Duodenal diverticula (DD) are present in 20% of adults.1,2 Bleeding is a rare event (0.14% of upper gastrointestinal bleeding) and there is no defined gold standard method of haemostasis.3,4
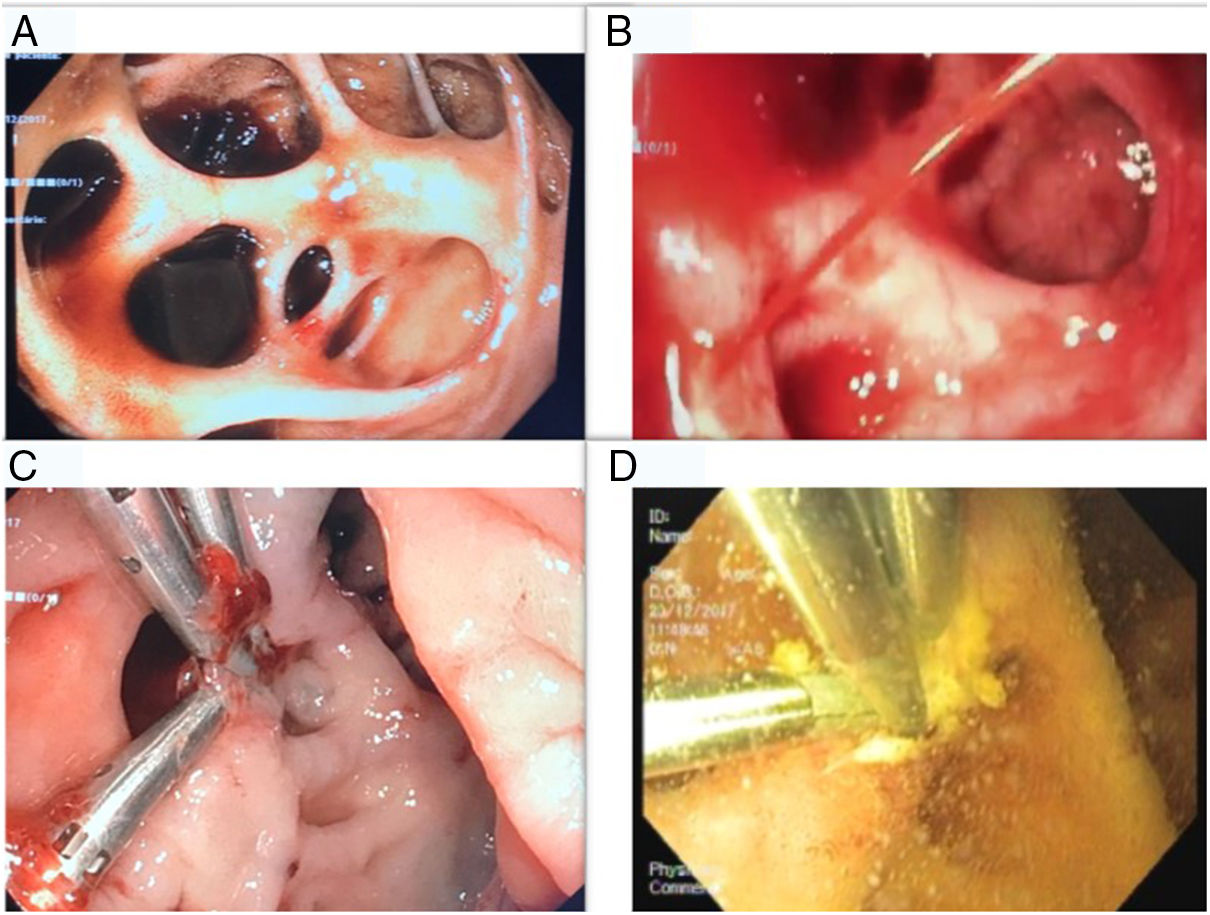
A 64-year-old female patient presented with melena with hemodynamic instability. At physical examination, she was tachycardic and nasogastric intubation did not show blood. Laboratory workup revealed acute normocytic anemia of 8.6g/dL. An upper endoscopy (UE) was performed and revealed a giant diverticulum of the second duodenal portion, without blood. She presented a new episode of hemodynamic instability and a contrast CT revealed blood in the DD. A second UE was performed using a conventional colonoscope and revealed blood in the DD (Fig. 1A). During observation, an arterial spurting of the DD was seen (Fig. 1B); it was controlled with epinephrine and 3 hemoclips (Fig. 1C). A second look endoscopy was performed, without evidence of rebleeding (Fig. 1D). The patient was discharged 5 days later.
Most common endoscopic approaches include injection, thermal and mechanic methods alone or combined.4 Although there are no available comparative studies, theoretically, clipping seems to be better than injection methods.1 It was suggested that air removal before hemoclip may reduce perforation.5
FundingNo funding.
Conflicts of interestNo conflicts of interest.