The use of nomograms which include the PSA may improve the predictive power of obtaining a prostate biopsy (PB) positive for cancer. We compare the use of three on-line nomagrams with the detection of primary malignant circulating prostate cells (CPCs) to predict the results of an initial PB in men with suspicion of prostate cancer.
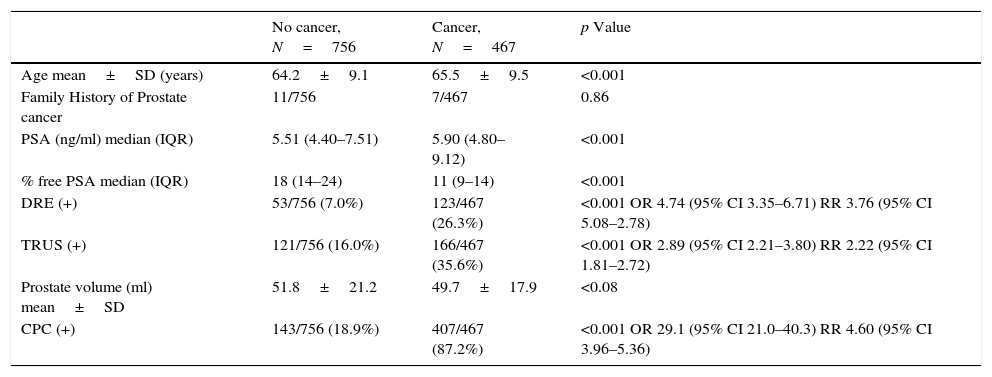
Methods and patientsConsecutive men with suspicion of prostate cancer underwent a 12 core TRUS prostate biopsy; age, total serum PSA, percent free PSA, family history, ethnic origin and prostate ultrasound results were used for risk assessment using the online nomograms.
Mononuclear cells were obtained by differential gel centrifugation from 8ml of blood and CPCs were identified using double immunomarcation with anti-PSA and anti-P504S. A CPC was defined as a cell expressing PSA and P504S and defined as negative/positive. Biopsies were classified as cancer/no-cancer. Areas under the curve (AUC) for each parameter were calculated and compared and diagnostic yields were calculated.
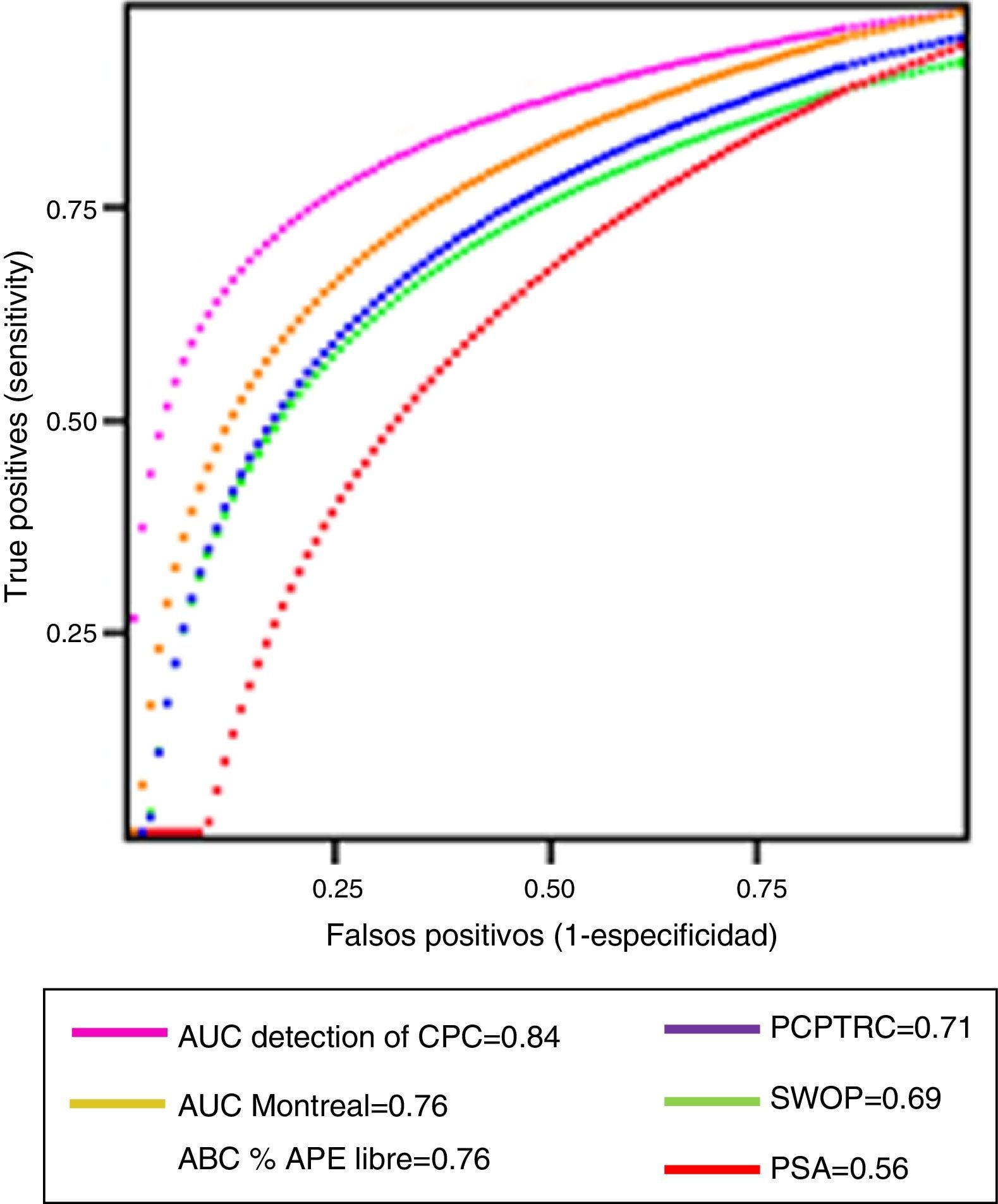
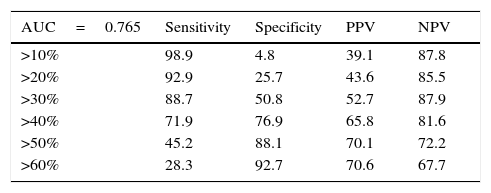
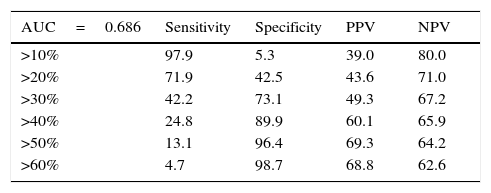
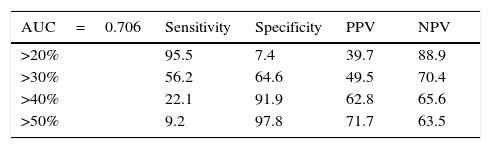
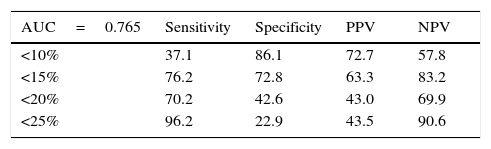
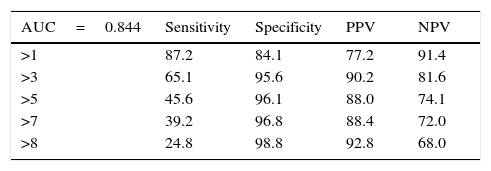
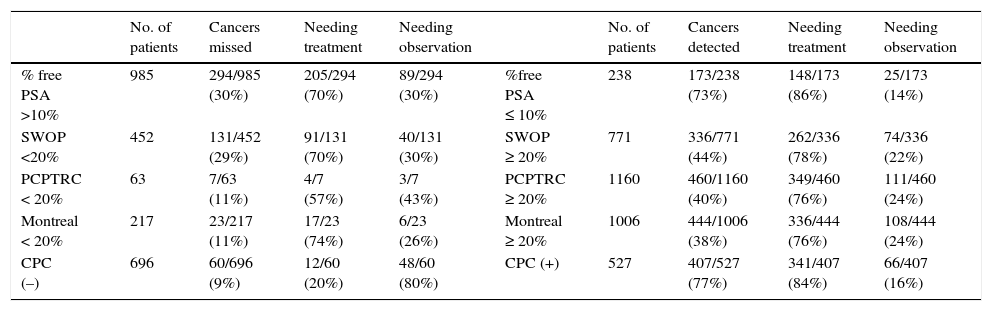
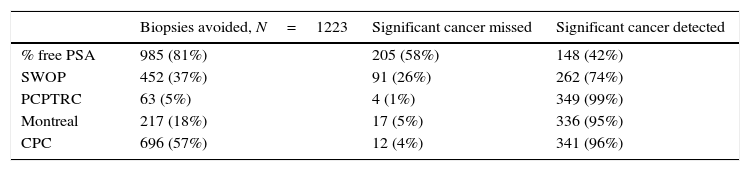
Results1223 men aged >55 years participated, 467 (38.2%) had a biopsy positive for cancer of whom 114/467 (24.4%) complied with the criteria for active observation. Area under the curve analysis showed CPC detection to be superior (p<0.001), avoiding 57% of potential biopsies while missing 4% of clinically significant prostate cancers.
ConclusionsThe CPC detection was superior to the nomograms in predicting the presence of prostate cancer at initial biopsy; its high negative predictive value potentially reduces the number of biopsies while missing few significant cancers, being superior to the nomograms in this aspect. Being a positive/negative test the detection of CPCs avoids defining a cutoff value which may differ between populations.
Los nomogramas que incluyen el PSA para predecir los resultados de una biopsia prostática son de utilidad en la clínica diaria. En este estudio de hombres con sospecha de cáncer prostático comparamos el uso de 3 nomogramas online con la detección de células prostáticas circulantes (CPC) para predecir los resultados de la biopsia prostática.
Métodos y pacientesUna serie de varones con sospecha de cáncer fueron sometidos a una biopsia prostática de 12 muestras. Se registraron la edad, APE total, porcentaje de APE libre, historia familiar de cáncer prostático, origen étnico y resultados de una ecografía transrectal. Se calculó el riesgo de cáncer prostático utilizando 3 nomogramas.
Se separaron las células mononucleares por centrifugación diferencial de 8ml sangre venosa e identificaron las CPC utilizando inmunocitoquímica con anti-APE y anti-P504S. Una CPC fue definida como una célula expresando APE y P504S y el test como positiva/negativa. La biopsia fue clasificada como cáncer/no-cáncer. Por cada parámetro el área bajo la curva fue calculada y los rendimientos diagnósticos comparados.
ResultadosUn total de 1.223 hombres>55 años participaron, 467 (38,2%) tuvieron una biopsia positiva para cáncer, de los cuales 114/467 (24,4%) tuvieron un cáncer no-significativo. El análisis del área bajo la curva mostró que la detección de las CPC fue superior (p<0,001), evitando el 57% de las biopsias prostáticas, mientras que no detectó el 4% de los cánceres significativos.
ConclusionesLa detección de CPC fue superior a los otros modelos para predecir los resultados de la biopsia prostática inicial, reduce potencialmente el número de biopsias innecesarias y no detecta solo una pequeña fracción de los pacientes con cáncer clínicamente significativos. Fue superior a los otros modelos en este aspecto, cuando considerados negativos los nomogramas no detectaron un número significativo de cánceres agresivos. De ser un test positivo/negativo, la detección de CPC evita la definición de un punto de corte, lo cual podría variar entre poblaciones diferentes.