Following cystectomy, approximately 50% of patients will present tumor recurrence. A recurrence may be local, systemic or occur in the urethra or upper urinary tract.
ObjectiveTo analyze the characteristics, risk factors and outcomes of patients with tumor recurrence following cystectomy so as to subsequently propose a cancer follow-up protocol.
Acquisition of evidenceAnalysis of original articles and reviews related to tumor recurrence and follow-up after radical cystectomy for urothelial tumor. Articles were obtained from Pubmed searches.
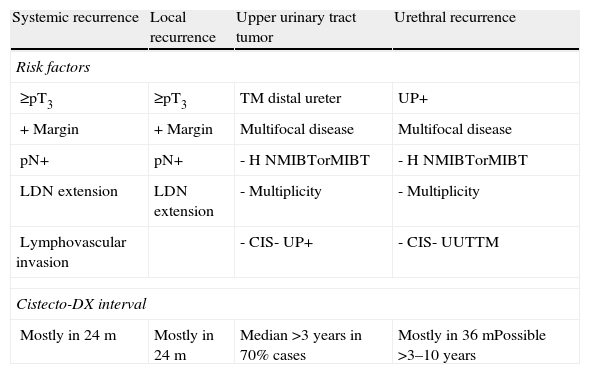
Summary of the evidenceSystemic and local recurrences following cystectomy appear in 20–35% and 5–15% of cases, respectively. Some 80–90% are diagnosed in the first 3 years, with the majority concentrated in the first 24 months. Common factors related to an increased risk of local and systemic recurrence are a pathologic stage ≥pT3, the presence of positive margins and the extension of the lymphadenectomy. The incidence of recurrence in the upper urinary tract and urethra is 2–6% and 4–6%, respectively. Both types of recurrence may appear late and share risk factors such as signs of multifocal disease, a history of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer, multiplicity, presence of ISC, urinary tract tumors and prostatic urethral tumors. Tumors in the distal ureteral cystectomy specimen and tumors in the prostatic urethra are also risk factors related to the appearance of tumors in the urinary tract and urethra, respectively.
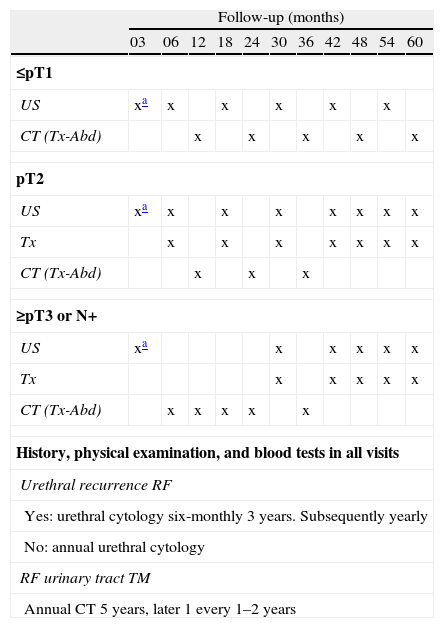
ConclusionUnderstanding the natural history of urothelial bladder carcinoma and the risk factors related to the appearance of tumor recurrence following cystectomy are essential for designing an appropriate follow-up protocol. The follow-up of patients with risk factors for local or systemic recurrence will achieve maximum efficiency during the first 3 years. The follow-up should be extended for patients with risk factors for presenting upper urinary tract or urethral tumors.
Después de cistectomía cerca del 50% de los pacientes presentarán recidiva tumoral, una recidiva que podrá ser local, sistémica o al nivel de la uretra o la vía urinaria superior.
ObjetivoAnalizar las características, factores de riesgo y evolución de los pacientes con recidiva tumoral tras cistectomía, para posteriormente proponer un protocolo de seguimiento oncológico.
Adquisición de evidenciaAnálisis de artículos originales y de revisión relacionados con recidiva tumoral y seguimiento después de cistectomía radical por tumor urotelial. Artículos obtenidos de la búsqueda en Pubmed.
Síntesis de evidenciaLas recidivas sistémicas y locales después de cistectomía aparecen sobre el 20–35% y el 5–15% de los casos respectivamente. El 80–90% se diagnostican en los 3 primeros años, concentrándose la mayoría en los primeros 24 meses. El estadio patológico ≥pT3, la presencia de márgenes positivos y la extensión de la linfedenectomía son factores comunes relacionados con un mayor riesgo de recidiva local y sistémica. Las incidencias de recidiva en la vía urinaria superior y la uretra se encuentran entre el 2–6% y 4–6% respectivamente. Ambos tipos de recidiva pueden aparecer de forma tardía y comparten como factores de riesgo la presencia de signos de enfermedad multifocal: historia de tumor vesical no músculo-invasivo, multiplicidad, presencia de CIS, tumor en la vía urinaria y tumor en la uretra prostática. El tumor en el uréter distal en la pieza de cistectomía y el tumor en la uretra prostática serán también factores de riesgo relacionados con la aparición de tumor en la vía urinaria y en la uretra respectivamente.
ConclusiónEl conocimiento de la historia natural del carcinoma urotelial de vejiga y de los factores de riesgo relacionados con la aparición de recidiva tumoral después de cistectomía son fundamentales para diseñar un protocolo de seguimiento adecuado. El seguimiento de pacientes con factores de riesgo de recidiva local o sistémica obtendrá su máximo rendimiento durante los 3 primeros años. En pacientes con factores de riesgo de presentar tumor en vía urinaria superior o en la uretra el seguimiento debe ser más prolongado.