Contralateral sensorineural hearing loss (CSNHL) after vestibular schwannoma (VS) is a severe complication, especially in those cases in which hearing preservation in the operated side was not possible. There are several theories that attempt to explain this issue, but there is no established guideline of treatment.
Material and methodsWe report 4 patients treated in our institution who developed a severe CSNHL after surgery.
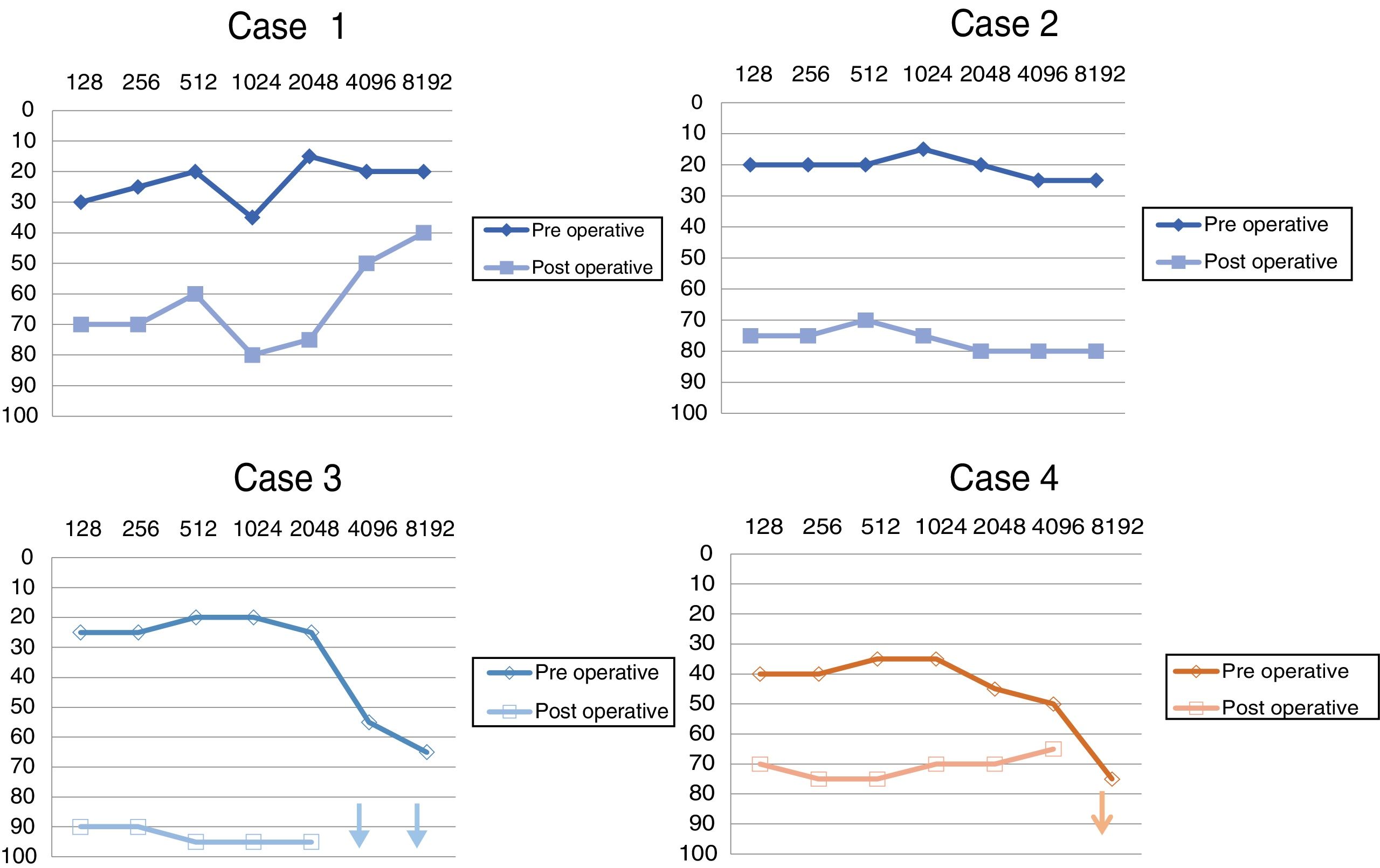
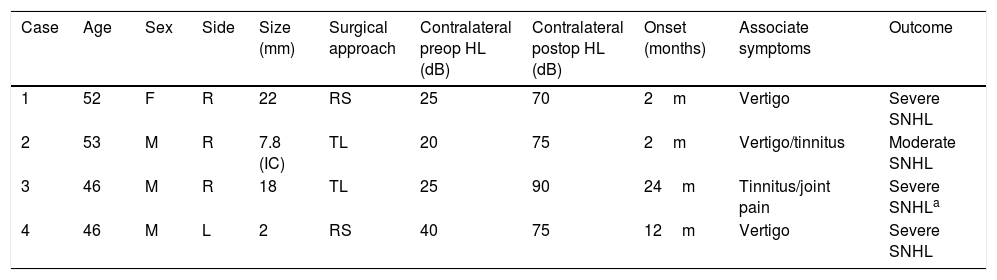
ResultsOf the 185 cases of VS treated with surgery, 4 patients (2.2%) developed a CSNHL after VS surgery. After medical treatment, partial recovery of hearing occurred in one patient the other 3 patients presented a well-established severe SNHL.
ConclusionsEstablished treatment guidelines do not exist, but the use of high doses of corticosteroids has been recommended and cochlear implant in cases with no recovery and complete hearing loss may be useful.
La hipoacusia neurosensorial contralateral (HNSC) tras cirugía de schwannoma vestibular (SV) es una complicación grave, especialmente en aquellos casos en los que la preservación de la audición del lado intervenido no fue posible. Existen varias teorías que intentan explicar este problema, pero no existe una guía de tratamiento en estos casos.
Material y métodosPresentamos los casos de 4 pacientes tratados en nuestro hospital que desarrollaron una HNSC severa tras cirugía de SV.
ResultadosDe los 185 casos de SV tratados con cirugía, 4 pacientes (2,2%) desarrollaron una HNSC después de la cirugía. Tras el tratamiento médico se produjo recuperación parcial de la audición en un paciente, los otros 3 pacientes presentaron una HNS severa.
ConclusionesNo existen guías de tratamiento, pero se recomienda el uso de altas dosis de corticosteroides y el implante coclear en casos sin recuperación y pérdida completa de la audición.