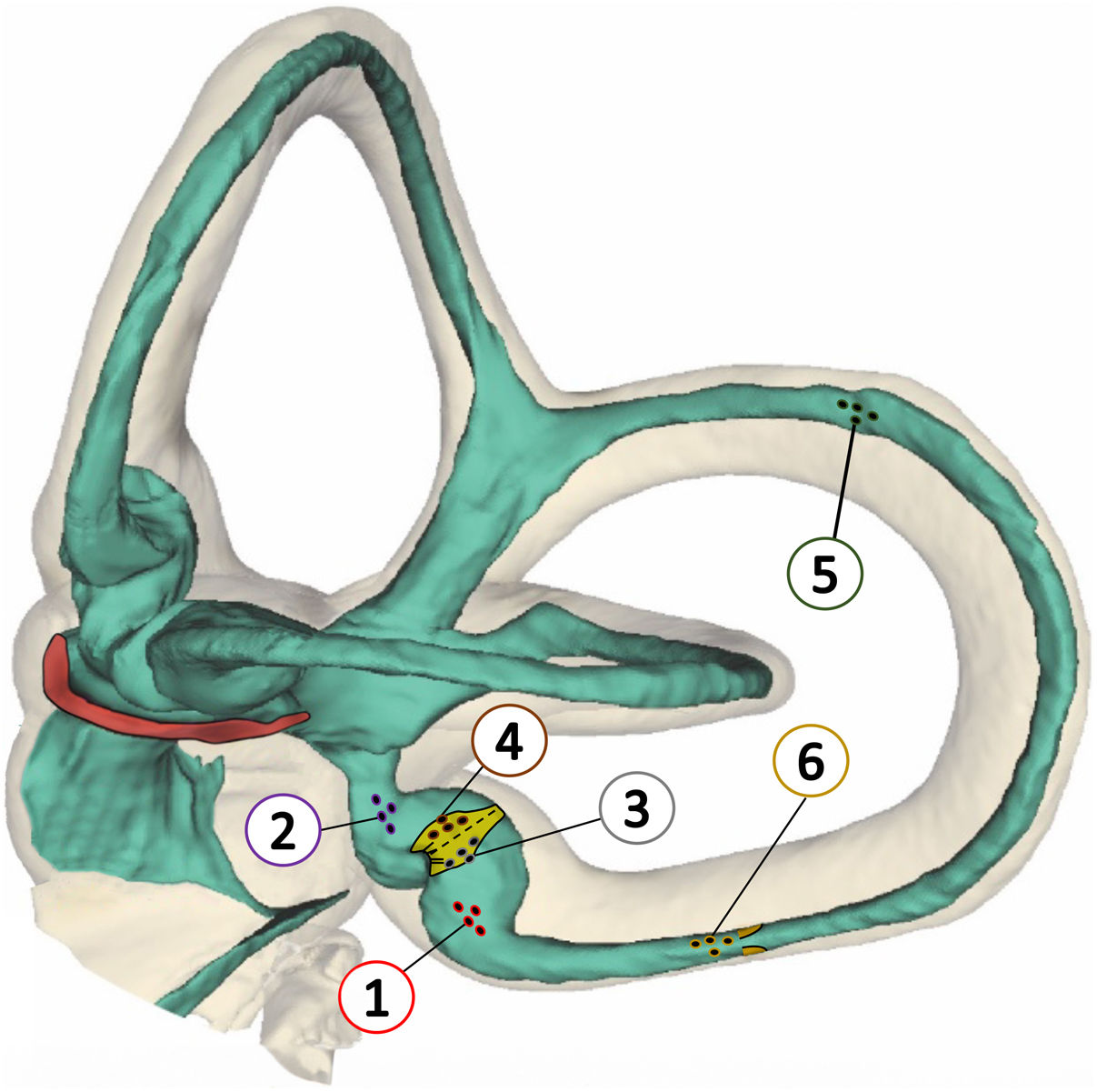
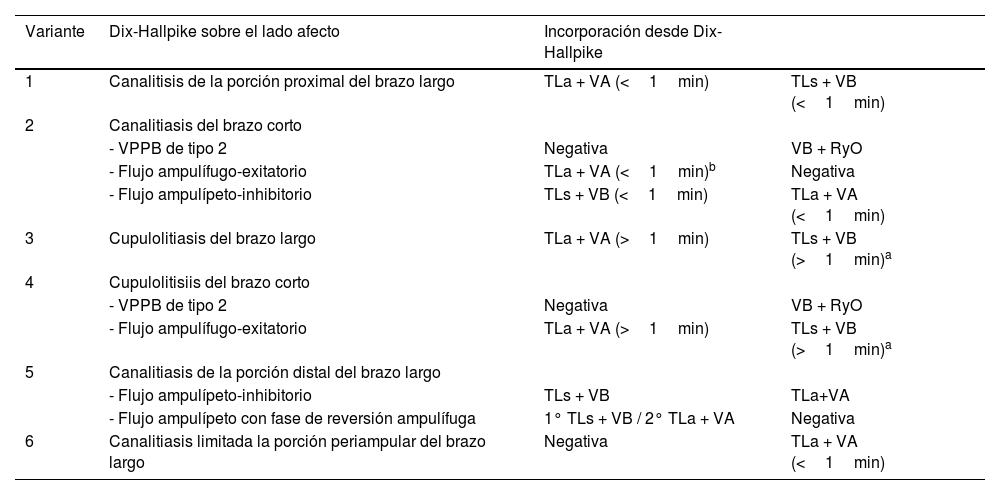
El vértigo posicional paroxístico benigno es la causa más frecuente de vértigo de origen periférico. Se caracteriza por episodios de vértigo recurrente de segundos de duración al adoptar una posición cefálica capaz de desplazar/movilizar otoconias presentes en la endolinfa de los conductos semicirculares. Estas provienen de la mácula del utrículo y generan corrientes endolinfáticas anormales. El tratamiento principal consiste en la realización de maniobras de reposición que tienen como objetivo movilizar las otoconias fuera del conducto afecto, por lo que la correcta identificación de este a la hora de realizar el diagnóstico es indispensable. Debido a su orientación espacial con respecto al utrículo y a la fuerza de la gravedad, el conducto que se afecta con más frecuencia es el conducto semicircular posterior (CSP). En los últimos años y gracias a los avances tecnológicos que nos han permitido una mejor valoración del nistagmo posicional durante las maniobras diagnósticas y terapéuticas, se han descrito diversos escenarios de afectación del CSP, en los que las otoconias se encuentran en otras partes del conducto y no en el lugar más frecuente y esperado que es flotando en la porción proximal del brazo largo. Debido a que en estos casos el pronóstico y la evolución de la enfermedad es distinta, es necesario estar familiarizado con la existencia de todas las posibles variantes. Este trabajo de revisión tiene como objetivo describir las seis variantes de afectación del CSP descritas hasta la fecha.
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo is the most common cause of peripheral vertigo. It is characterized by short and recurrent episodes of vertigo, trigged by specific head movements that displace otoconia within the semicircular canals. The movement of dislodge otoconia from the utricle cause abnormal positional endolymphatic currents. Primary treatment involves reposition maneuvers aimed at moving the displaced otoconia out the affected canal, therefore correct identification of the affected canal is essential for the diagnosis. The posterior semicircular canal (PSC) is the most frequently affected due to its spatial orientation and the force of gravity. Recent technological advances have allowed for better assessment of positional nystagmus during diagnostic and therapeutic maneuvers, revealing various possible scenarios of PSC involvement. Regarding the PSC, otoconia may be found in different parts of the canal, and not just in the expected location, floating in the long arm of the canal. The understanding of these variants is crucial, as the prognosis and the disease progression differ in such cases. This review aims to describe the six possible variants of PSC involvement described so far.