Although Multidisciplinary Teams (MDTs) are recommended in the management of Advanced Prostate Cancer (APC), their functioning in real practice has been poorly evaluated. We carried out a multicenter study with the objective of evaluating the functioning of uro-oncology MDTs in 6 hospitals.
Materials and methodsA descriptive cross-sectional study was performed. The level of Compliance with the Fundamental Quality Requirements (CFQR) of the MDTs was evaluated by means of a questionnaire filled out by the coordinators of the MDTs in each hospital. The information on the perspective of the members of the MDTs was evaluated through an anonymous survey.
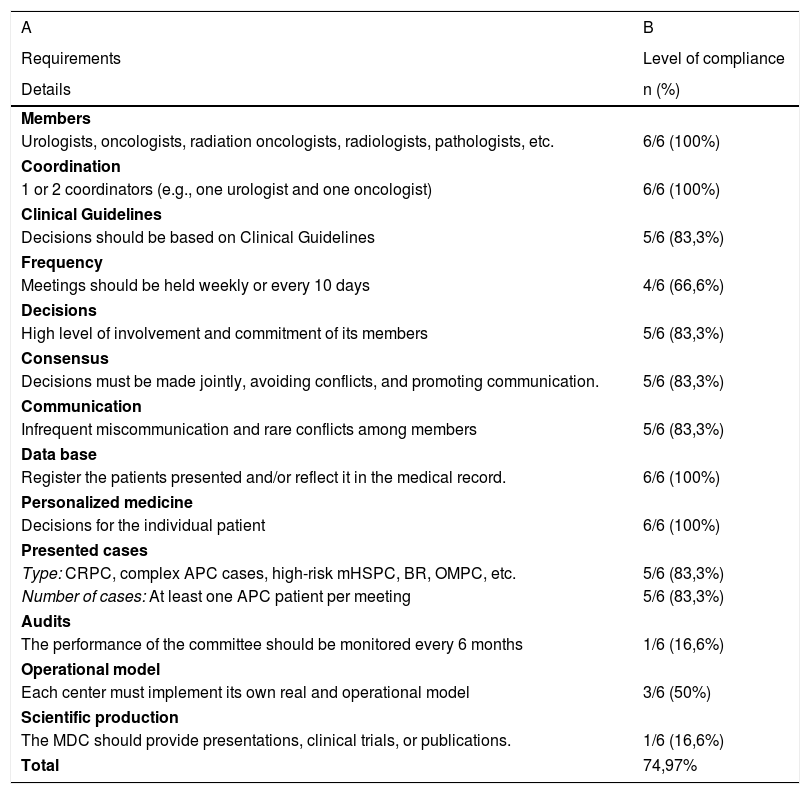
ResultsA high level of CFQR in MDTs was evidenced (75%), showing deficiencies in terms of protocol update, agendas, audits, and scientific production.
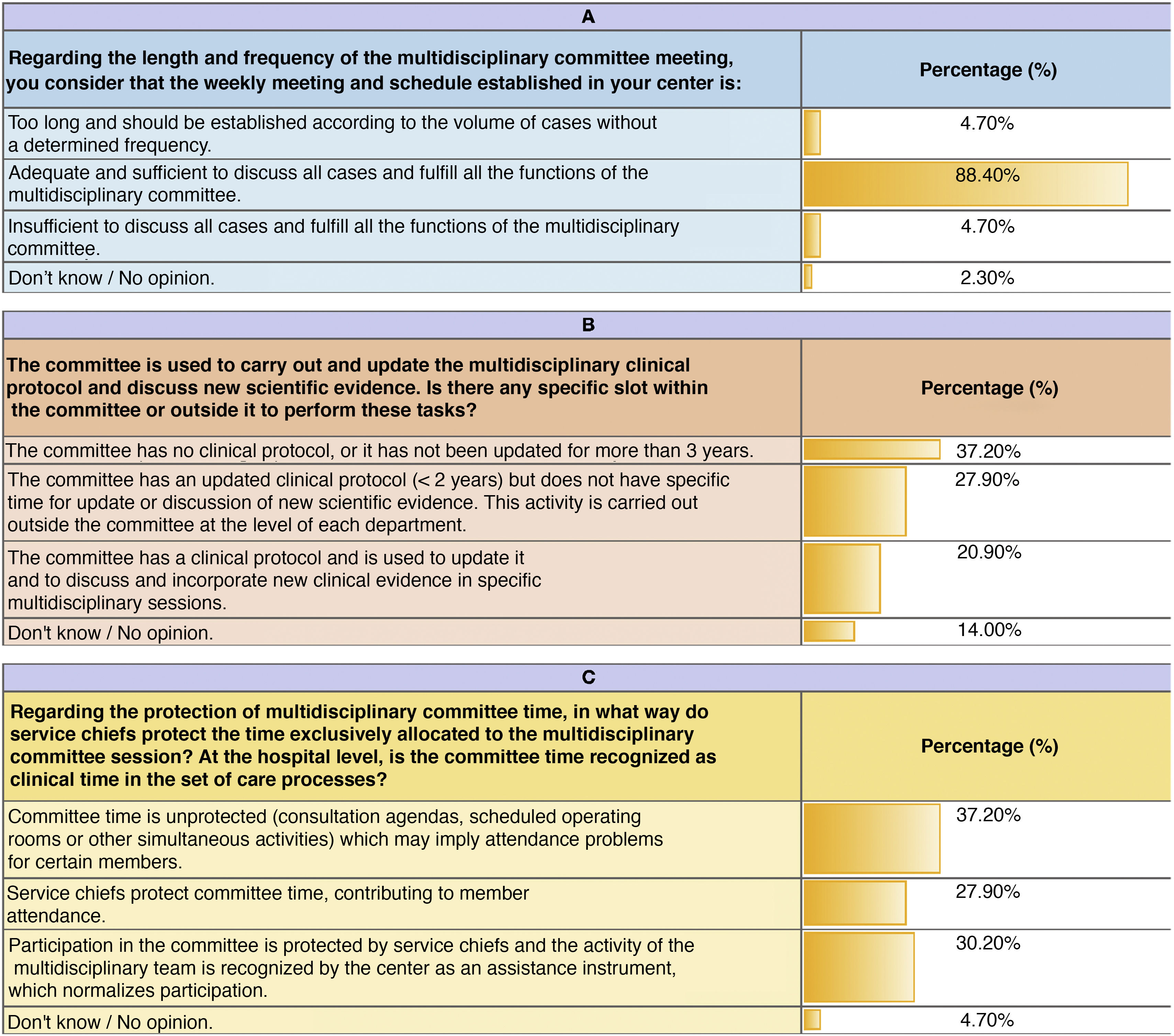
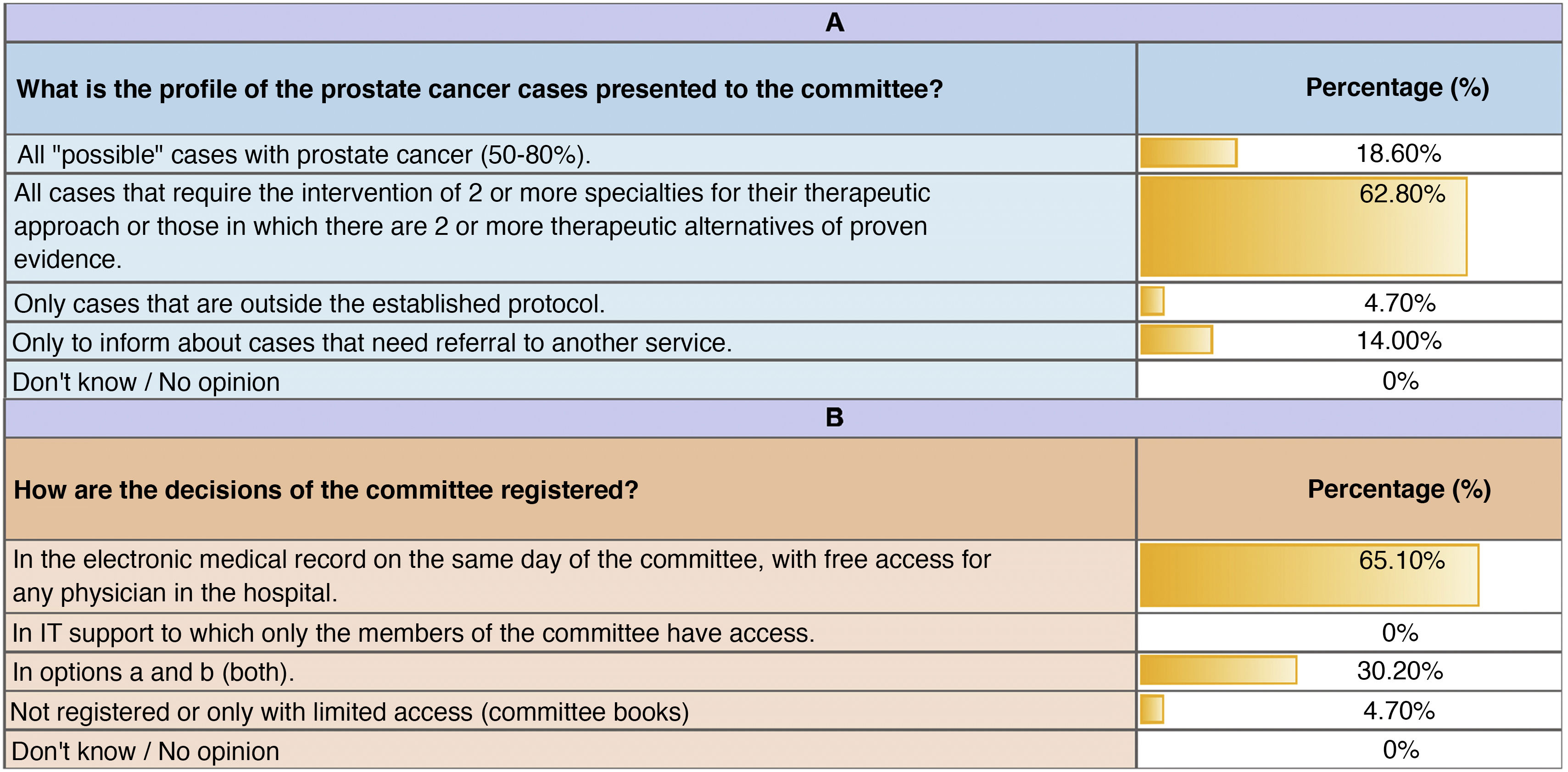
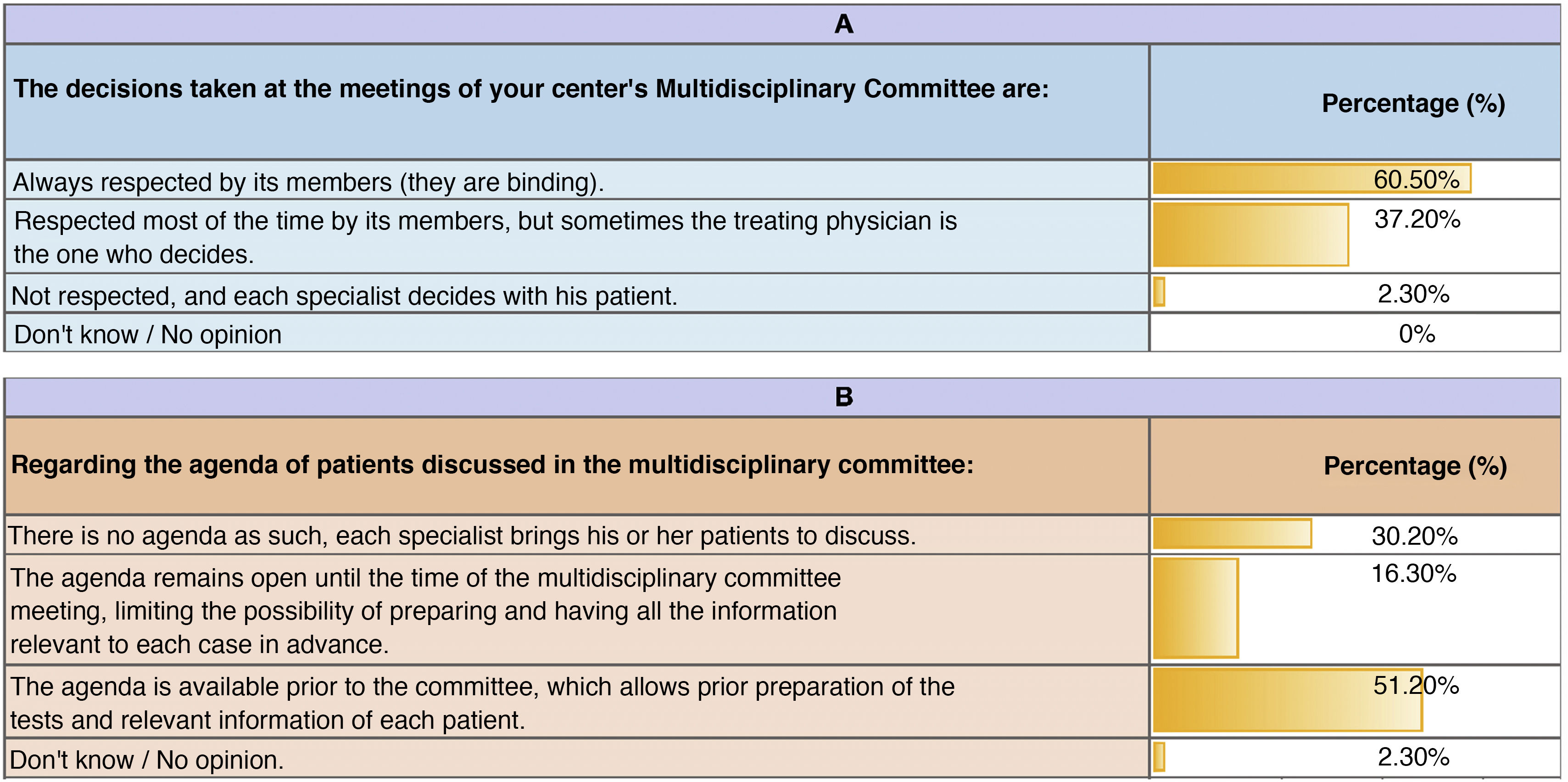
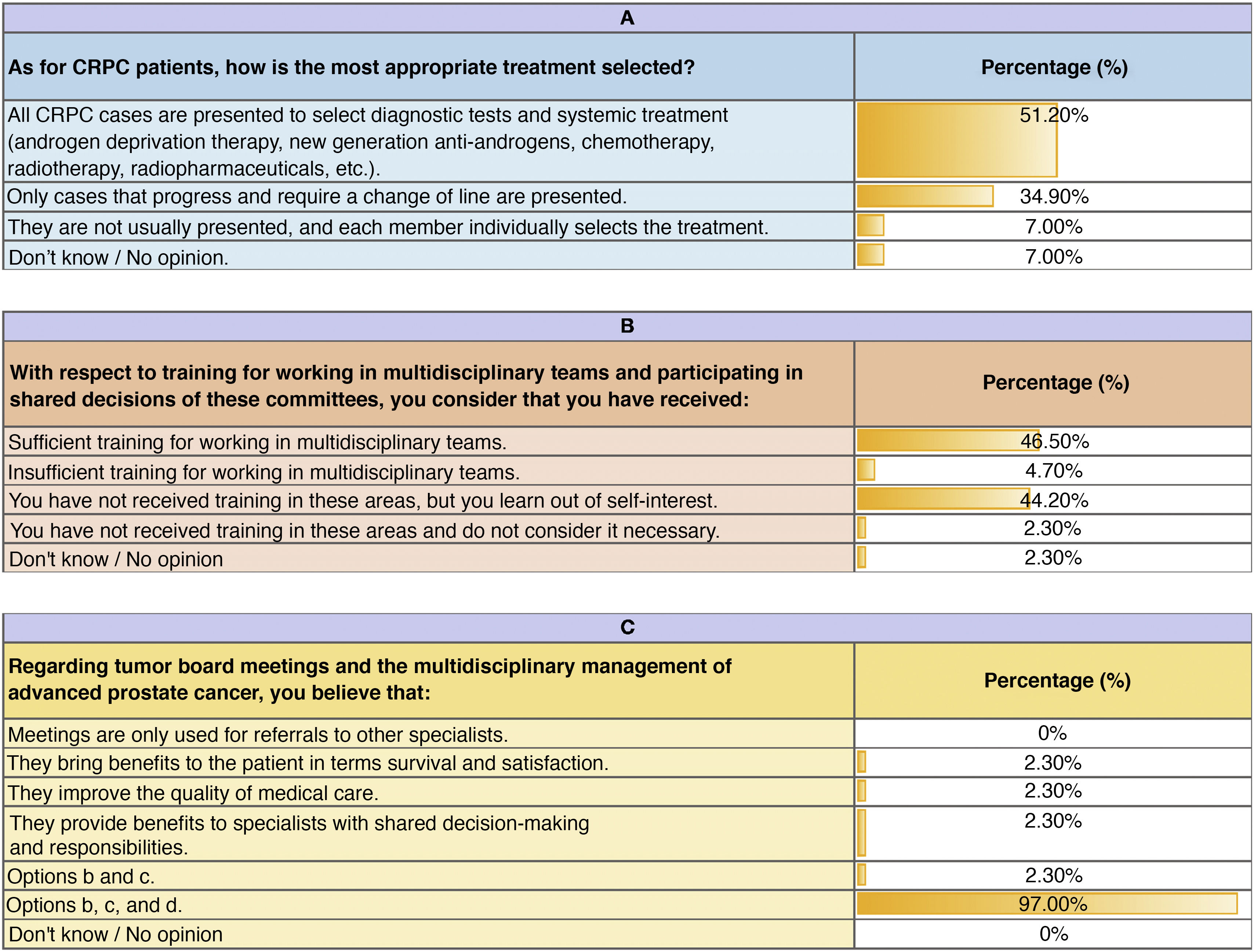
The survey was answered by 62.32% of the 69 physicians surveyed (urologists, oncologists, radiation therapists, radiologists, and pathologists). The 88.4% consider the duration of the meetings appropriate. There are disparate opinions concerning the protection of the MDT meeting time as well as protocol update. Of the patients with APC presented at the MDTs meeting, 62,8% require intervention from two specialties. Only 50% of respondents believe that all CRPC cases are discussed and that there is a prior agenda. The decisions made by the MDTs are reflected in the clinical history in 65.1% and are binding only in 60.5% of the cases. Half of the respondents have not been trained in MDTs. Most participants (90.7%) agree on the fact that MDTs. convey benefits.
ConclusionsThe evaluations of the MDTs identify rectifiable deficiencies by modifying hospital inertia and care planning.
Aunque los comités multidisciplinares (CMD) están recomendados en el manejo del Cáncer de Próstata Avanzado (CPA), su funcionamiento en práctica real se ha evaluado escasamente. Desarrollamos un estudio multicéntrico con el objetivo de evaluar el funcionamiento de los CMD urooncológicos en 6 hospitales.
Materiales y métodosRealizamos un estudio transversal descriptivo. El nivel de Cumplimiento de los Requisitos de Calidad Fundamentales (CRCF) de los CMD, se evaluó aplicando un cuestionario a los coordinadores de los CMD de cada hospital. La perspectiva de los miembros de los CMD se evaluó aplicando una encuesta anónima telemática.
ResultadosEvidenciamos un alto nivel de CRCF en los CMD (75%), mostrando deficiencias en la actualización de protocolos, agendas, auditorías y producción científica. La encuesta fue respondida por un 62,32% de los 69 médicos encuestados (urólogos, oncólogos, radioterapéutas, radiólogos y anatomopatólogos). El 88,4% considera adecuado el tiempo de las reuniones. Existen opiniones dispares sobre la protección del tiempo de las reuniones y la actualización de protocolos. El 62,8% de los pacientes presentados requieren la intervención de dos especialidades. La mitad de los encuestados cree que se discuten todos los casos de CPRC y que existe una agenda previa. Las decisiones del CMD quedan reflejadas en la historia clínica en un 651% y son vinculantes en un 605%. La mitad de los encuestados niegan capacitación en CMD. La mayoría de los participantes (907%) avalan los beneficios de los CMD.
ConclusionesLas evaluaciones de los CMD identifican deficiencias subsanables modificando la inercia hospitalaria y la planificación asistencial.