Technological advances have prompted a change in the management of urolithiasis. Endourological techniques are gaining importance because they are highly effective treatments. The aim of this study was to answer the question of whether extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) is still a competitive alternative compared with other therapeutic modalities.
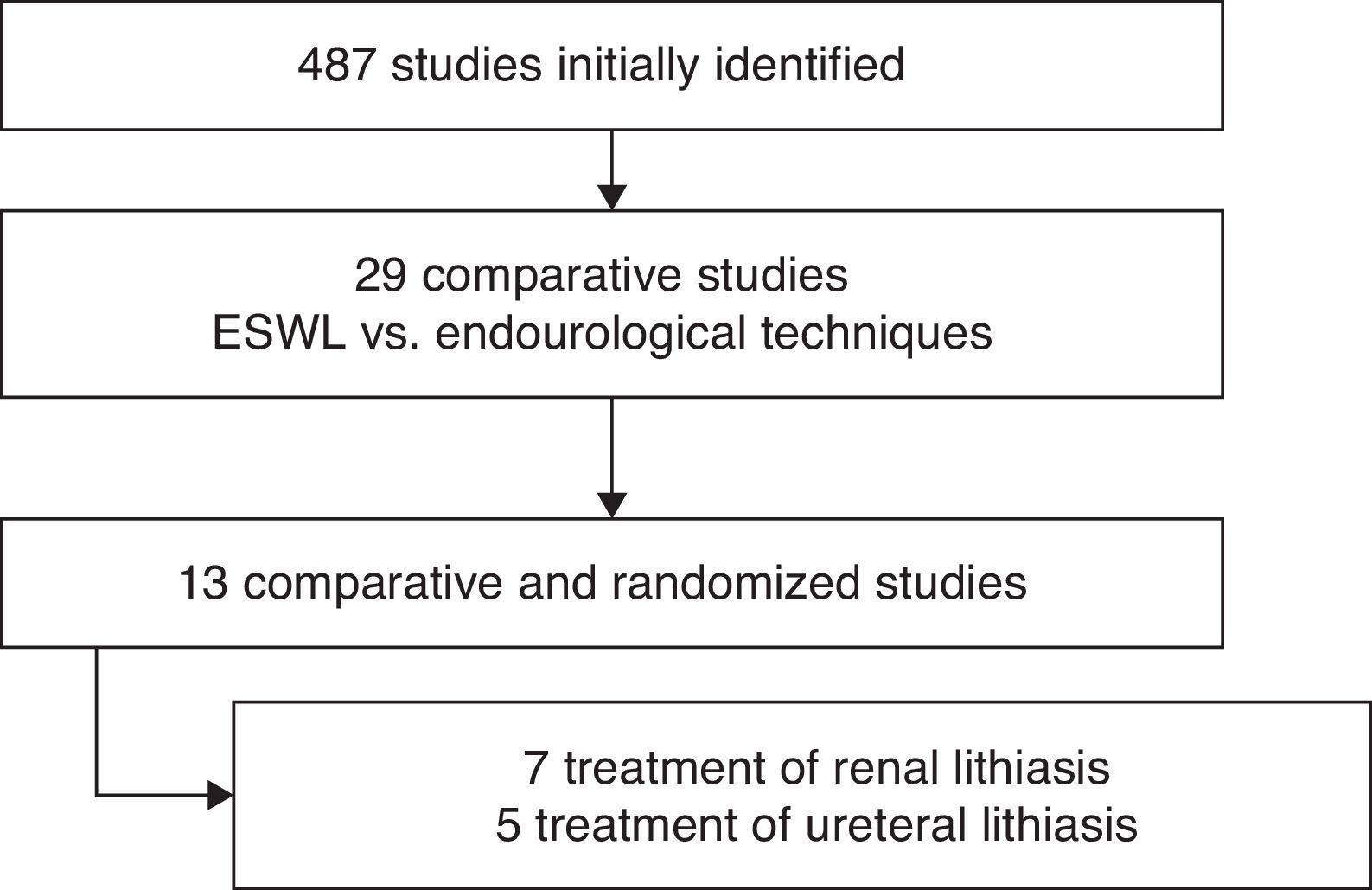
Acquisition of evidenceWe conducted a literature search of articles published in the past 5 years. We identified 12 randomized and comparative studies and assessed the methodology and results of the study variables. We performed a narrative synthesis of the included studies. To summarize the variables, we used the mean and standard deviation for continuous variables and absolute numbers and percentages for the qualitative variables.
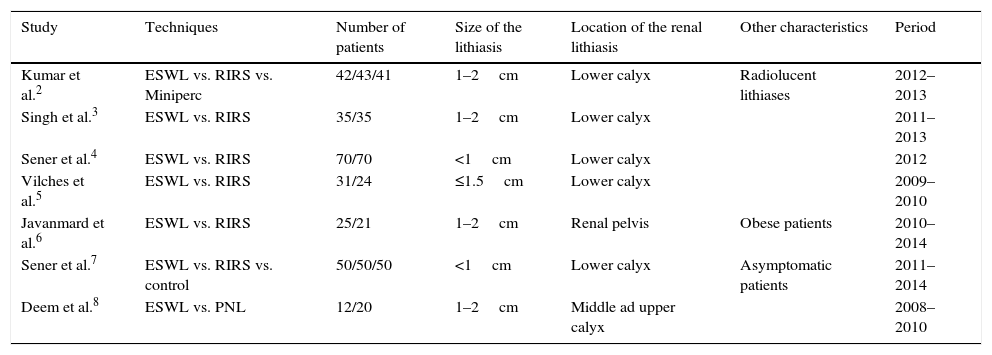
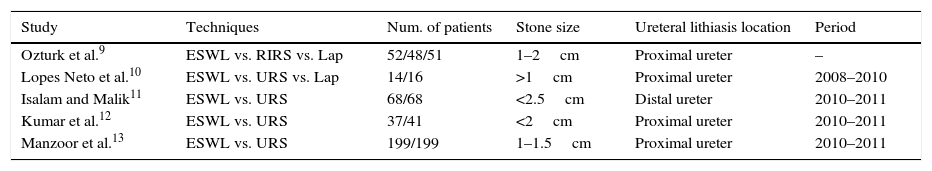
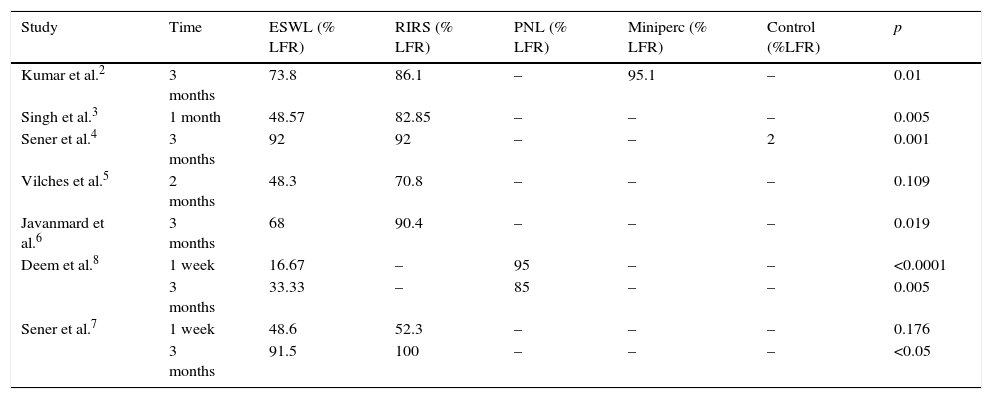
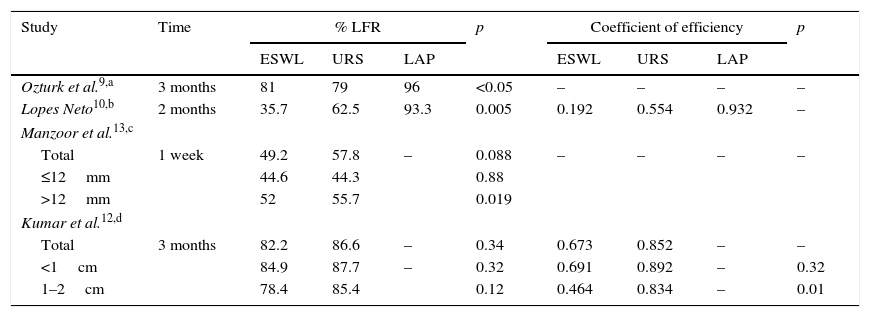
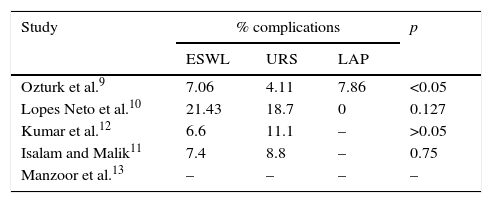
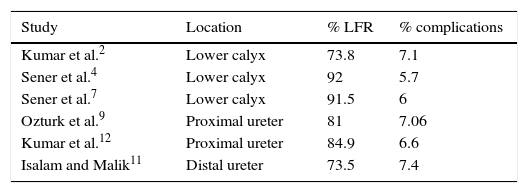
Analysis of the evidenceOf the studies reviewed, 7 evaluated the various treatments for nephrolithiasis and 5 evaluated the treatments for ureteral lithiasis. At the renal level, a stone-free rate of 33.33–91.5% at 3 months was reached with ESWL, while a rate of 90.4–100% was achieved with the other endourological techniques, without finding statistically significant differences in the studies. At the ureteral level, a stone-free rate of 73.5–82.2% at 3 months was reached with ESWL, while a rate of 79–94.1% was achieved with the other endourological techniques, without finding statistically significant differences in the studies.
ConclusionThere is a lack of homogeneity among the published studies. ESWL is a minimally invasive treatment that with an appropriate technique and patient selection achieves high effectiveness, thus maintaining an important role at this time.
Los avances tecnológicos han motivado un cambio en el manejo de la urolitiasis. Las técnicas endourológicas están cobrando mayor importancia, ya que son tratamientos altamente eficaces. El objetivo de este trabajo es responder a la cuestión de si la LEOCH sigue siendo una alternativa competitiva frente a otras modalidades terapéuticas.
Adquisición de la evidenciaSe realizó una búsqueda bibliográfica de artículos publicados en los últimos 5 años. Fueron identificados 12 estudios aleatorizados y comparativos. Se evaluó la metodología y el resultado de las variables estudiadas. Se ha realizado una síntesis narrativa de los estudios incluidos. Para resumir las variables se ha utilizado la media y la desviación estándar en variables continuas, y para variables cualitativas el número absoluto y el porcentaje.
Análisis de la evidenciaDe los estudios revisados, 7 trabajos evaluaban los distintos tratamientos para litiasis renales y 5 para litiasis ureterales. A nivel renal, con LEOCH se alcanza una TLL a los 3 meses entre 91,5-33,33%, mientras que con otras técnicas endourológicas entre 100-90,4%, sin encontrar diferencias estadísticamente significativas en todos los estudios. A nivel ureteral con LEOCH se alcanza una TLL a los 3 meses entre 82,2-73,5%, mientras que con otras técnicas endourológicas entre 94,1-79%, sin encontrar diferencias estadísticamente significativas todos los estudios.
ConclusiónExiste una falta de homogeneidad entre los estudios publicados. La LEOCH es un tratamiento mínimamente invasivo, que con una adecuada técnica y selección del paciente alcanza una elevada efectividad, manteniendo un papel importante en la actualidad.