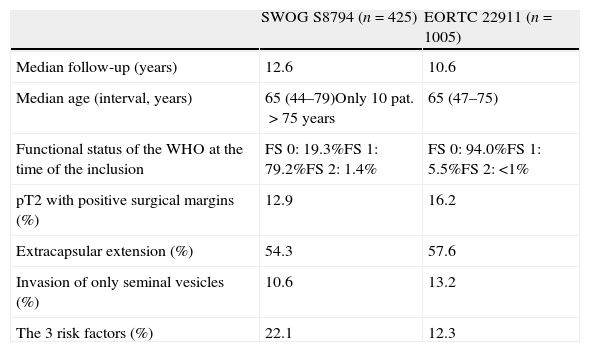
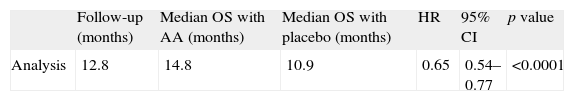
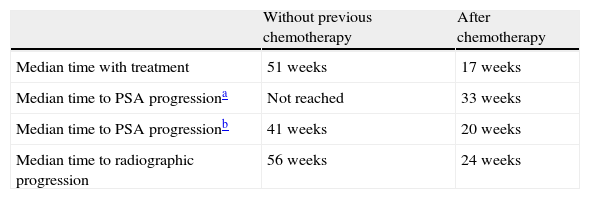
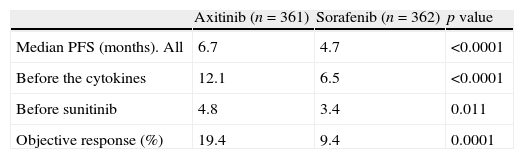
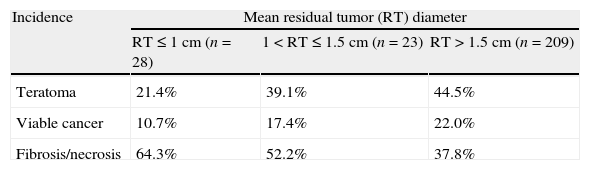
ResultsThe OncoUrology Forum committee considered the following messages important. The PIVOT study shows that radical prostatectomy reduces the specific mortality of prostate cancer (PCa) compared to follow-up in observation, in localized high risk PCa or PSA>10ng/mL. Dissection of the pelvic lymph nodes should be done in all the patients with bladder cancer treated by radical cystectomy, regardless of the tumor stage, in accordance with baseline analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) data. An analysis of the SEER of patients with renal cancer concluded that the radical nephrectomy is associated to worse cardiovascular and overall survival compared to those treated with partial nephrectomy in localized renal cell carcinoma of ≤2cm. In patients with nonseminomatous germ cells cancer, retroperitoneal lymph node dissection should not be omitted when the residual tumor size is ≤1cm because of the considerably high risk of teratoma and viable cancer.
ConclusionsAlthough these studies do not offer a final response for all the oncourological subjects, these results will have an impact on the daily clinical practice.
Exponer los nuevos hallazgos en urología oncológica con impacto en la práctica clínica presentados en las principales reuniones anuales (EAU, ESTRO, AUA, ASCO y ASTRO).
MétodosLos informadores del OncoUrology Forum seleccionan y clasifican los resúmenes sobre cáncer genitourinario en función del impacto sobre la práctica clínica presente o futura. Este documento incluye los resúmenes con mayor puntuación.
ResultadosLa comisión del OncoUrology Forum consideró importantes los siguientes mensajes. El estudio PIVOT demuestra que la prostatectomía radical reduce la mortalidad específica del cáncer de próstata (CaP), en comparación con seguimiento en observación, en CaP localizado de alto riesgo o PSA>10 ng/ml. La disección de los ganglios linfáticos pélvicos debería hacerse en todos los pacientes con cáncer vesical tratados mediante cistectomía radical, independientemente del estadio tumoral, de acuerdo con un análisis de la base de datos Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER). Un análisis de la SEER de pacientes con cáncer renal concluyó que la nefrectomía radical se asocia a peor supervivencia global y cardiovascular, en comparación con la nefrectomía parcial, en carcinoma de células renales localizado y ≤2cm. En pacientes con tumor de células germinales no seminomatoso, no se debe omitir la disección de los ganglios linfáticos retroperitoneales tras quimioterapia cuando el tamãno tumoral residual es ≤1cm, debido al riesgo considerablemente alto de teratoma y cáncer viable.
ConclusionesAunque estos estudios no ofrecen una respuesta final para todos los temas oncourológicos, sus resultados tendrán impacto en la práctica clínica diaria.