Given the high prevalence of erectile dysfunction in male population between 40 and 70 years old and the effect of radical prostatectomy on this domain, it is important to perform a baseline study.
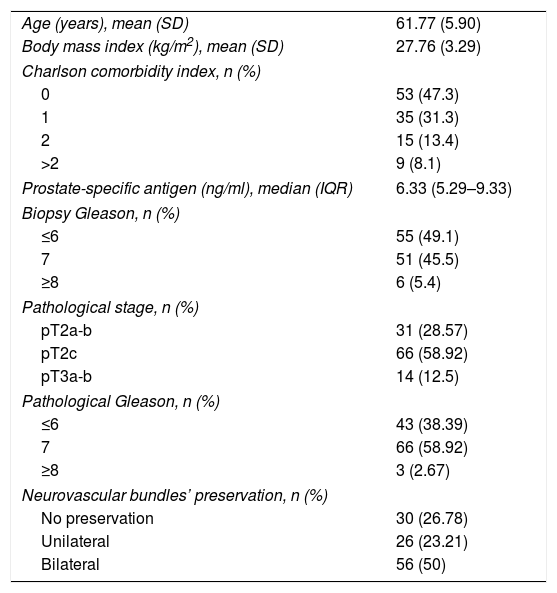
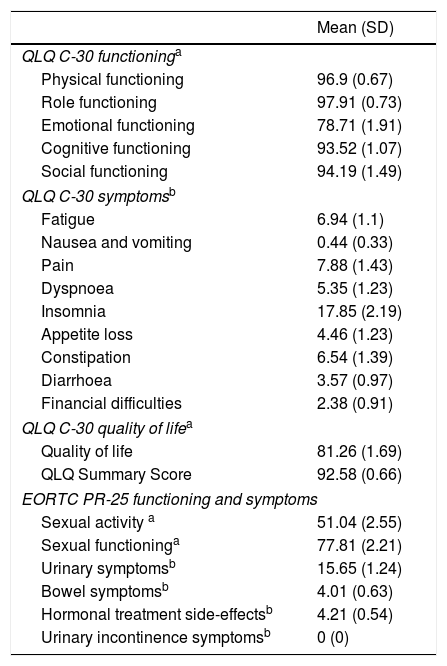
Material and methodsPrior radical prostatectomy, erectile function has been assessed prospectively in 112 prostate cancer patients using the erectile function (EF) domain of the International Index of Erectile Function (EF-IIEF), Erectile Hardness Score (EHS) and a penile doppler ultrasound (PDUS). Comorbidities and Charlson index were collected. The EORTC QLQ C-30 and PR-25 tests were administered.
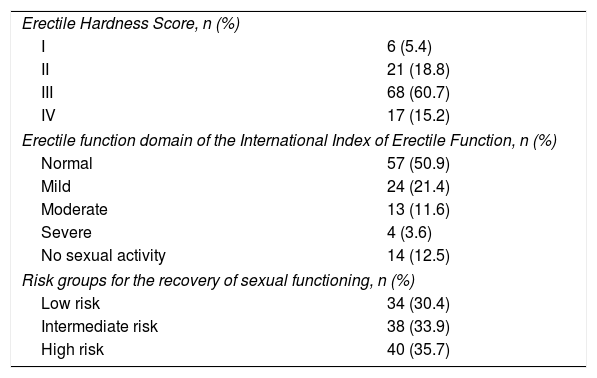
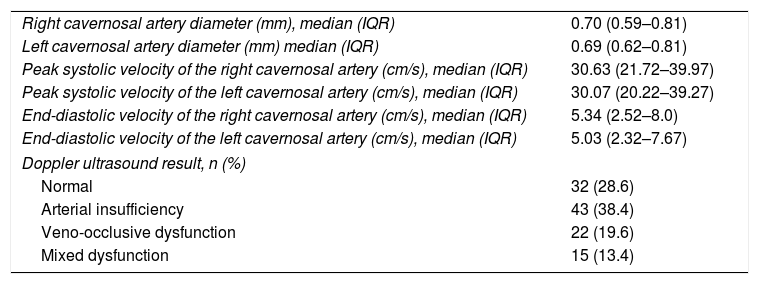
ResultsAccording to EF-IIEF questionnaire, 50.9% of patients showed normal EF and EHS grade 3–4 erection was achieved in the 75.9%. PDUS was normal only in 28.6% of patients and 51.8% showed arterial insufficiency. We found a significant association (p<0001) between categorised EF-IIEF (normal, mild/moderate/severe) and the EHS value. Between PDUS (normal vs. pathologic) and EHS (3–4 vs. 1–2) statistically significant association (p=0.005) was found. Just 35.3% of patients with EHS 3–4 showed normal PDUS. Correlation between the PDUS and the EF-IIEF (≥26 vs. 26) was statistically significant (p=0.043). Moreover, only 38.6% of patients with EF-IIEF≥26 had a normal PDUS.
ConclusionsIn order to predict EF recovery after surgery, global assessment is required. Solely self-administered tests are not enough. In this baseline study, PDUS can play an important role.
La disfunción eréctil peneana tiene una prevalencia alta entre los 40-70 años, por lo que es importante su valoración basal antes de la prostatectomía radical.
Material y métodosSe ha evaluado la función eréctil (FE) de 112 pacientes con cáncer de próstata previamente a la prostatectomía radical, mediante el dominio de la FE del Índice Internacional de Función Eréctil (IIEF), el test Erectile Hardness Score (EHS) y una ecografía doppler de pene (EDP). Se recogieron comorbilidades, el índice de Charlson y se administró el test de calidad de vida de la EORTC QLQ C-30 y PR-25.
ResultadosUn 50,9% de la población tenían una FE normal usando el cuestionario IIEF y un 75,9% conseguían una erección grado 3-4 en el EHS. Únicamente el 28,6% presentaban una EDP normal, y el 51,8% mostraron insuficiencia arterial. Encontramos una asociación significativa (p<0,0001) entre el IIEF categorizado y el valor de EHS. Se encontró una asociación significativa (p=0,005) entre la presencia en la EDP (normal vs. patológico) y el EHS (3-4 vs. 1-2). Solo el 35,3% de los pacientes con un EHS de 3-4 tenían una EDP normal. También encontramos una asociación significativa (p=0,043) entre la EDP y la FE valorada según el IIEF (≥26 vs. 26). Únicamente tenían una EDP normal el 38,6% de los pacientes con IIEF≥26.
ConclusionesEs importante una valoración global de la FE para poder valorar las expectativas de recuperación de dicha función tras la cirugía y no reducirla únicamente a test autoadministrados, pudiendo jugar un papel importante la EDP.