There is growing interest in the use of more aggressive therapeutic modalities for treating metastatic prostate cancer. In this study, we examine the use of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for patients with oligorecurrent prostate cancer.
We analyzed the biochemical response and toxicity of patients who underwent this therapy at our centre.
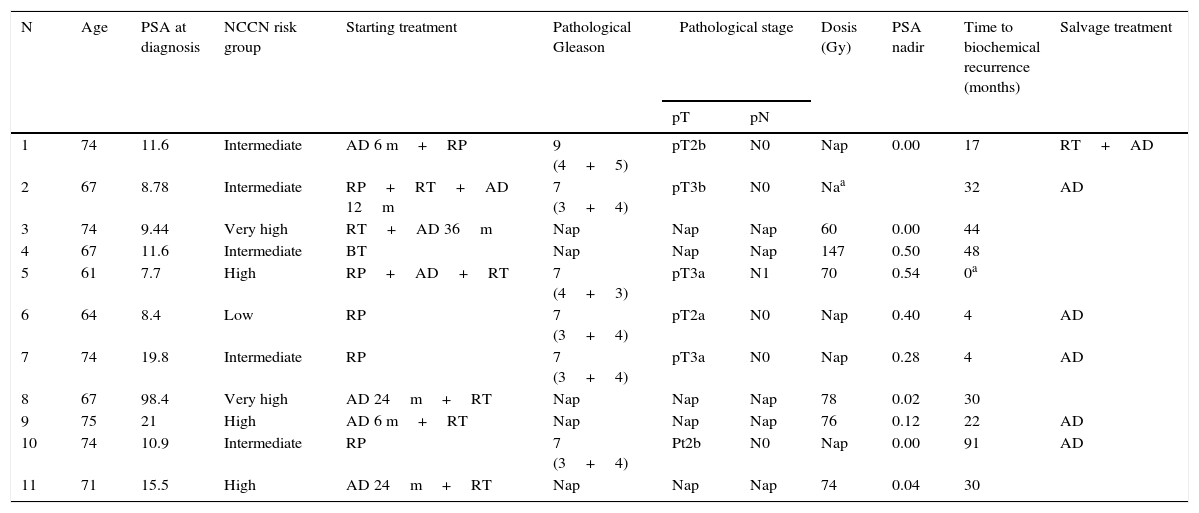
Material and methodWe selected patients who experienced oligorecurrence between January 2015 and December 2016 and were administered SBRT. The association of androgen deprivation (AD) was left in each case to the decision of the tumor committee.
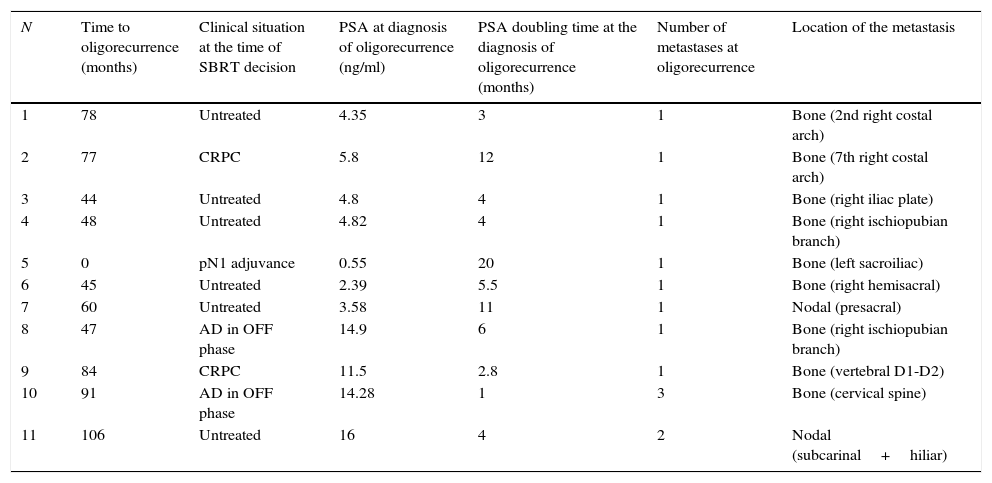
We describe the clinical situation at diagnosis of oligorecurrence, the treatment administered and the biochemical response.
We considered a biochemical response to be a 50% reduction in the absolute prostate-specific antigen (PSA) readings.
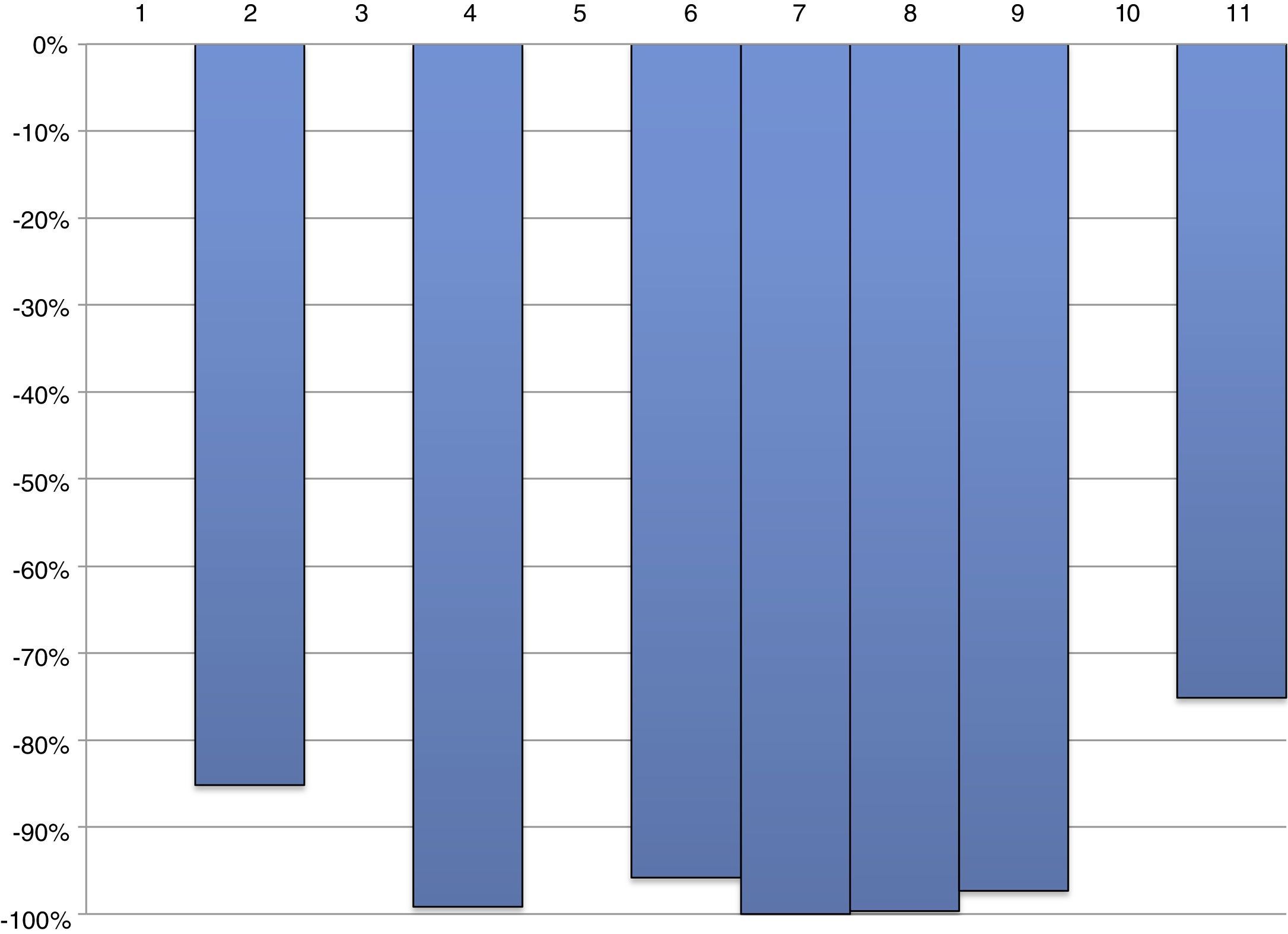
ResultsSBRT was administered to 11 patients with bone (82%) and/or lymph node oligometastasis (18%). The treatment regimen for bone oligometastasis was 27Gy divided into 3 sessions, while the treatment for lymph node oligometastasis reached 70Gy. Seven patients had no treatment at the time of diagnosis, 2 were in the castration-resistant phase, 1 patient was in the off phase of intermittent AD, and 1 patient had adjuvant AD for pN1. Seven patients presented a biochemical response with a PSA reduction of 75-100%. The response was not assessable in 4 patients due to the continuing adjuvant AD. With a mean follow-up of 10.5 months, only 2 patients had progressed. Grade 1 gastrointestinal toxicity was detected in only 1 patient.
ConclusionOur data suggest that the use of SBRT in carefully selected patients with metastatic oligorecurrence of prostate cancer can achieve biochemical response and potentially delay progression and the use of systemic treatments.
Existe un interés creciente por el uso de modalidades terapéuticas más agresivas en el cáncer de próstata metastásico. En el presente estudio abordamos el uso de la radioterapia estereotáctica (SBRT) en pacientes con cáncer de próstata oligorecurrente.
Analizamos la respuesta bioquímica y la toxicidad de los pacientes a quienes se les administró en nuestro centro.
Material y métodoSe seleccionaron los pacientes que padecieron una oligorrecurrencia desde enero de 2015 hasta diciembre de 2016 y se administro¿ SBRT. La asociación de privación androgénica (DA) quedo¿ a decisión de cada caso en el comité de tumores.
Describimos la situación clínica al diagnóstico de las oligorrecurrencias, el tratamiento administrado y la respuesta bioquímica.
Consideramos respuesta bioquímica un descenso del 50% en las cifras absolutas del PSA.
ResultadosSe administró SBRT a 11 pacientes con oligometástasis óseas (82%) y/o ganglionares (18%). El esquema de tratamiento en las óseas fue de 27Gy repartidos en 3 sesiones, mientras que en las ganglionares se llegó a 70Gy. Siete pacientes no tenían ningún tratamiento en el momento del diagnóstico, 2 estaban en fase de resistencia a la castración, un paciente estaba con DA intermitente fase OFF y un paciente con DA adyuvante por pN1. Siete pacientes presentaron una respuesta bioquímica con disminución de PSA entre el 75% y el 100%. En 4 pacientes la respuesta no fue valorable por persistir con DA adyuvante. Con un seguimiento medio de 10,5 meses solo han progresado 2 pacientes. Únicamente se detectó toxicidad gastrointestinal grado i en un paciente.
ConclusiónNuestros datos sugieren que el uso de la SBRT en pacientes cuidadosamente seleccionados oligorrecurrentes metastásicos de cáncer de próstata puede lograr respuesta bioquímica y potencialmente retrasar la progresión y el uso de tratamientos sistémicos.