The most common postoperative complications of velopharyngeal insufficiency surgery are postoperative bleeding and airway obstruction or obstructive sleep apnoea. Consequently, the aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of low level laser therapy (LLLT) during the first postoperative days in children undergoing superiorly based pharyngeal flap (SBF) surgery.
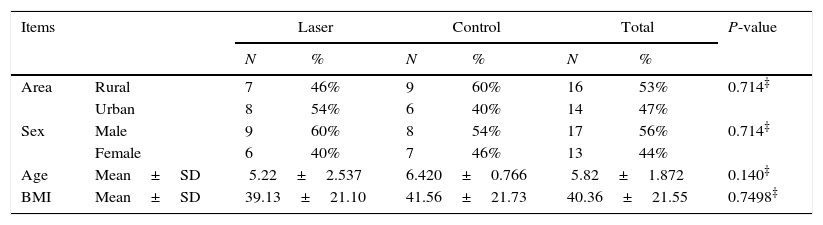
Materials and methodsA randomized double blind clinical study on 30 children divided on two groups 15 patients each, who underwent SBF. LLLT was used in a group and the other was a control group. The study was conducted in academic tertiary care medical centres between 2013 and 2015. The degree of edema, oxygen saturation, occurrence of obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) and steroid administration were recorded.
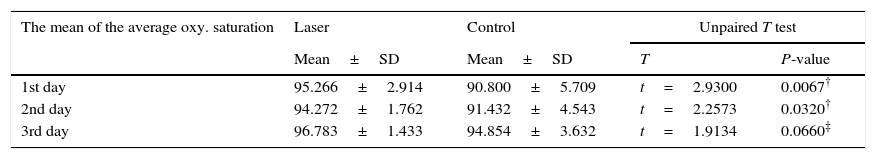
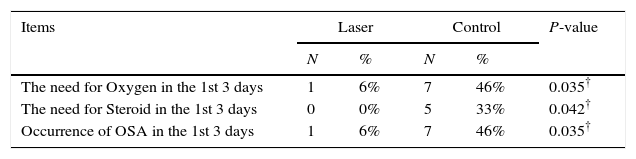
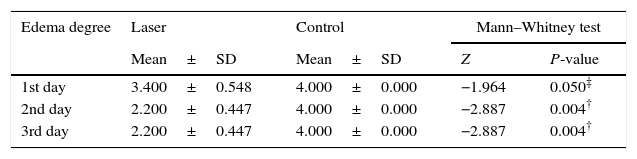
ResultsThe mean of the average oxygen saturation was significantly less in the control group in the 1st and 2nd day as compared to the laser group. The need for oxygen and the incidence of OSA in the first 3 days were significantly higher in the control group as compared to the laser group. The degree of edema showed no significant difference in the first day but was significantly higher in the control group in the 2nd and 3rd days. Hence, the need of steroids was significantly higher in the control group in the first 3 days.
ConclusionsPreliminary results showed that low level laser therapy is effective in reducing the incidence of early postoperative airway obstruction after SBF operations.
La más común de las complicaciones postoperatorias tras la cirugía de la insuficiencia velofaríngea son el sangrado y la obstrucción postoperatoria de las vías respiratorias, o la apnea obstructiva del sueño. Por lo tanto, el objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar el efecto de la terapia láser de baja intensidad durante los primeros días del postoperatorio en niños sometidos a colgajo faríngeo de base superior (SBF).
MétodosEstudio clínico aleatorizado doble ciego en 30 niños, entre el grupo de láser y el grupo control, que fueron sometidos a SBF. El estudio se llevó a cabo en dos centros médicos académicos de atención terciaria, entre 2013 y 2015. Se registró grado de edema, la saturación de oxígeno, la aparición de apnea obstructiva del sueño y la necesidad de esteroides.
ResultadosDurante los 3 primeros días, la media de la saturación de oxígeno muestra cambios significativos entre los dos grupos. Por otra parte, la necesidad de oxígeno en los primeros 3 días muestra también cambios significativos entre los dos grupos. Así como la incidencia de apnea obstructiva del sueño. El grado de edema no muestra ningún cambio significativo en el primer día, pero sí en los 2 días siguientes. Por lo tanto, la necesidad de esteroides en los primeros 3 días también muestra cambios significativos entre los dos grupos.
ConclusionesLos resultados preliminares mostraron que la terapia con láser de baja intensidad es eficaz en la reducción de la incidencia de obstrucción de vía aérea en el postoperatorio temprano después de las operaciones SBF.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora