In the historical series, the diagnostic yield of lumbosacral magnetic resonance imaging to rule out occult spinal dysraphism (or occult myelodysplasia), requested by pediatric urology, ranged from 2% to 15%. The aim of this study was to define our cost-effectiveness in children with urinary symptoms and to define endpoints that increase the possibility of finding occult spinal dysraphism.
Patients and methodsA screening was conducted on patients with urinary dysfunction for whom an magnetic resonance imaging was requested by the pediatric urology clinic, for persistent symptoms after treatment, voiding dysfunction or other clinical or urodynamic findings. We analyzed clinical (UTI, daytime leaks, enuresis, voiding dysfunction, urgency, renal ultrasonography, lumbosacral radiography, history of acute urine retention, skin stigma and myalgia) and urodynamic endpoints (hyperactivity or areflexia, voiding dysfunction, interrupted pattern, accommodation value and maximum flow). A univariate analysis was conducted with SPSS 20.0.
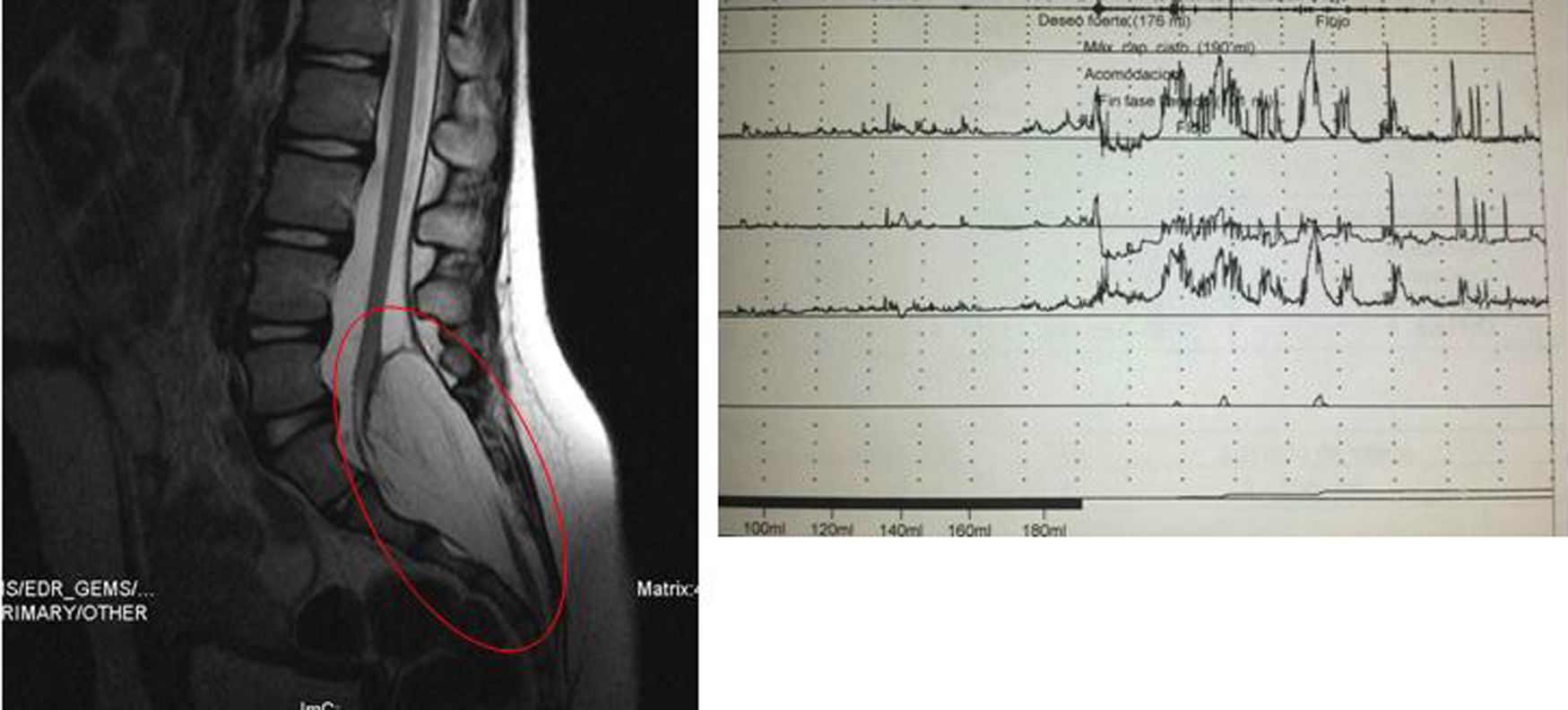
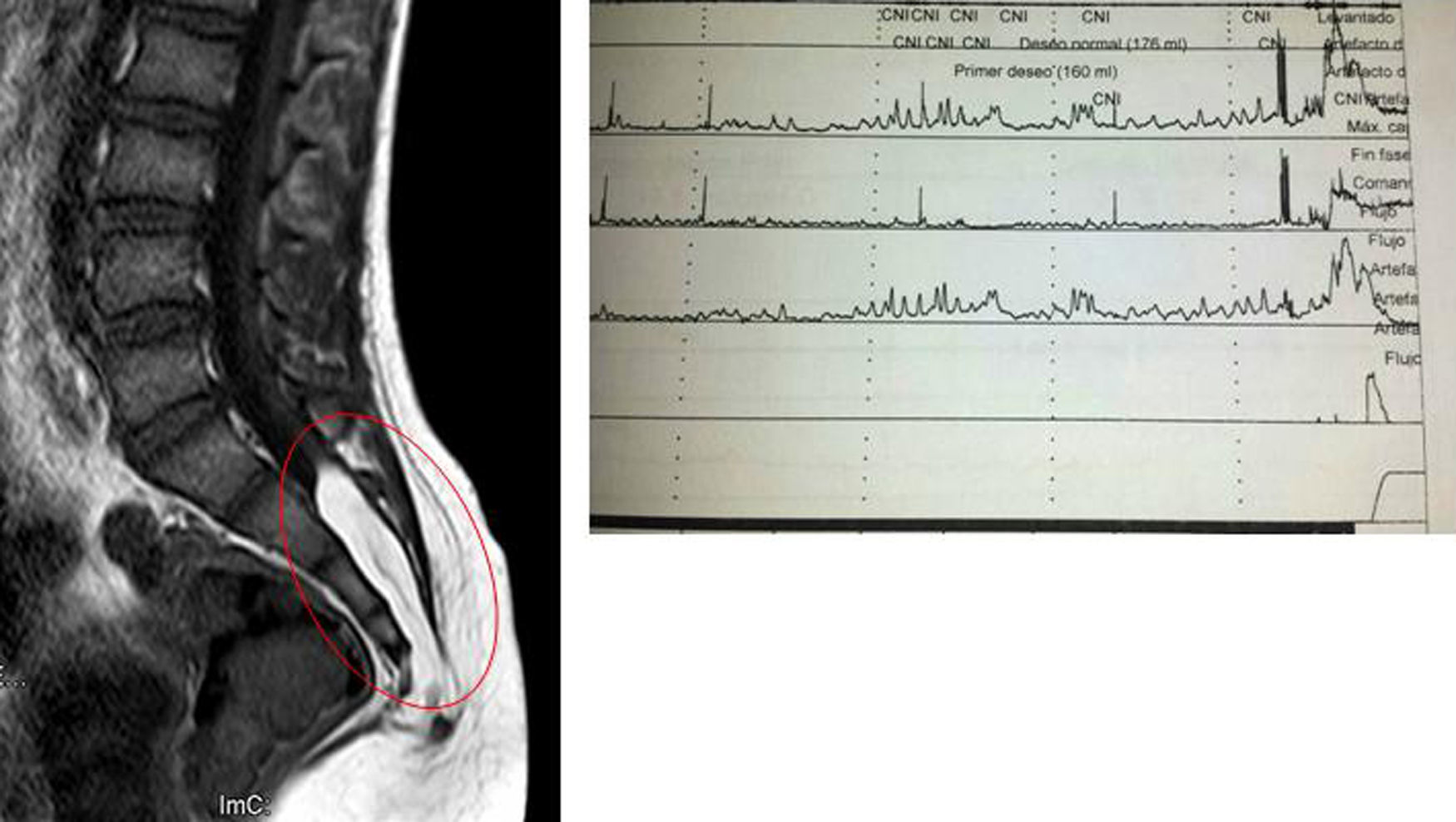
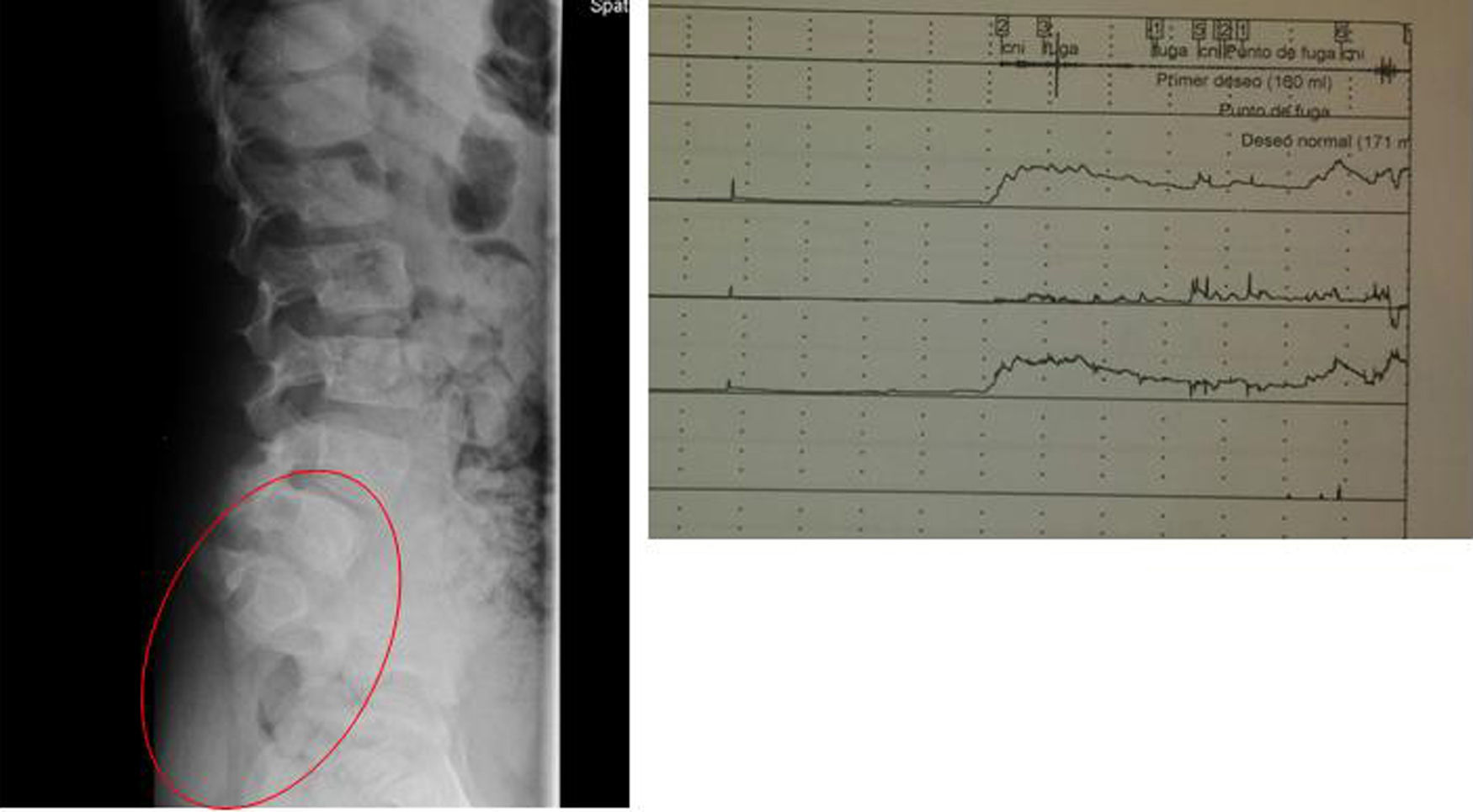
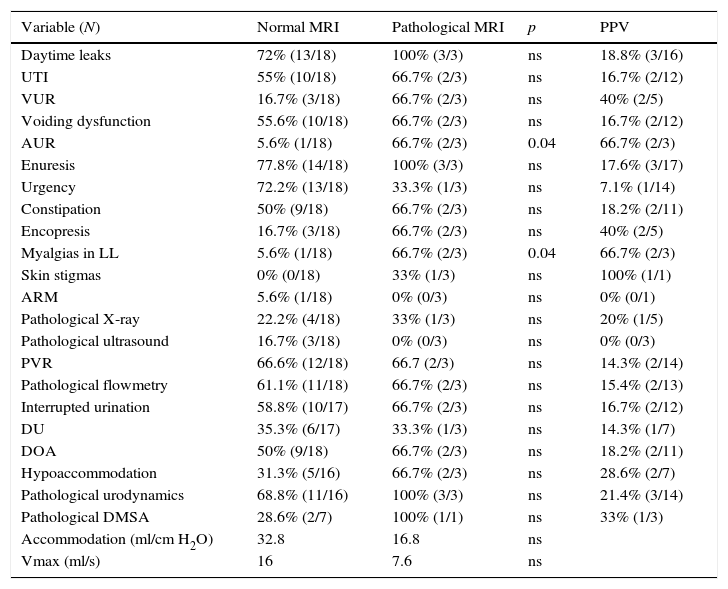
ResultsWe analyzed 21 patients during the period 2011–2015. The median age was 6 years (3–10). Three patients (14.3%) had occult spinal dysraphism: one spinal lipoma, one filum lipomatosus and one caudal regression syndrome with channel stenosis. The endpoints with statistically significant differences were the myalgias and the history of acute urine retention (66.7% vs. 5.6%, p=0.04; OR= 34; 95% CI: 1.5–781 for both endpoints).
ConclusionsThe diagnostic yield of magnetic resonance imaging requested for children with urinary dysfunctions without skin stigma or neuro-orthopedic abnormalities is low, although nonnegligible. In this group, the patients with a history of acute urine retention and muscle pain (pain, “cramps”) can experience a greater diagnostic yield or positive predictive value.
En series históricas, la rentabilidad diagnóstica de la resonancia magnética lumbosacra para descartar disrafismo espinal oculto (o mielodisplasia oculta), solicitada desde urología pediátrica oscila entre el 2 y 15%. El objetivo del estudio es definir nuestra rentabilidad en niños con síntomas miccionales, y definir variables que aumenten la posibilidad de encontrar disrafismo espinal oculto.
Pacientes y métodosSelección de pacientes con disfunciones miccionales a los que se solicitó resonancia magnética desde las consultas de urología pediátrica, por persistencia de síntomas tras tratamiento, disfunción de vaciado, o por otros hallazgos clínicos o urodinámicos. Se analizaron variables clínicas (ITU, fugas diurnas, enuresis, disfunción de vaciado, urgencia, ecografía renal, radiografía lumbosacra, antecedentes de retención aguda de orina, estigmas cutáneos, mialgias) y urodinámicas (hiperactividad o arreflexia, micción disfuncional, patrón interrumpido, valor de acomodación y flujo máximo). Análisis univariante con SPSS 20.0.
ResultadosAnalizamos a 21 pacientes en el periodo 2011-2015. Mediana de edad: 6 años (3-10). Tres pacientes (14,3%) presentaron disrafismo espinal oculto: un lipoma raquídeo, un filum lipomatoso y un síndrome de regresión caudal con estenosis de canal. Las variables con diferencia estadísticamente significativa fueron las mialgias y el antecedente de retención aguda de orina (66,7 vs. 5,6%; p=0,04; OR=34; IC95%: 1,5-781 para ambas variables).
ConclusionesLa rentabilidad diagnóstica de la resonancia magnética solicitada a niños con disfunciones miccionales sin estigmas cutáneos ni alteraciones neuroortopédicas es baja, aunque no desdeñable. En este grupo, los pacientes con antecedentes de retención aguda de orina y/dolor muscular (dolor, «calambres») pueden presentar una rentabilidad diagnóstica o valor predictivo positivo mayor.