Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) is an important complication in patients with spinal cord injury due to its frequency and morbidity. One of the most extended therapeutic options is endoscopic injection of obliteration substances in the urethral meatus.
ObjectiveTo analyze the prognostic factors of VUR treatment using obliterative substances in patients with spinal cord injury.
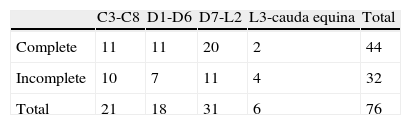
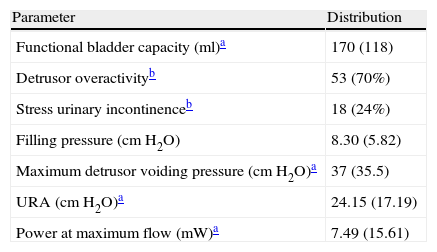
Material and methodsA prospective study was performed in a cohort of 76 patients (age 48.9±14.4 years), of both genders, with spinal cord injuries, who underwent endoscopic treatment of the VUR during the years 2008–2011. In all the patients, a clinical history was obtained and a pre-operative videourodynamic study was performed. Another study was carried out at 7.32 months (standard deviation: 6.28 months) of the intervention. Treatment consisted in endoscopic injection of dextranomer/hyaluronic acid copolymer (62 cases) and polydimethylsiloxane (14). The statistical tests applied were the Fisher's exact test and the Student's T test comparing the means. Bilateral significance level was established at 95%.
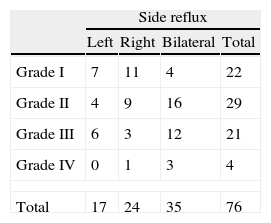
ResultsResolution of VUR was achieved in 46 cases (61%). The statistically significant prognostic factors were age (younger aging cured patients), bilaterality and reflects great (greater grade in bilaterality in the cases with persistence of reflux) and presence of neurogenic detrusor overactivity (greater percentage in the cases of reflux persistence). Stress urinary incontinence (greater percentage in cured patients), contractile potency (lower percentage in cured patients) and urethral resistance (greater percentage in cured patients) were also statistically significant prognostic factors.
ConclusionsAmong the prognostic factors that affected the endoscopic treatment results of the VUR in patients with neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction (NLUTD), anatomical as well as functional factors were found.
El reflujo vesicoureteral (RVU) constituye una complicación importante en pacientes con lesión medular por su frecuencia y morbilidad. Una de las opciones terapéuticas más extendidas es la inyección endoscópica de sustancias obliterantes en el meato ureteral.
ObjetivoAnalizar los factores pronósticos del tratamiento del RVU mediante sustancias obliterantes en pacientes con lesión medular.
Material y métodosSe realizó un estudio prospectivo en una cohorte de 76 pacientes (edad 48,9±14,4 años), de ambos sexos, con lesión medular sometidos a tratamiento endoscópico del RVU, durante los años 2008 a 2011. A todos los pacientes se les realizó una historia clínica y un estudio videourodinámico preoperatorio y a los 7,32 meses (desviación típica: 6,28 meses) de la intervención. El tratamiento consistió en la inyección endoscópica de copolímero de ácido hialurónico (62 casos) y polidimetilsiloxano (14). Las pruebas estadísticas aplicadas fueron el test exacto de Fisher y la prueba de comparación de medias de la «t» de Student. El nivel de significación se fijó en el 95% bilateral.
ResultadosLa resolución del RVU se consiguió en 46 casos (61%). Los factores pronósticos estadísticamente significativos fueron la edad (menor edad en los pacientes curados), la bilateralidad y el grado del reflujo (mayor grado y bilateralidad los casos de persistencia del reflujo) y la presencia de hiperactividad neurógena del detrusor (mayor porcentaje en el caso de persistencia del reflujo), la incontinencia urinaria de esfuerzo (mayor porcentaje en pacientes curados), la potencia contráctil (menor en pacientes curados) y la resistencia uretral (mayor en pacientes curados).
ConclusionesEntre los factores pronósticos que influyen en el resultado del tratamiento endoscópico del RVU en pacientes con disfunción neurógena del tracto urinario inferior (DNTUI) se encuentran tanto factores anatómicos como funcionales.