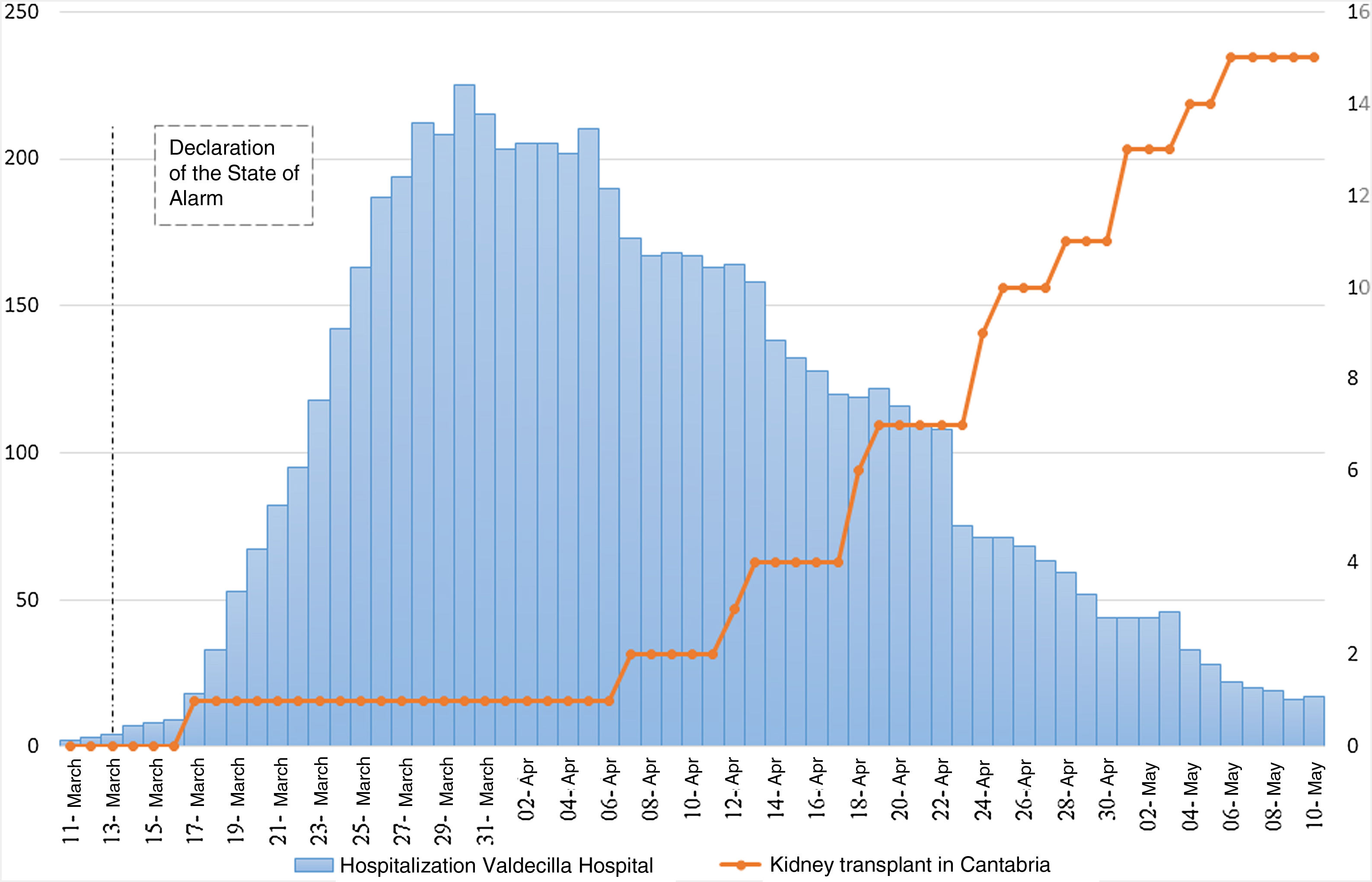
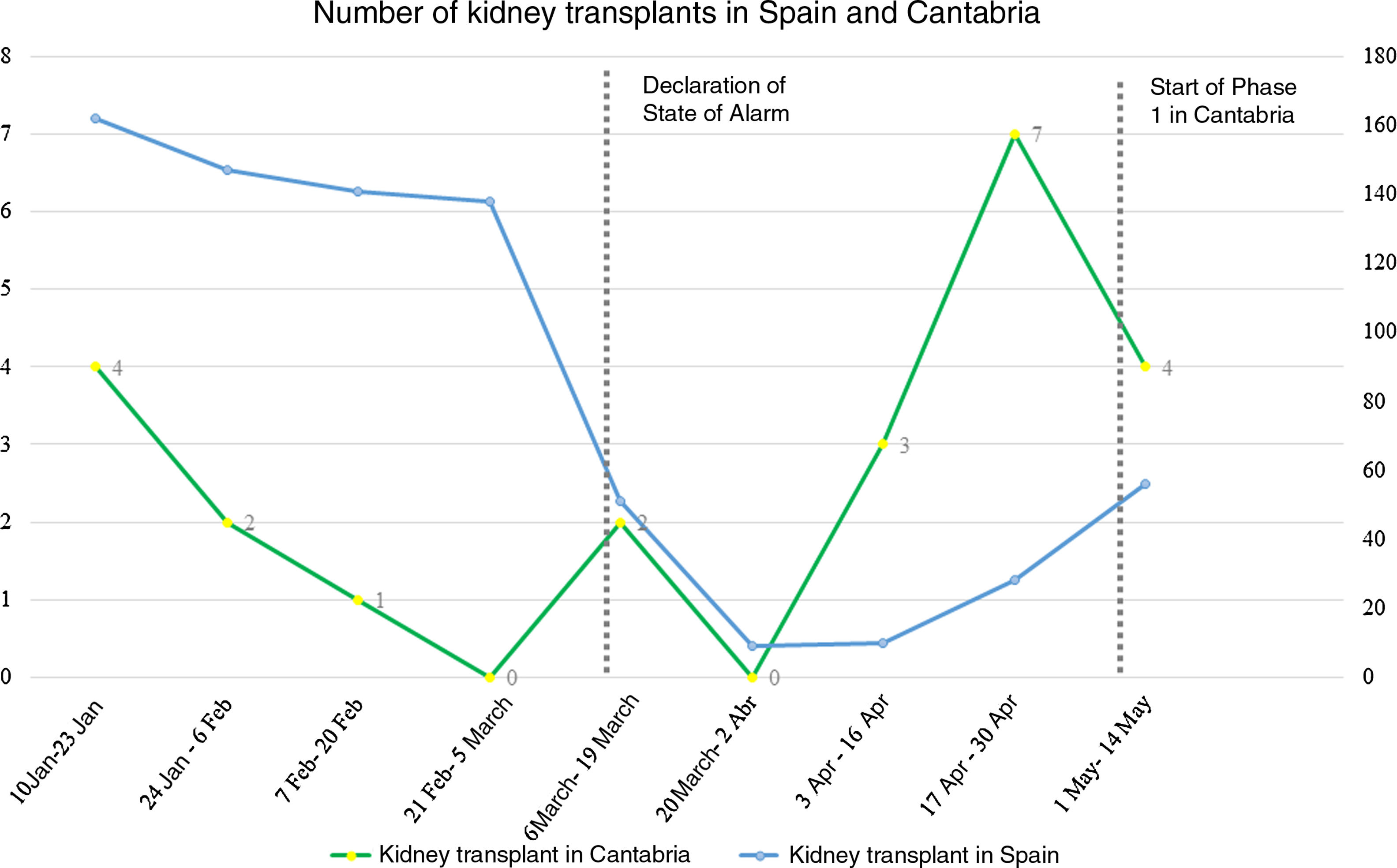
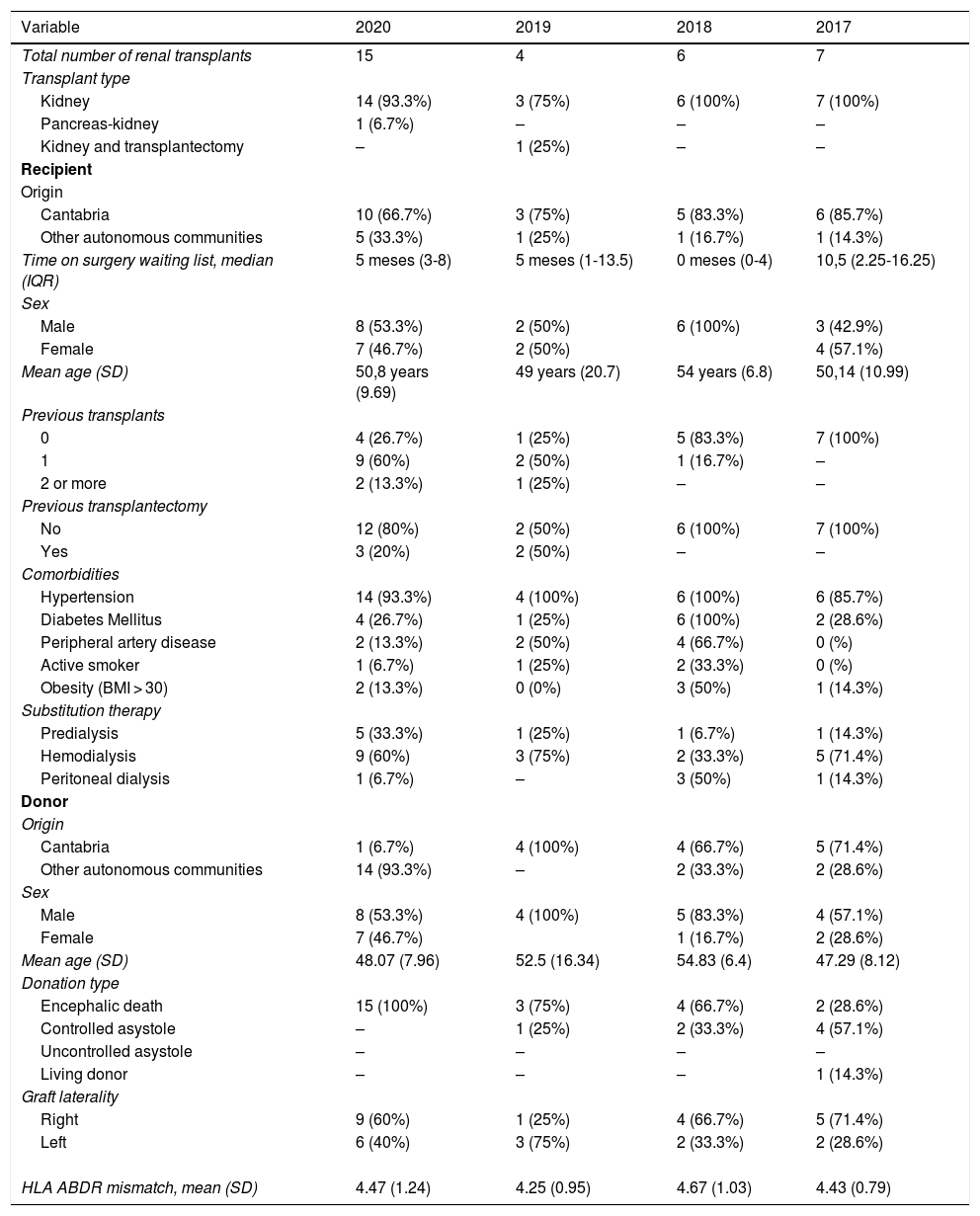
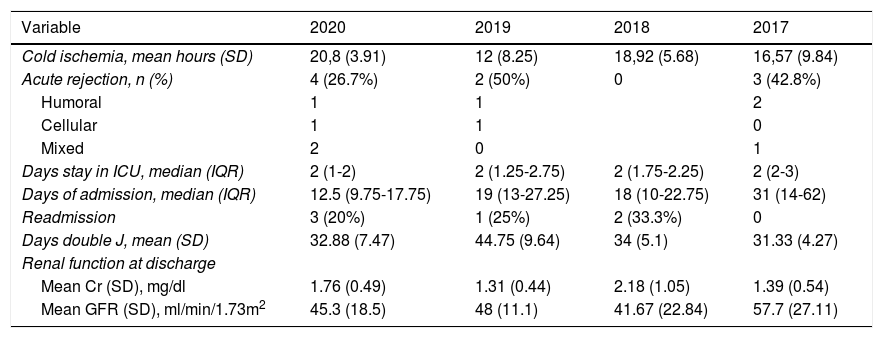
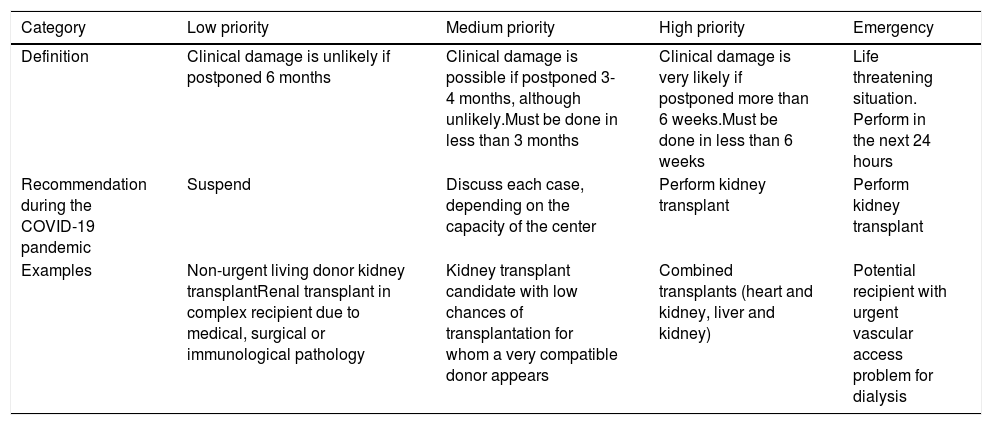
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the national transplant activity has been reduced due to the overload of the health system and concern for patient safety in this situation. The aim of our work is to expose the activity of kidney transplantation in Cantabria during the state of alarm, as well as to assess the safety of the transplantation program.
Material and methodsRetrospective study of kidney transplants performed in our Center from the beginning of the state of alarm until the beginning of the lockdown easing in Cantabria. Descriptive analysis of the demographic data of recipients and their donors, intraoperative data and postoperative outcomes. Comparative analysis with the data of the same period in 2017–2019, by means of the X2 for categorical variables, Student’s T and Mann-Whitney U tests in case of quantitative variables of normal and non-normal distribution, respectively.
ResultsFifteen kidney transplants were performed in the period described. Delayed renal function (DRF) was seen in 7.5% of patients, and 26.6% showed data of acute rejection; no patient presented COVID-19 disease.
Comparative analysis showed a remarkable increase in the number of transplants in comparison with previous periods (15 vs 5.6), at the expense of donors from outside Cantabria (93.3%). We found no statistically significant differences in terms of cold ischemia time (p 0.77), DRF (p 0.73), need for dialysis (p 0.54), or appearance of post-surgical complications (p 0.61).
ConclusionsThe evolution of the pandemic in our region, and the adoption of strict protective measures has allowed the early and safe resumption of the renal transplantation program, increasing the number of transplants performed compared to previous years and maintaining comparable early post-operative results.
Durante la pandemia COVID-19, la actividad nacional de trasplante se ha visto reducida por la sobrecarga del sistema sanitario, y la preocupación por la seguridad de los pacientes en esta situación. El objetivo de nuestro trabajo es exponer la actividad de trasplante renal en Cantabria durante el estado de Alarma, así como valorar la seguridad del programa de trasplante.
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de los trasplantes renales realizados en nuestro Centro desde el inicio del estado de Alarma hasta el inicio del desconfinamiento en Cantabria. Análisis descriptivo de los datos demográficos de receptores y sus donantes, datos intraoperatorios y resultados postoperatorios. Análisis comparativo con los datos del mismo periodo de 2017–2019, mediante los estadísticos X2 para variables categóricas, T-Student y U de Mann-Whitney en caso de variables cuantitativas de distribución normal y no normal, respectivamente.
ResultadosSe realizaron 15 trasplantes renales en el periodo descrito. 7,5% de pacientes presentaron función renal retrasada (FRR), 26,6% mostró datos de rechazo agudo; ningún paciente presentó enfermedad por COVID-19. En el análisis comparativo, llamativo aumento del número de trasplantes frente a periodos anteriores (15 vs 5,6), a expensas de donantes de fuera de Cantabria (93,3%). No encontramos diferencias estadísticamente significativas en cuanto a tiempo de isquemia fría (p 0,77), FRR (p 0,73), necesidad de diálisis (p 0,54), o aparición de complicaciones postquirúrgicas (p 0,61).
ConclusionesLa evolución de la pandemia en nuestra región y la adopción de medidas de protección rigurosas ha permitido reiniciar el programa de trasplante renal de una forma temprana y segura, aumentando el número de trasplantes realizados frente a años anteriores y manteniendo unos resultados postoperatorios tempranos comparables.