Relacionar la clínica de disfagia con la enfermedad de Forestier-Rotes-Querol o hiperostosis esquelética difusa idiopática (HEDI), desorden por osificación del ligamento cervical anterior común y calcificaciones en otras articulaciones.
Pacientes y métodosRevisión del historial clínico-radiológico de 455 pacientes que en 5 años consultaron en nuestro centro por disfagia, remitidos desde Atención Primaria o diferentes especialidades. El diagnóstico de HEDI se estableció en función de los criterios descritos por Resnick.
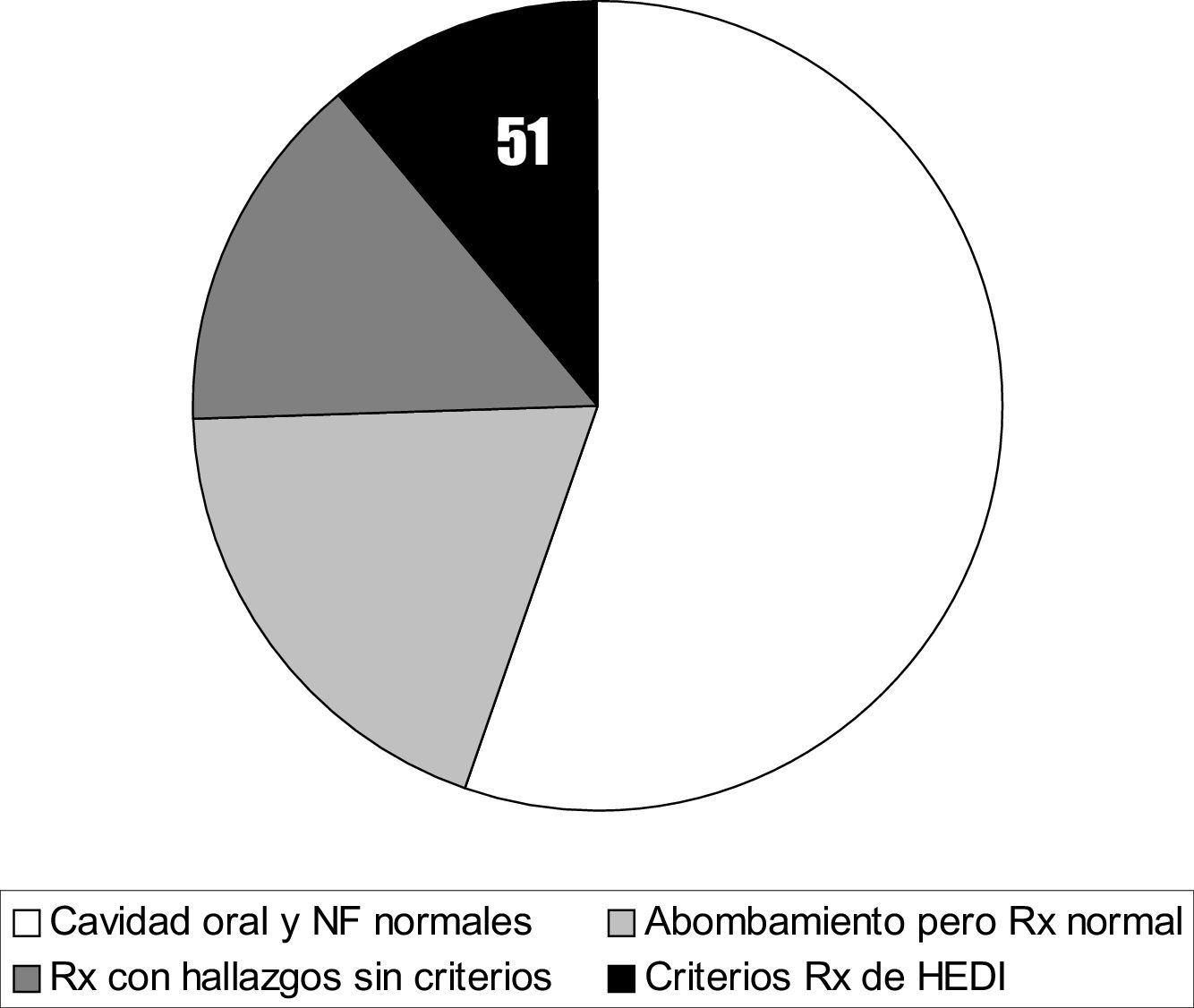
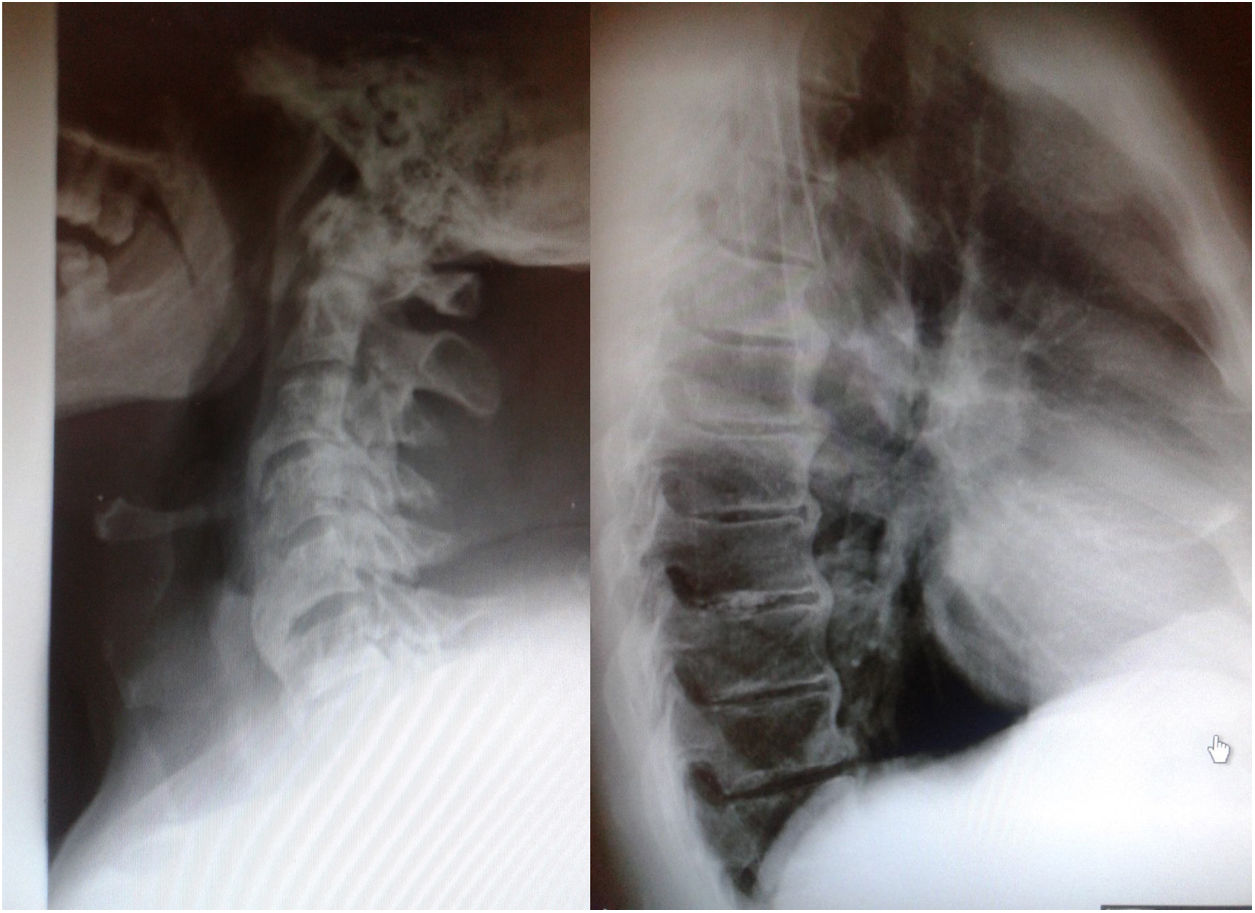
ResultadosSobre un volumen total de 32.544 pacientes atendidos, el 1,4% consultó por disfagia alta. En 51 casos con esta sintomatología —el 11,2% de los sujetos— pudieron verificarse datos congruentes con los hallazgos radiológicos diagnósticos de HEDI. La incidencia observada fue de 7:100.000 habitantes-año. Dos casos con disfagia severa mejoraron con la retirada del hueso cervical neoformado.
ConclusionesLa HEDI supone una osificación interarticular anquilosante habitualmente sistémica pero asintomática. Al manifestarse, distorsiona principalmente las funciones de cuello y vías altas, generando sobre todo disfagia. Unos pocos casos requieren cirugía liberadora de estas calcificaciones.
To relate symptoms of dysphagia to Forestier-Rotes Querol disease or diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH), a disorder due to ossification in the anterior longitudinal ligament and calcifications in other entheses.
Patients and methodsReview of clinical and radiological findings in 455 outpatients attended at our Centre with dysphagia, for 5years, referred from dental, trauma, neurological or primary health care. A diagnosis of DISH was established using Resnick's criteria.
ResultsWe detected 51 cases with dysphagia consistent with DISH diagnostic criteria – 11.2% of subjects suffering this symptom- out of 32544 outpatients attended. An incidence of 7:100000 inhabitants per year was observed. Two cases showed significant improvement after removing the new bone in the spine.
ConclusionsDISH is an ankylosing ossification between the joints, frequently systemic but showing no clinical symptoms. When symptoms manifest, neck movements and upper airways are involved, mainly dysphagia. A few cases need surgery to relieve the calcification processes.