To study the usefulness of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the initial evaluation and in the response assessment in primary brain lymphoma.
Material and methodsA retrospective analysis was carried out on 18 patients diagnosed with primary brain lymphoma, a histological subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, on whom an initial 18F-FDG PET/CT and MRI was performed, with 7 of the cases being analyzed after the completion of treatment in order to assess response and clinical follow up.
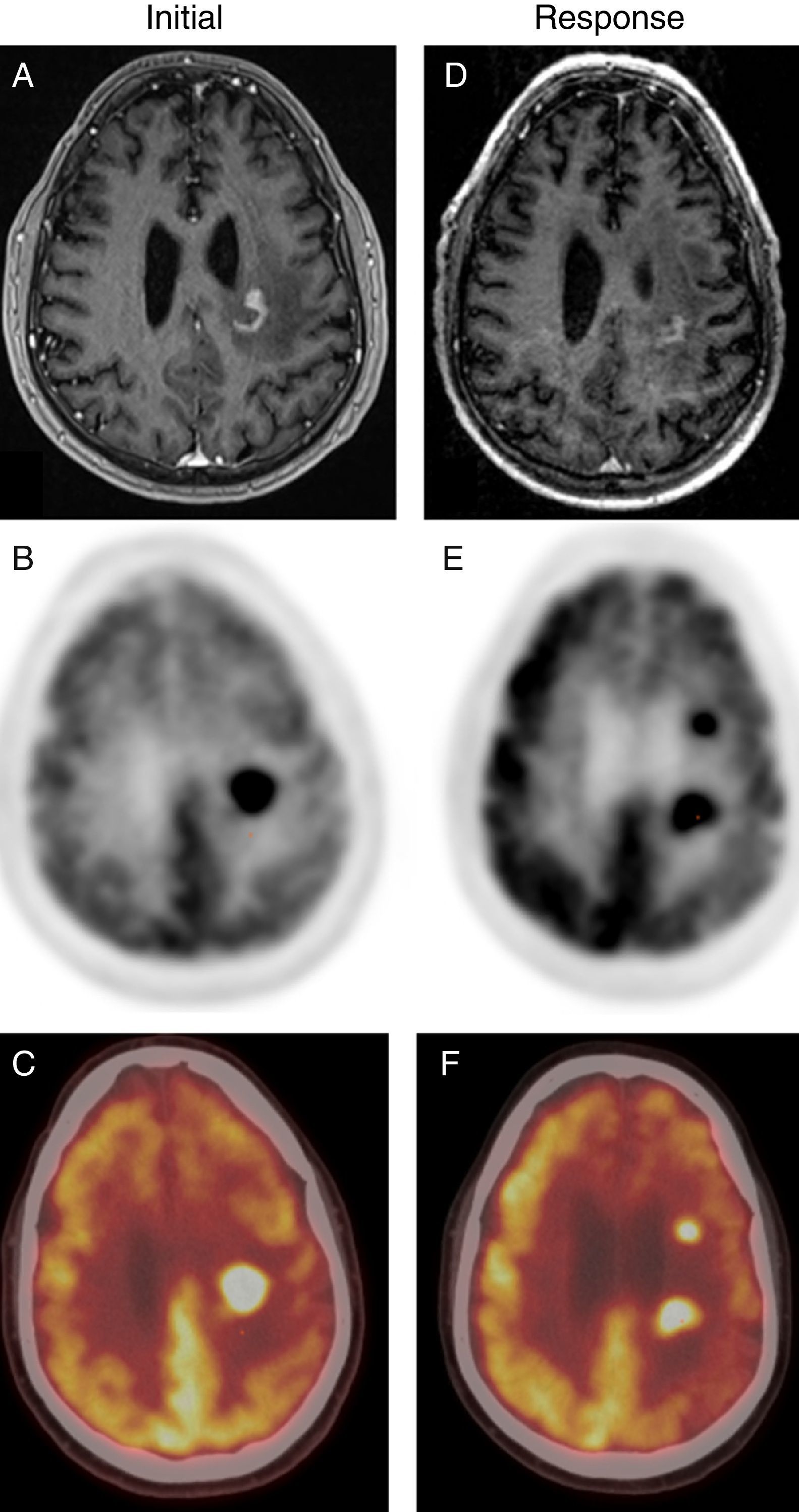
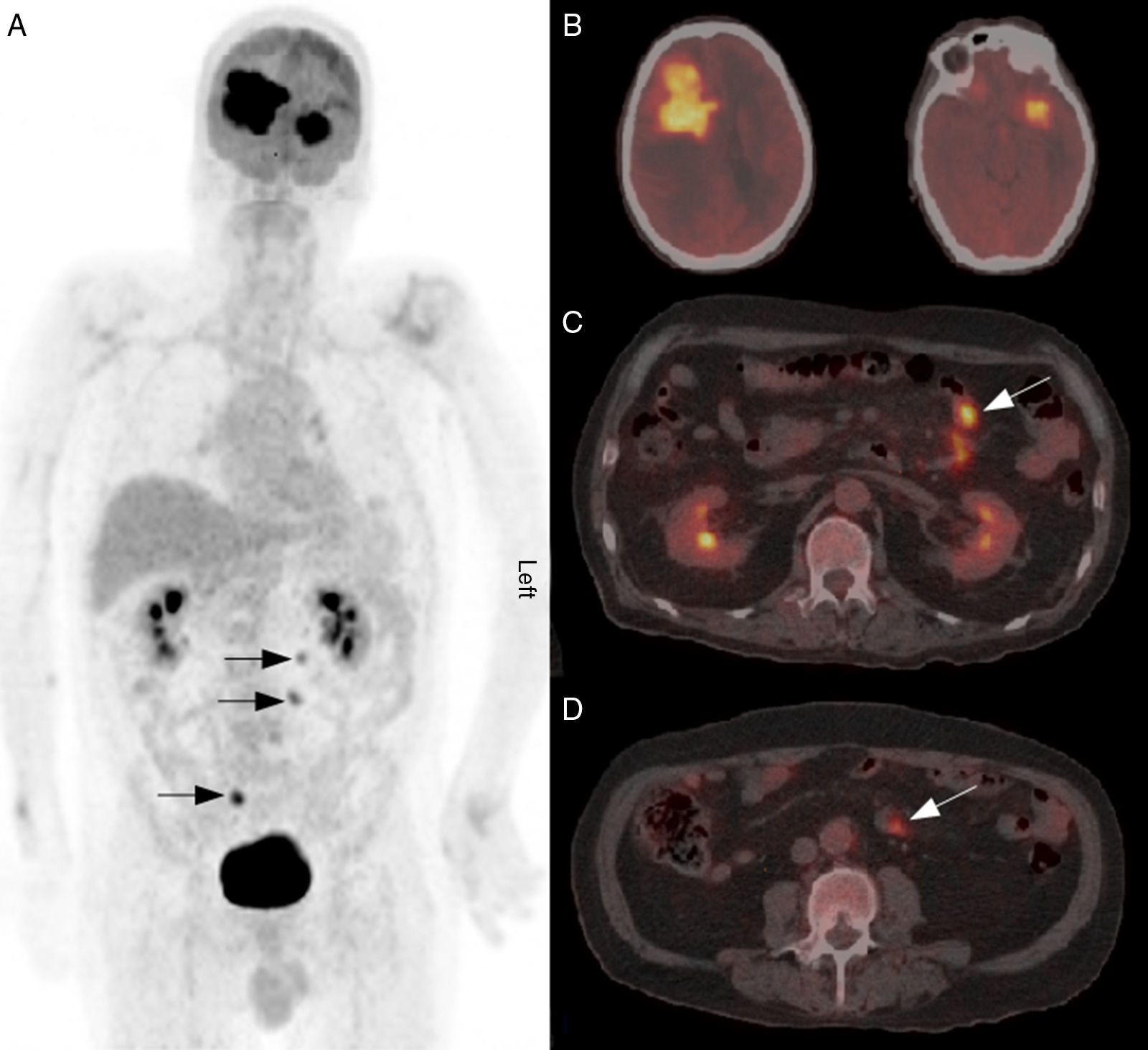
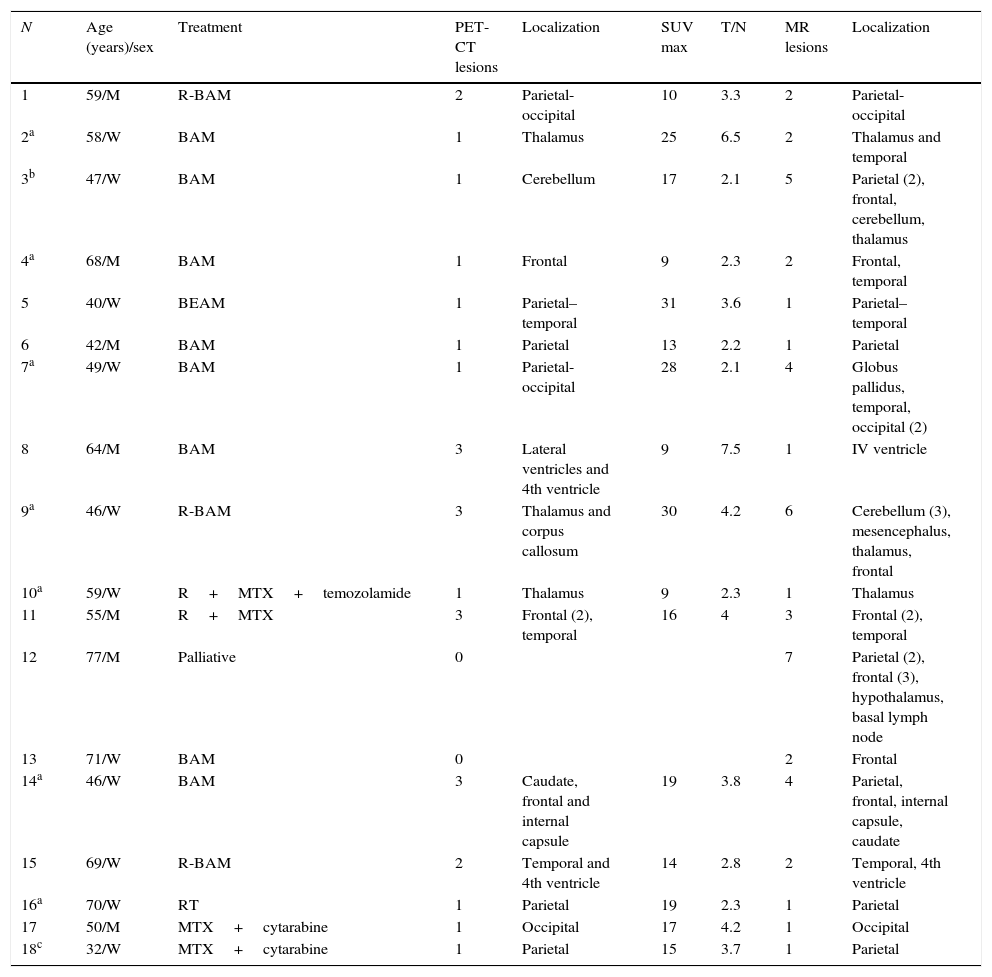
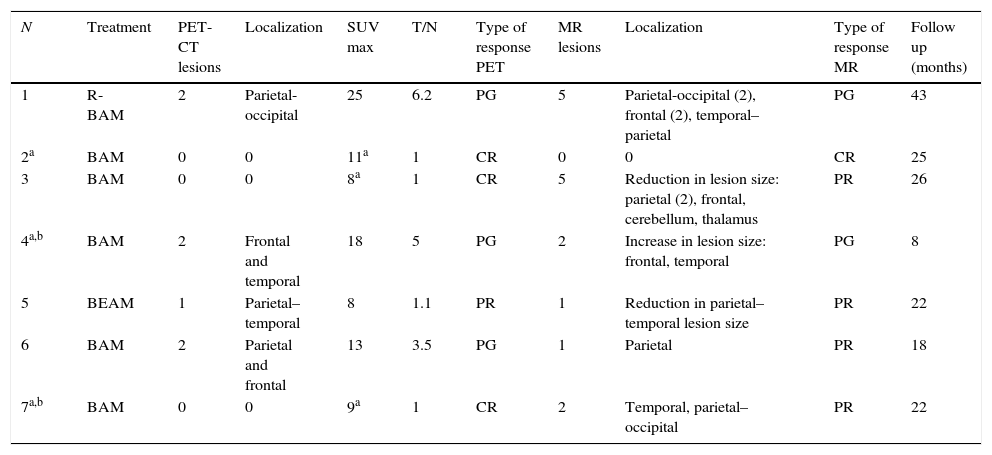
ResultsInitial 18F-FDG PET/CT showed 26 hypermetabolic foci, whereas 46 lesions were detected by MRI. The average SUV maximum of the lesions was 17.56 with T/N 3.55. The concordance of both tests for identifying the same number of lesions was moderate, obtaining a kappa index of 0.395 (p<0.001). In the evaluation of treatment, MRI identified 16 lesions compared to 7 pathological accumulations observed by 18F-FDG PET/CT. The concordance of both tests to assess type of response to treatment was moderate (kappa index 0.41) (p=0.04). In both the initial evaluation and the assessment of the response to treatment, PET/CT led to a change strategy in 22% of patients who had lesions outside the cerebral parenchyma.
ConclusionsMRI appears to be the method of choice for detecting brain disease in patients with primary brain lymphoma, whereas 18F-FDG PET/CT seems to play a relevant role in the assessment of extra-cerebral disease.
Estudiar la utilidad de la 18F-FDG PET/TC en la evaluación inicial y valoración de la respuesta al tratamiento en el linfoma cerebral primario.
Material y métodosSe analizaron retrospectivamente 18 pacientes diagnosticados de linfoma cerebral primario, subtipo histológico linfoma difuso de células grandes B, habiéndose realizado en todos ellos un estudio con 18F-FDG PET/TC y RM inicial y, en 7 casos, también tras la realización de tratamiento con el fin de valorar la respuesta.
ResultadosLa 18F-FDG PET/TC inicial detectó un total de 26 depósitos hipermetabólicos frente a un total de 46 lesiones de la RM. La media del SUV máximo de las lesiones fue de 17,56 y del T/N, de 3,55. La concordancia de ambas pruebas para identificar el mismo número de lesiones fue moderada, obteniendo un índice kappa de 0,395 (p<0,001). En la valoración de la respuesta al tratamiento la RM identificó 16 lesiones frente a los 7 acúmulos patológicos de la 18F-FDG PET/TC. La concordancia de ambas pruebas para valorar el tipo de respuesta al tratamiento fue moderada (índice kappa 0,41) (p=0,04). Tanto en la evaluación inicial como en la valoración de la respuesta al tratamiento la PET/TC facilitó un cambio de estrategia en un 22% de los pacientes que presentaron lesiones fuera del parénquima cerebral.
ConclusionesLa RM parece ser la técnica de elección en la valoración de la enfermedad cerebral en pacientes con linfoma cerebral primario, mientras que la PET/TC ha demostrado tener un papel importante en la valoración de la enfermedad extracerebral.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)