Members of the genus Campylobacter are recognized as causative agents of infectious diseases in humans and animals throughout the world. These bacteria are curved to spiral rods and have a single polar flagellum. Campylobacter fetus subsp. venerealis and Campylobacter fetus subsp. fetus are the causative agents of bovine genital campylobacteriosis, one of the most important venereal diseases in Argentina, which characteristically produces embryonic death and occasional abortion1.
Regarding Campylobacter pathogenesis, there is limited knowledge about the mechanisms involved in host-bacteria interaction in the venereal environment, adhesion, chemotaxis or tissue tropism4.
Campylobacter fetus is highly adapted to mucosal surfaces. Bacterial adhesion is an important initial step in infection. Pathogens use surface-located adhesins to interact with specific host cell receptors. Although some bacterial structures involved in the adhesion process are still unknown, there is evidence that the lipopolysaccharide and the flagellum participate in bacterial adherence. The flagellum also enables bacterial movement through the mucus4.
The challenge of cell lines such as HeLa, Hep-2, CHO, VERO, MDBK has allowed the evaluation of different species of Campylobacter strains isolated from humans and animals3,5. Cell adhesion and invasion for different Campylobacter species have been confirmed; however invasion has not been demostrated for C. fetus2.
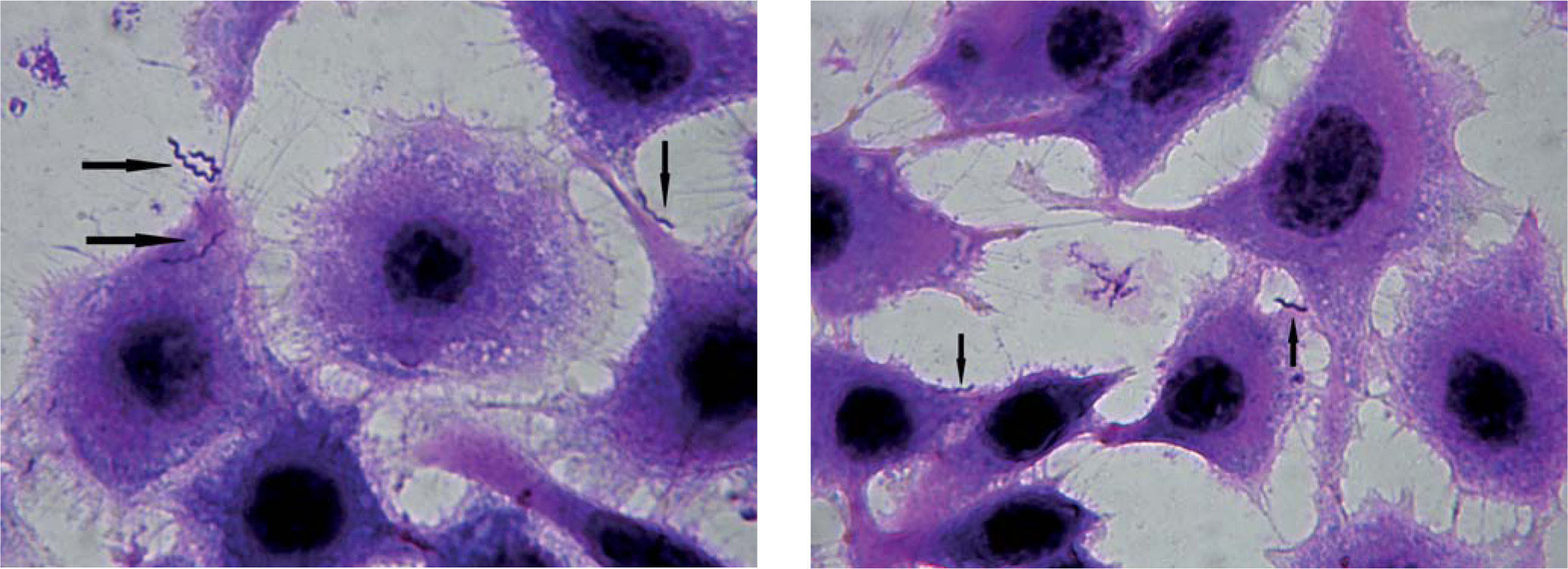
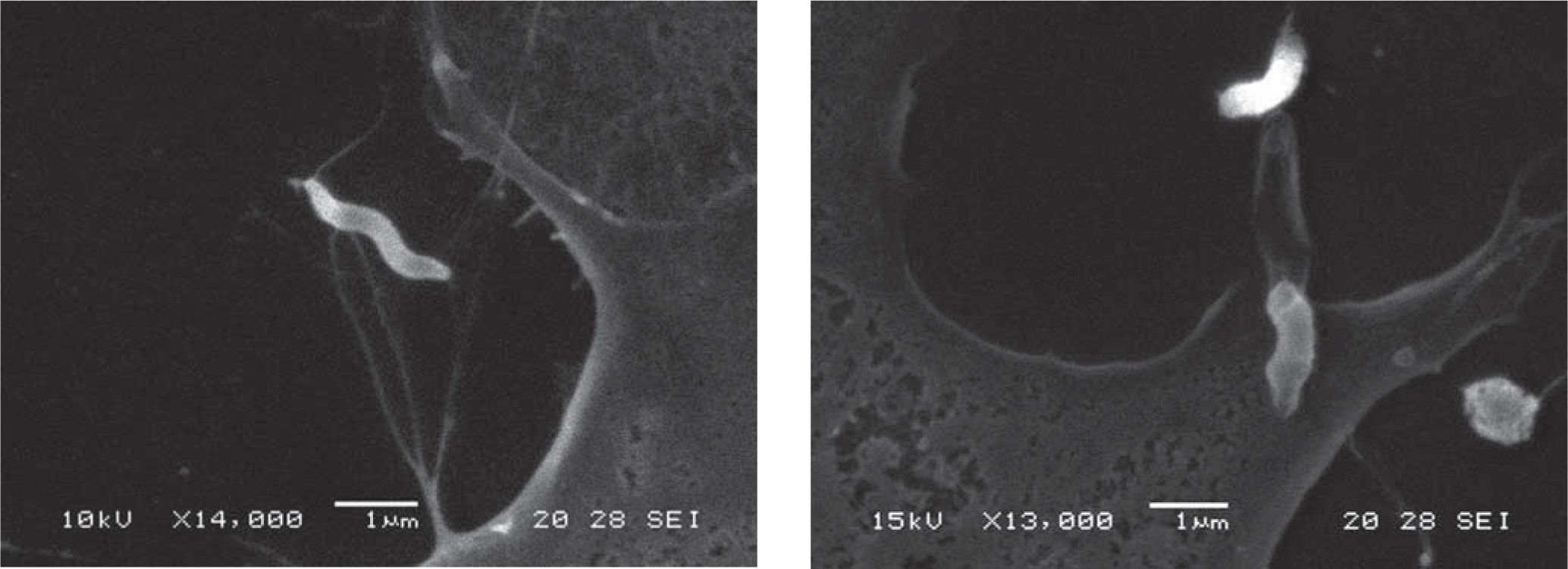
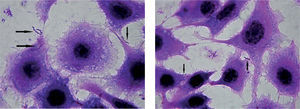
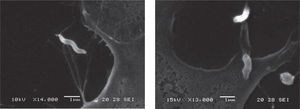
C. fetus subsp. venerealis adhesion to MDBK cells was analyzed and confirmed by optical microscopy (Figs. 1 and 2) and scanning electron microscopy (Figs. 3 and 4). It was observed that the bacterium attaches by the apical portion involving the flagellum in the adhesion, which could indicate the presence of adhesins on it.