To evaluate the efficacy of 2 different techniques: shock wave lithotripsy (SWL) vs. super-mini percutaneous nephrolithotomy (SMP), in terms of success as well as complication rates in pediatric renal stones sizing <25mm.
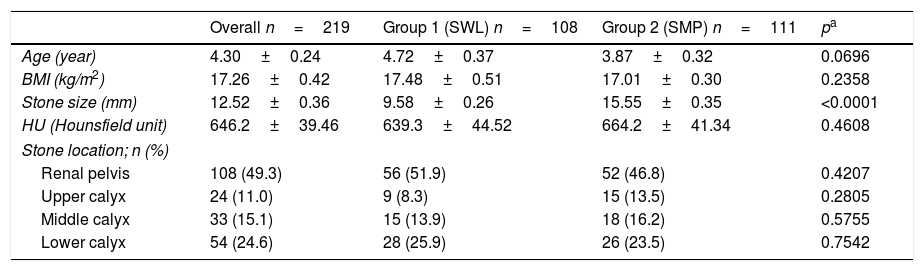
Patients and methodsA total of 219 children (aging between 1 and 17 years) undergoing 2 different treatment modalities (SWL vs. SMP) for kidney stones <25mm were included. Depending on the type of the procedure applied, children were divided into 2 different groups: group 1 (n=108), children treated with SWL, and group 2 (n=111), children treated with SMP. All treatment related parameters (stone free rates, number of sessions, treatment duration, hospitalization, presence of the residual fragments, complications as well as the need for additional interventions) were noted and evaluated between 2 groups in a comparative manner.
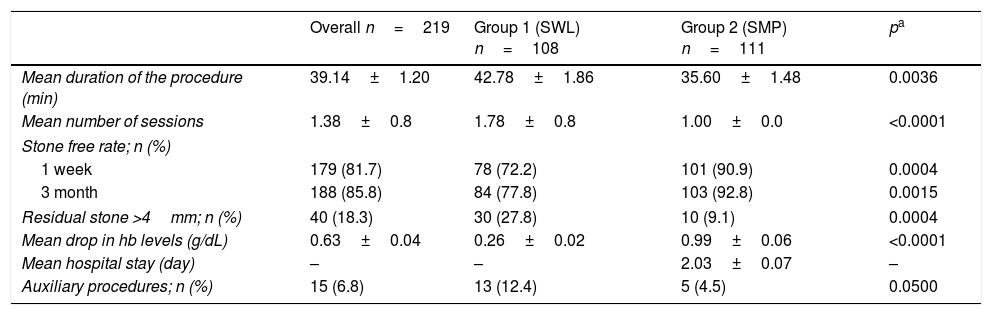
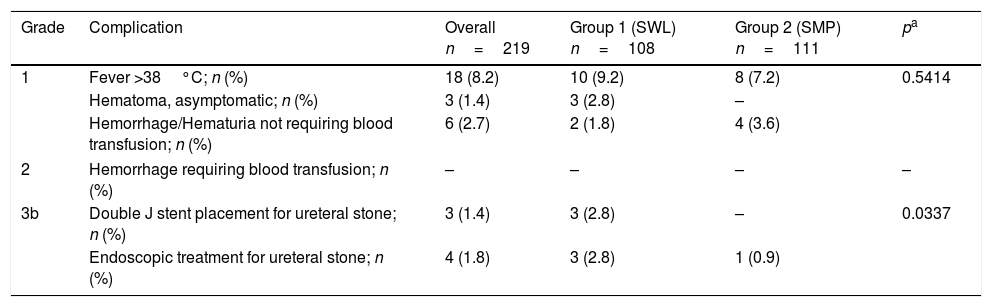
ResultsEvaluation of our data has clearly demonstrated that the percentage of residual fragments after SWL was significantly higher when compared with SMP. Although SWL required several sessions under general anesthesia in a certain per cent of the cases (54.6%), SMP was successful in one session in all of the cases. Last but not least, in addition to the similar minor complication rates observed in both group of cases, no major complication observed in any case and no case in both groups again required blood transfusion after these 2 procedures with no significant drop rates in hemoglobin levels.
ConclusionsAlthough SWL is still the preferred treatment modality for the majority of kidney stones in children due to its safe and non-invasive nature, SMP modality may be applied as a valuable alternative in this specific patient population for its excellent stone free rates obtained in a single session and acceptable complication rates in the minimal invasive management of stones <25mm.
Evaluar la eficacia de 2 técnicas diferentes, la litotricia por ondas de choque (LOC) frente a la supermini nefrolitotomía percutánea (SMP), en términos de éxito y tasas de complicaciones en cálculos renales pediátricos de tamaño<25mm.
Pacientes y métodosSe incluyeron un total de 219 niños (edades comprendidas entre uno y 17 años) sometidos a 2 modalidades de tratamiento diferentes (LOC vs. SMP) para cálculos renales<25mm. Dependiendo del tipo de procedimiento aplicado, los niños se dividieron en 2 grupos diferentes: grupo 1 (n=108), formado por niños tratados con LOC, y grupo 2 (n=111), integrado por niños tratados con SMP. Todos los parámetros relacionados con el tratamiento (tasas libres de cálculos, número de sesiones, duración del tratamiento, hospitalización, presencia de fragmentos residuales, complicaciones así como la necesidad de intervenciones adicionales) se observaron y evaluaron entre 2 grupos de forma comparativa.
ResultadosLa evaluación de nuestros datos ha demostrado claramente que el porcentaje de fragmentos residuales fue significativamente mayor en los casos sometidos a procedimiento de LOC en comparación con SMP. Aunque LOC requirió varias sesiones bajo anestesia general en un cierto porcentaje de los casos (54,6%), SMP tuvo éxito en una sesión en todos los casos. Por último, pero no por ello menos importante, además de las tasas de complicaciones menores similares observadas en ambos grupos de casos, no se observó ninguna complicación grave y ningún caso requirió transfusión de sangre después de estos 2 procedimientos, sin tasas significativas de descenso en los niveles de hemoglobina.
ConclusionesAunque la LOC sigue siendo la modalidad de tratamiento preferida para la mayoría de los cálculos renales en niños por su naturaleza segura y no invasiva, la modalidad de SMP puede aplicarse como una alternativa valiosa en esta población específica de pacientes por sus excelentes tasas de ausencia de cálculos obtenidas en una sesión única y tasas de complicaciones aceptables en el manejo invasivo mínimo de cálculos<25mm.