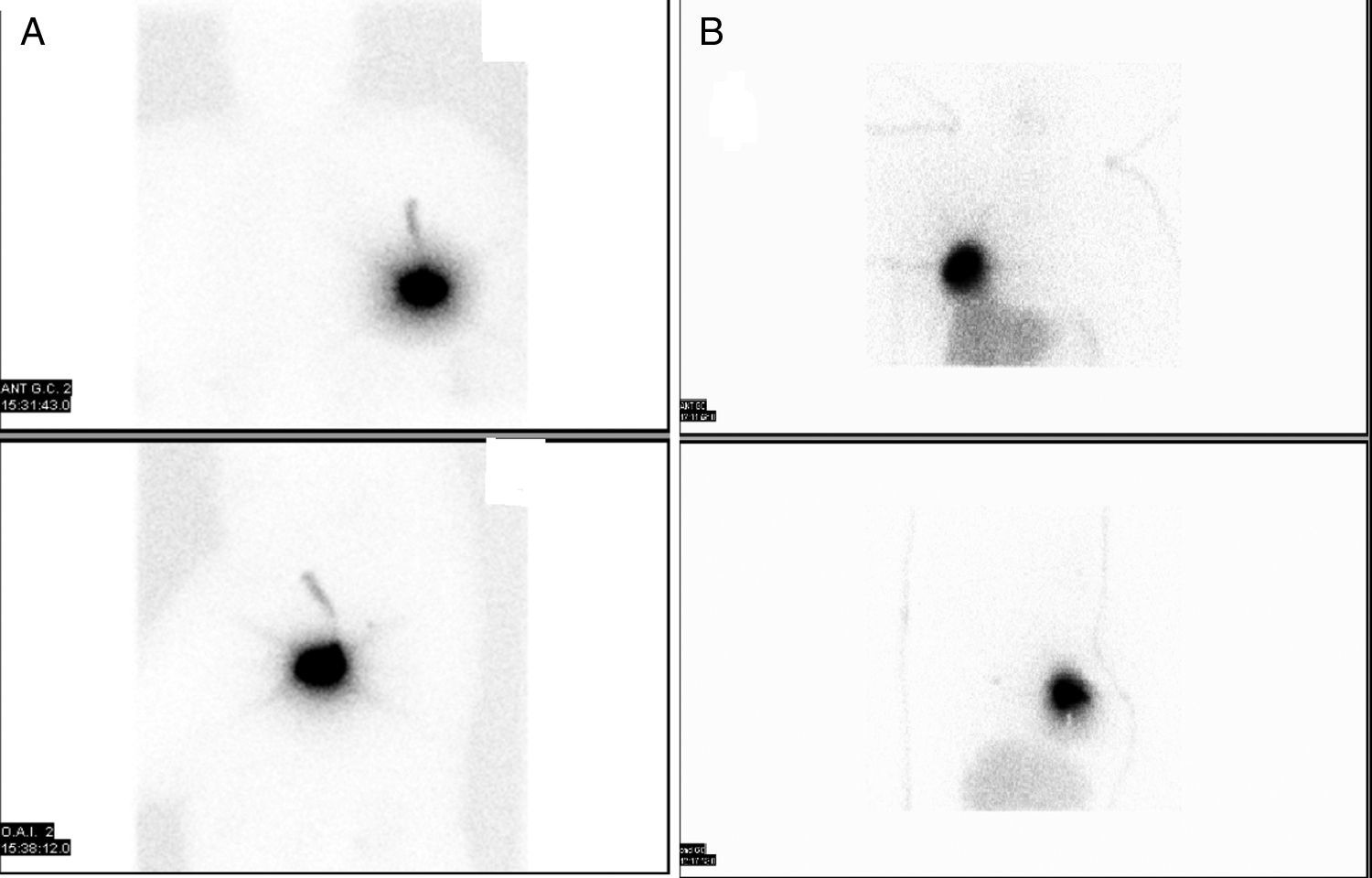
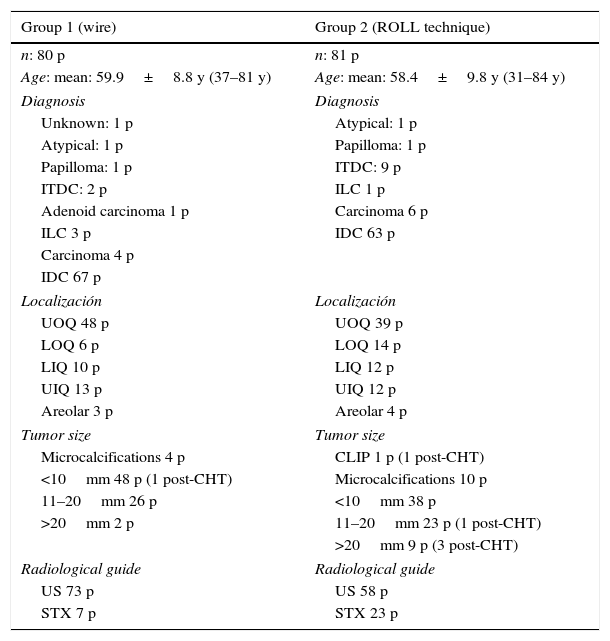
To evaluate the efficiency of radioguided occult lesion localizing in non-palpable breast lesions (NPBL) compared to the surgical wire technique.
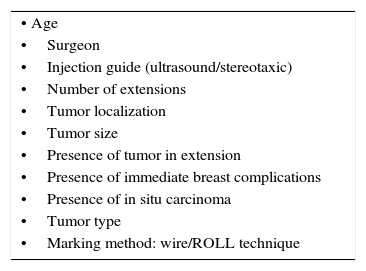
MethodA prospective study was conducted on 161 women with NPBL, of whom 80 were marked with the wire (group 1), whereas 81 women were marked with an intratumor injection of 99mTc-nanocoloid (group 2). The NPBL were located by ultrasound or stereotactic guidance. The lumpectomies were performed following the wire direction in group 1, and with the aid of a gamma-probe in group 2. Surgical margins were then checked, determining the need of extension if the margin was less than 5mm in the intra-surgical study, and less than 2mm in the deferred study. Data were collected on the mean number detected by surgery, surgical margins, number of extensions, presence of residual tumor in the extension, second surgeries, lumpectomy volume, as well as total resected volume, volume/tumor ratio, and complications.
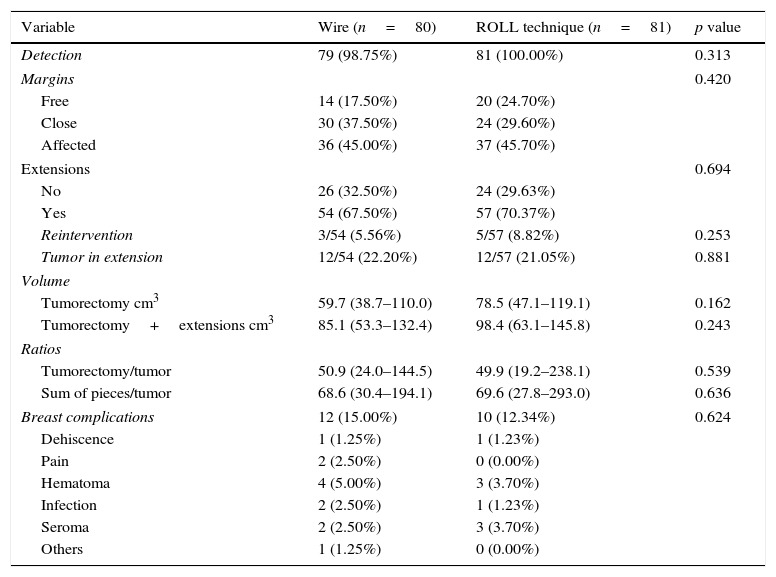
ResultsNo significant differences were observed between the two groups in the mean number detected, surgical margins, number of extensions, presence of residual tumor in the extension, second surgeries, lumpectomy volume, total resected volume, volume/tumor ratio or complications. The multivariate analysis showed that the determining factors of the resected volume were the radiological guidance technique, as well as the surgeon.
ConclusionsThe radioguided occult lesion localizing technique helps in the detection and resection of NPBL with the same efficiency as the surgical wire, and adds the possibility of sentinel node detection in the same surgery. The determining factors of the resected volume were the radiological guidance technique and the surgeon.
Evaluar la eficacia de la localización radioguiada de lesiones no palpables de mama (LNPM) respecto al arpón quirúrgico.
MétodoSe han estudiado prospectivamente 161 mujeres con LNPM, 80 marcadas con arpón (grupo 1) y 81 con inyección intratumoral de 99mTc nanocoloide (grupo 2). Las lesiones se localizaron por ecografía o estereotaxia. Las tumorectomías se realizaron en el grupo 1 siguiendo la dirección del arpón y en el grupo 2 con la ayuda de una sonda gammadetectora. Posteriormente se comprobaron los márgenes quirúrgicos, determinando la necesidad de ampliación si el margen era menor a 5mm en el estudio intraoperatorio y menor a 2mm en el estudio diferido. Se recogieron datos de porcentaje de detección quirúrgica, afectación de márgenes quirúrgicos, número de ampliaciones, presencia de lesión residual en la ampliación, número de reintervenciones, volumen de la tumorectomía y volumen total extraído, ratio volumen/tumor y complicaciones.
ResultadosNo hubo diferencias significativas entre ambos grupos en porcentaje de detección, afectación de márgenes, número de ampliaciones, presencia de lesión residual en la ampliación, reintervenciones, volumen de la tumorectomía, volumen total extraído, ratio volumen/tumor y complicaciones. El análisis multivariante mostró que los factores condicionantes del volumen extraído son la técnica de marcaje radiológico y el cirujano.
ConclusionesLa técnica de localización radioguiada de lesiones ocultas permite la detección y exeresis de las LNPM con la misma eficacia que el arpón y añade la posibilidad de detección simultánea del ganglio centinela. Los condicionantes del volumen extraído son la técnica de marcaje radiológico y el cirujano.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)