Several studies have already shown that changes in the AR gene may be associated with a more aggressive disease phenotype and even castration-resistant prostate cancer. Thus, we investigated cytogenetic and molecular alterations linked to AR.
Materials and methodsTo evaluate AR methylation, we performed a cytogenetic-molecular analysis using fluorescence in situ hybridization that uses specific probes for the AR gene (Xq11.12) and the X chromosome centromere. For AR activity, we performed a qualitative analysis of human androgen receptor activity. To analyze the expression of AR in PC3 and LNCaP cell lines, we used qPCR assays.
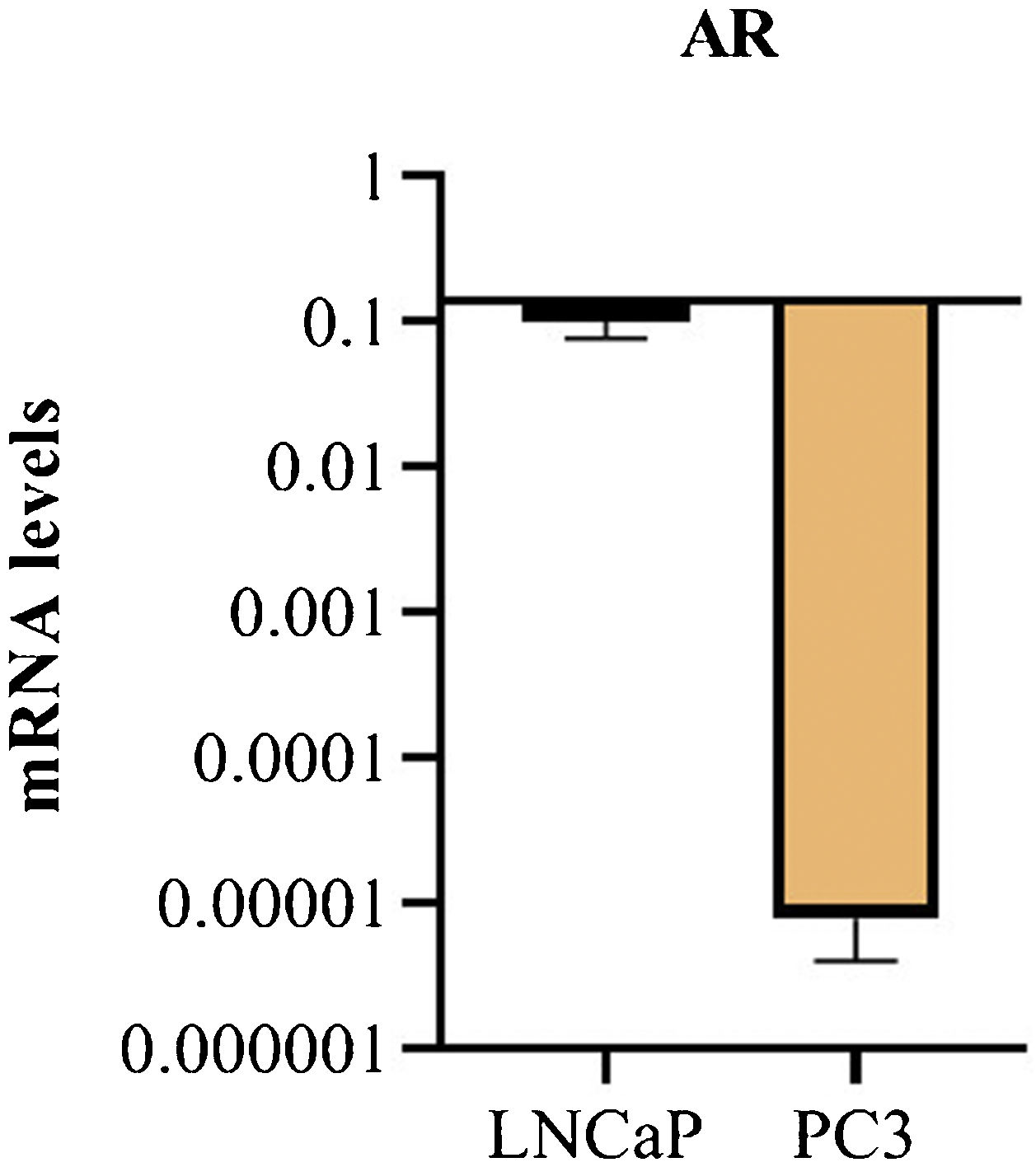
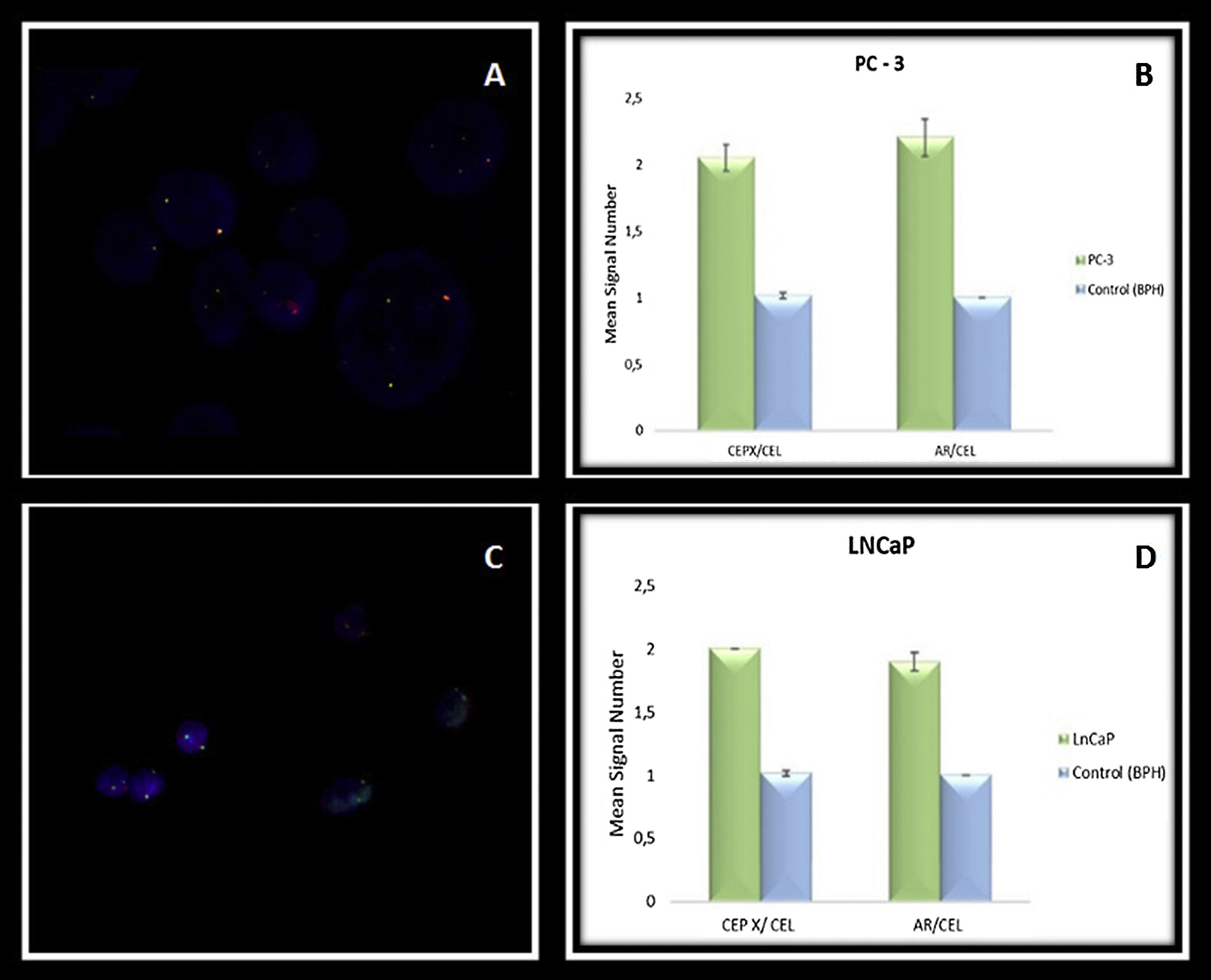
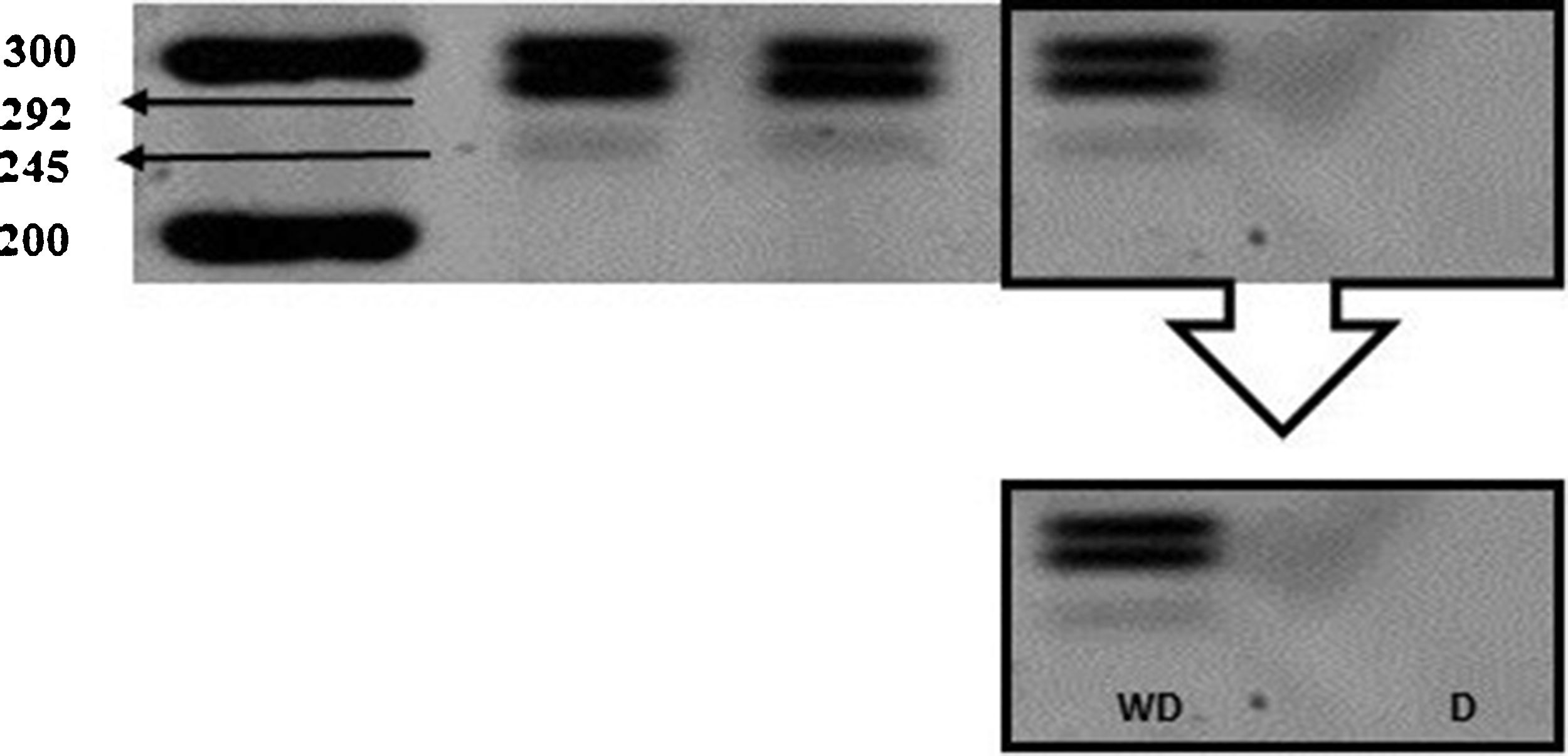
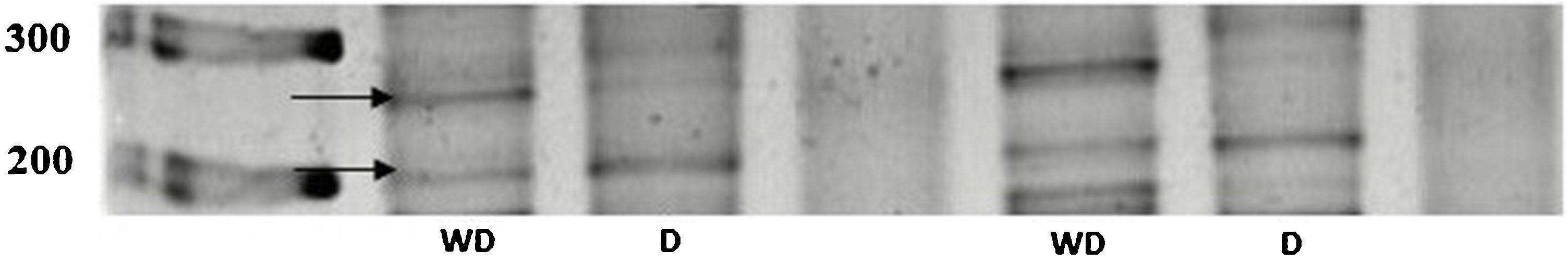
ResultsIn the qPCR assay, we found downregulation of AR in the PC3 cell line compared with the LNCaP. We found the presence of X chromosome polysomy in PC-3 and LNCaP cell lines by FISH assay. In the HUMARA-Q assay, we found two X chromosomes/cell and the activity of both AR in the PC-3 cell line. In LNCaP cells, we found two X chromosomes/cell and methylation of only one AR.
ConclusionCastration-resistant prostate cancer phenotype represents a significant challenge in the setting of urological management. The X chromosomes and AR-linked alterations may contribute to a better understanding of the disease. However, further studies should be performed in an attempt to elucidate as much as possible the role of AR in the castration-resistant prostate cancer phenotype.
Diversos estudios han demostrado que los cambios en el gen RA pueden estar asociados a un fenotipo de enfermedad más agresivo e incluso al cáncer de próstata resistente a la castración. Por este motivo, hemos investigado las alteraciones citogénicas y moleculares asociadas al RA.
Materiales y métodosPara evaluar la metilación del RA, realizamos un análisis citogenético-molecular mediante hibridación fluorescente in situ que utiliza sondas específicas para el gen del RA (Xq11.12) y el centrómero del cromosoma X. Respecto a la actividad del RA, realizamos un análisis cualitativo de la actividad del receptor de andrógenos humano. Para analizar la expresión del RA en las líneas celulares PC3 y LNCaP, utilizamos ensayos de qPCR.
ResultadosEn el ensayo qPCR, encontramos una regulación a la baja del RA en la línea celular PC3 en comparación con la LNCaP. Hallamos la presencia de polisomía del cromosoma X en las líneas celulares PC-3 y LNCaP mediante el ensayo FISH. En el ensayo HUMARA-Q encontramos la presencia de dos cromosomas X/célula y actividad en ambos RA de la línea celular PC-3. En las células LNCaP hallamos la presencia de dos cromosomas X/célula y la metilación de solo un RA.
ConclusiónEl fenotipo del cáncer de próstata resistente a la castración representa un gran desafio en el tratamiento urológico. Estos cromosomas X y las alteraciones ligadas al RA pueden contribuir a una mejor comprensión de la enfermedad; sin embargo, deben realizarse más estudios para arrojar más luz sobre el papel del RA en el fenotipo del cáncer de próstata resistente a la castración.