To review our experience in robot-assisted radical cystectomy, assessing the complications and oncological and functional results.
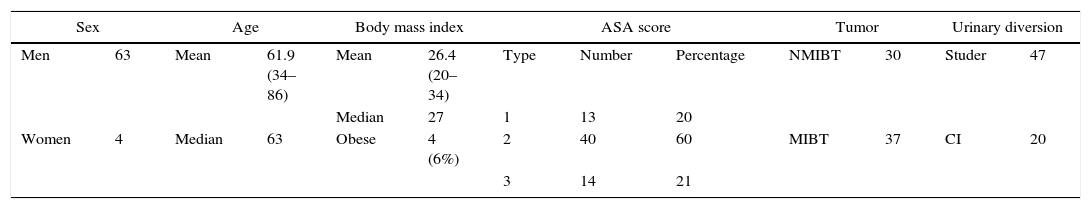
Materials and methodsFrom 2007 to 2014, we performed 67 robot-assisted radical cystectomies combined with lymphadenectomy in 61 cases. The operations were performed on 37 patients due to muscle-invasive tumors and on 30 due to high-risk nonmuscle-invasive tumors. Urinary diversion was conducted extracorporeally, using a Studer neobladder in 47 cases.
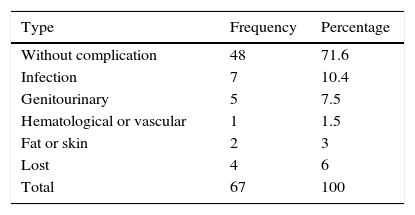
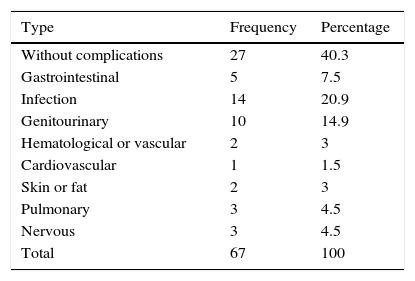
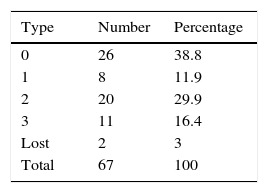
ResultsThe mean blood loss was 300mL. No case required conversion to open surgery. The median number of lymph nodes extracted was 16 (range 3–33). Pathology revealed 16 pT0, 15 pTis, -pT1-pTa and 44 muscle-invasive tumors, 8 pN+ and 1 with positive margins. The mean hospital stay was 9 days. With a median follow-up of 16 months, 9 (13%) patients were readmitted after the discharge, most for infections associated with the vesical catheter and other catheters. Forty patients (59.7%) presented complications (most were Clavien grade 1–2). There was recurrence during the follow-up in 4 cases (6%), and 4 (5.9%) patients died from cancer. Nineteen (28.3%) patients had complications after 30 days, most of which were urinary tract infections. Of the 47 patients with a neobladder, 45 (96%) had proper daytime continence and 42 (89%) had proper nighttime continence. Ninety percent and 64% of the patients with previously normal sexual function and reduced sexual function, respectively, were able to preserve sexual function with or without drug treatment.
ConclusionsRobot-assisted radical cystectomy plus lymphadenectomy, with extracorporeal reconstruction of the urinary diversion, offers good oncological and functional results without increasing the number of complications.
Revisar nuestra experiencia en cistectomía radical robótica, valorando las complicaciones, resultados oncológicos y funcionales.
Material y métodosDesde el 2007 al 2014 realizamos 67 cistectomías radicales robóticas asociadas a linfadenectomía en 61 casos. En 37 pacientes por tumor músculo-invasivo y en 30 por no músculo-invasivo de alto riesgo. La derivación urinaria se realizó de forma extracorpórea, siendo con neovejiga tipo Studer en 47 casos.
ResultadosLa pérdida hemática media fue 300ml. Ningún caso requirió conversión a cirugía abierta. La mediana de ganglios extraídos fue 16 (rango: 3-33). La anatomía patológica reveló 16 pT0, 15 (pTis,-pT1-pTa) y 44 tumores músculo-invasivos, 8 pN+ y uno con márgenes positivos. La estancia media hospitalaria fue 9 días. Con una mediana de seguimiento de 16 meses, 9 (13%) reingresaron tras el alta, la mayoría por infecciones asociadas a catéteres y sonda vesical. Cuarenta pacientes (59,7%) presentaron complicaciones (la mayoría Clavien 1-2). En 4 casos (6%) hubo recurrencia durante el seguimiento y fallecieron por enfermedad oncológica 4 (5,9%). Diecinueve (28,3%) pacientes tuvieron complicaciones después de 30 días, siendo en su mayoría infecciones urinarias. De 47 pacientes con neovejiga presentan una correcta continencia diurna 45 (95%) y nocturna del 89%. De los pacientes con función sexual previa normal o disminuida un 90% y 64% respectivamente conservan función sexual con o sin uso de tratamiento farmacológico.
ConclusionesLa cistectomía radical más linfadenectomía robótica, con reconstrucción extracorpórea de la derivación urinaria, ofrece buenos resultados oncológicos y funcionales sin aumentar el número de complicaciones.