The objective of this study is to analyze the impact (in terms of safety and saving of hospital costs) of the implementation of a new protocol for the correction of pelvic organ prolapse (POP) by minimally invasive sacrocolpopexy (MISC) with 24-h hospital stay.
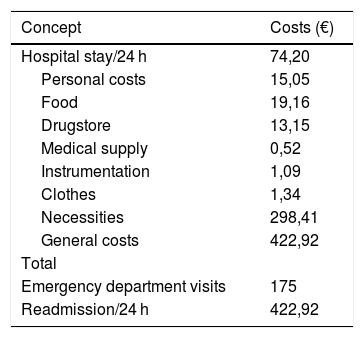
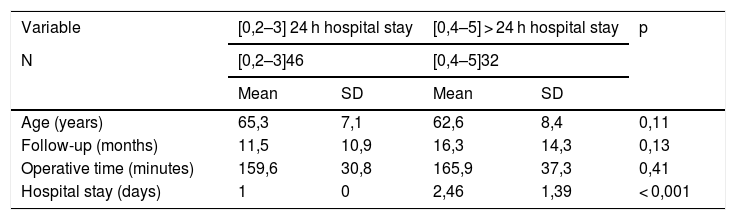
Material and methodsProspective observational study of the first 78 MISC procedures performed consecutively. 46 procedures (59%) were performed with 24-h hospital stay, and 32 (41%) required more than 24 h. The postoperative complications were determined for each group: visits to the Emergency Department, reoperations, and the average cost per procedure regarding hospital stay and ER visits. The cost model was established according to the data of the Analytical Accounting System of the Jiménez Díaz Foundation Hospital and of the Official State Gazette of Madrid.
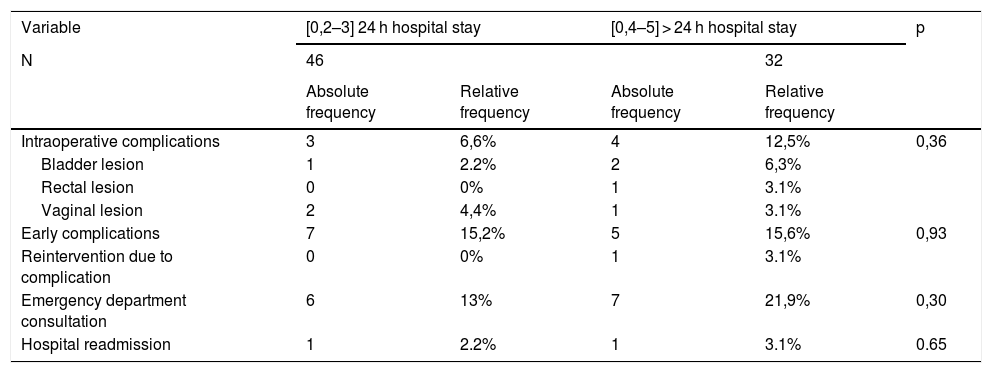
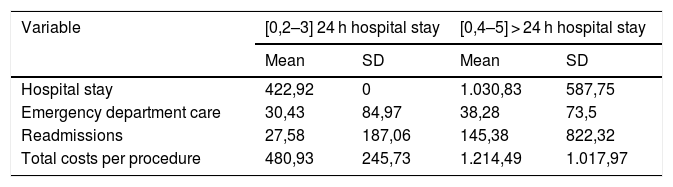
ResultsThere were no differences regarding intraoperative or postoperative complications between both groups. The number of visits to the Emergency Department, reinterventions or hospital re-admissions was lower in the 24-h hospital stay group, without reaching statistical significance. The implementation of the MISC protocol with 24-h hospital stay represented a saving of 607.91€ per procedure in hospital costs.
ConclusionsCorrection of the POP with MISC with a 24-h hospital discharge policy was feasible and safe in at least 59% of the patients, with similar complications, visits to the Emergency Department or hospital readmission rates.
El objetivo del presente estudio es analizar el resultado de la implementación de una vía clínica para la corrección del prolapso de órganos pélvicos (POP) mediante colposacropexia mínimamente invasiva (CSMI) con 24 horas de ingreso en términos de seguridad y ahorro de costes de hospitalización.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional prospectivo de los primeros 78 procedimientos de CSMI realizados de forma consecutiva. 46 procedimientos (59%) se realizaron con estancia hospitalaria de 24 horas mientras que 32 (41%) precisaron más de 24 horas. Para cada grupo se determinaron las complicaciones postoperatorias, visitas al Servicio de Urgencias, reintervenciones y el coste medio por procedimiento en términos de estancia hospitalaria y atención en el Servicio de Urgencias. El modelo de costes se estableció según los datos del Sistema de Contabilidad Analítica del Hospital Fundación Jiménez Díaz y del boletín oficial de la Comunidad de Madrid.
ResultadosNo se encontraron diferencias entre ambos grupos respecto a las complicaciones intraoperatorias o postoperatorias. Las consultas en el Servicio de Urgencias, reintervenciones o reingresos hospitalarios fue menor en el grupo de 24 horas de ingreso sin alcanzar la significación estadística. Mediante la implementación de la vía clínica de CSMI con 24 horas de ingreso se objetivo un ahorro de 607,91€ por procedimiento en estancia hospitalaria.
ConclusionesLa corrección del POP mediante CSMI con política de alta hospitalaria de 24 horas es factible y segura en al menos el 59% de las pacientes sin objetivarse mayor número de complicaciones, visitas al Servicio de Urgencias o reingresos hospitalarios.