Nowadays, it is almost impossible not to link most of the sources of modern knowledge to information of 2.0 technologies. The aim of this review is to analyze the role of scientific social media (Sc-SoMe) and its potential applications in urology.
Material and methodsA literature search was carried out using the PubMed database until July 2018. The research was performed with the following terms: “Social Media”, “urology”, “science”, “research”.
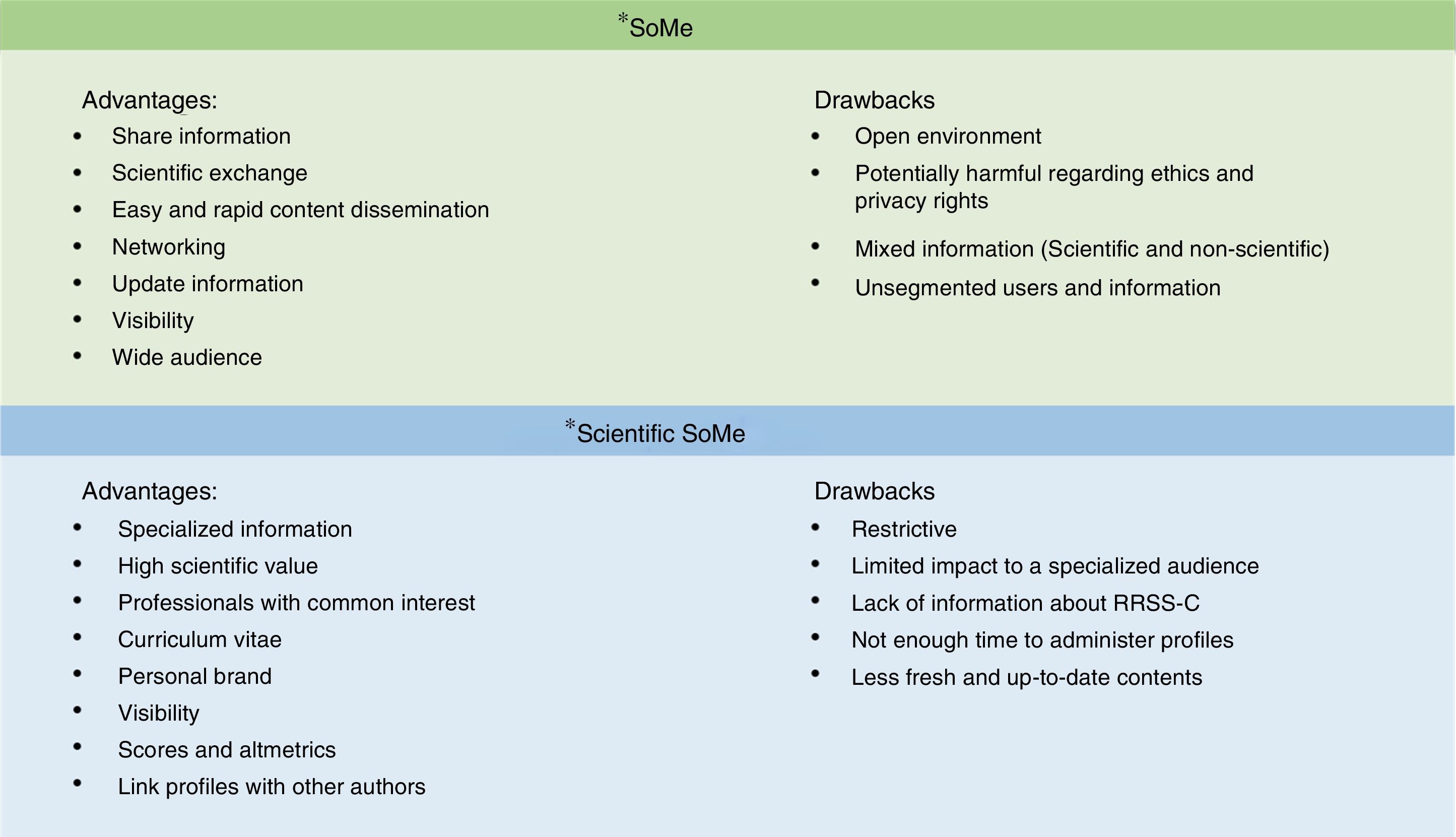
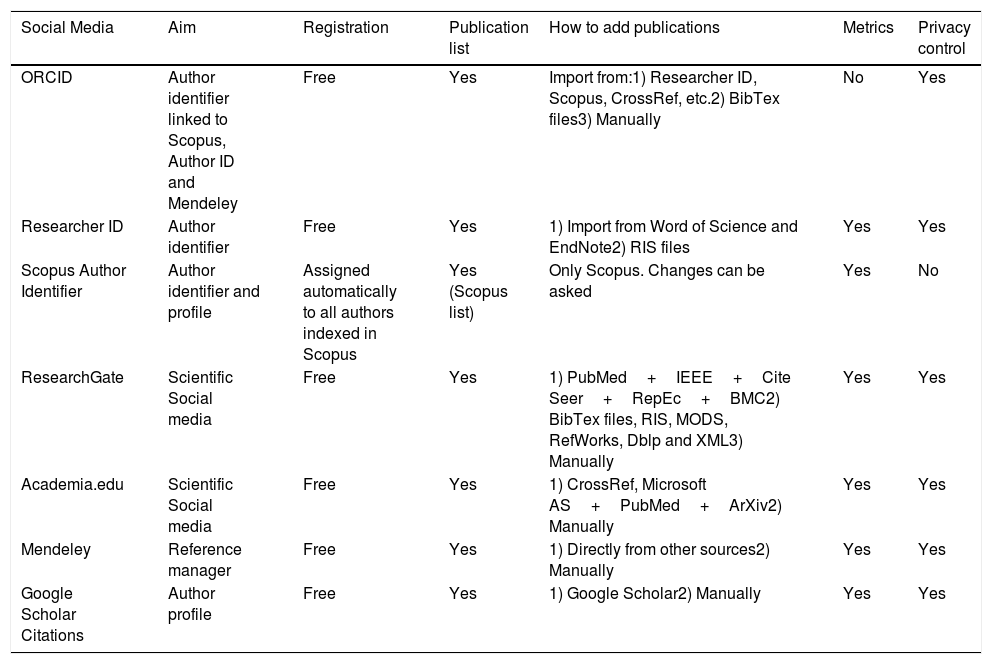
ResultsSocial media (SoMe) offers integrated services and easy tools for communication, collaboration and participation. Popular prototypical platforms of SoMe are Facebook, Twitter or Instagram. SoMe not only influence private life and personal communication, but these also affect business and science sectors. In this sense, the term Sc-SoMe describes the impact and usage of 2.0 technologies platforms on scientific work. There are different models of Sc-SoMe such as author identifiers which are unique identifiers that allow managing the professional identity of each researcher, distinguishing them from other researchers and unequivocally associating their work and author profiles. This helps us manage our own academic profile and control the information available about us and ensure that other researchers are finding correct and complete information about our research and career. Examples of Sc-SoMe are: ResearchGate, ORCID, Mendeley among others.
ConclusionsSc-SoMe should not only provide important information and services for literature and literature search. These could also be an important catalyst for promoting appropriate and helpful services in the context of a new concept of science, the science 2.0.
Hoy en día es casi imposible desvincular la mayoría de las fuentes de conocimiento e información modernos a las tecnologías 2.0. El objetivo de este trabajo es realizar una revisión de las redes sociales (RRSS) científicas (RRSS-C) y el papel que estas desempeñan en la urología actual.
Material y métodosSe realizó una búsqueda bibliográfica en la base de datos PubMed hasta julio de 2018. Se utilizaron los siguientes términos de búsqueda: «Redes sociales», «Urología», «Ciencia», «Investigación».
ResultadosLas RRSS ofrecen servicios integrados y herramientas sencillas para la comunicación, la colaboración y la participación. Las instancias prototípicas populares de las redes son Facebook, Twitter o Instagram. Las RRSS no solo han afectado la vida privada y la comunicación personal, sino que también han tenido un alto impacto en el mundo empresarial y la ciencia. En este sentido, el término RRSS-C describe el uso de las plataformas de tecnologías 2.0 en el trabajo científico. Existen diferentes modelos de RRSS-C. Están los identificadores de autor, que son identificadores únicos que permiten gestionar la identidad profesional de cada investigador, distinguiéndolos de otros investigadores y asociando inequívocamente su trabajo. Los perfiles de autor nos ayudan a gestionar nuestro propio perfil académico y a controlar la información disponible sobre nosotros. De esta manera nos aseguramos de que otros investigadores encuentren información correcta y completa sobre nuestra carrera e investigación. Algunos ejemplos de RRSS-C son: ResearchGate, ORCID y Mendeley, entre otros.
ConclusionesLas RRSS-C no solo deben proporcionar información y servicios importantes para la literatura y búsqueda de esta, sino que también podrían ser un catalizador importante para promover servicios apropiados y útiles en el contexto de un nuevo concepto de ciencia, la ciencia 2.0.