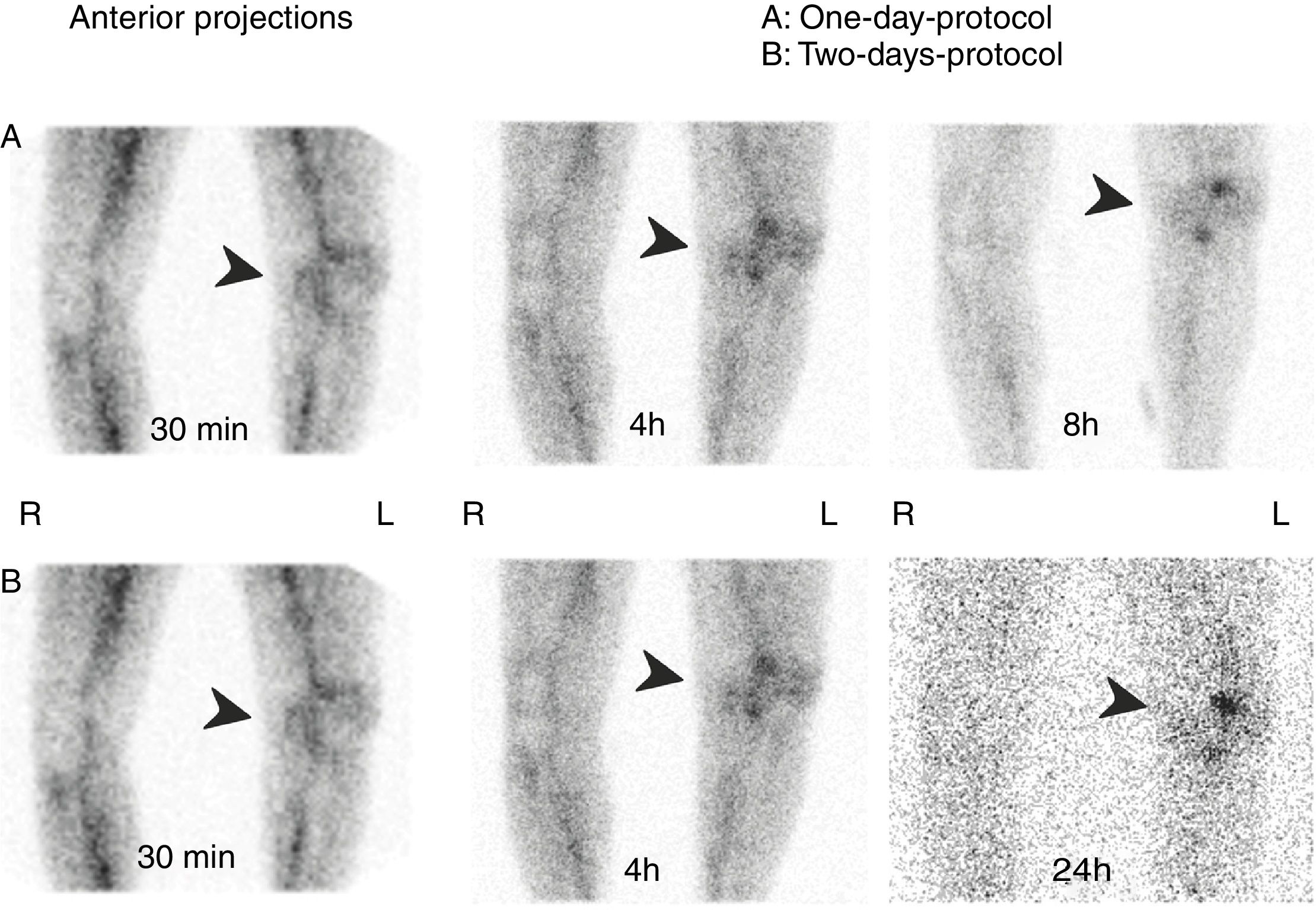
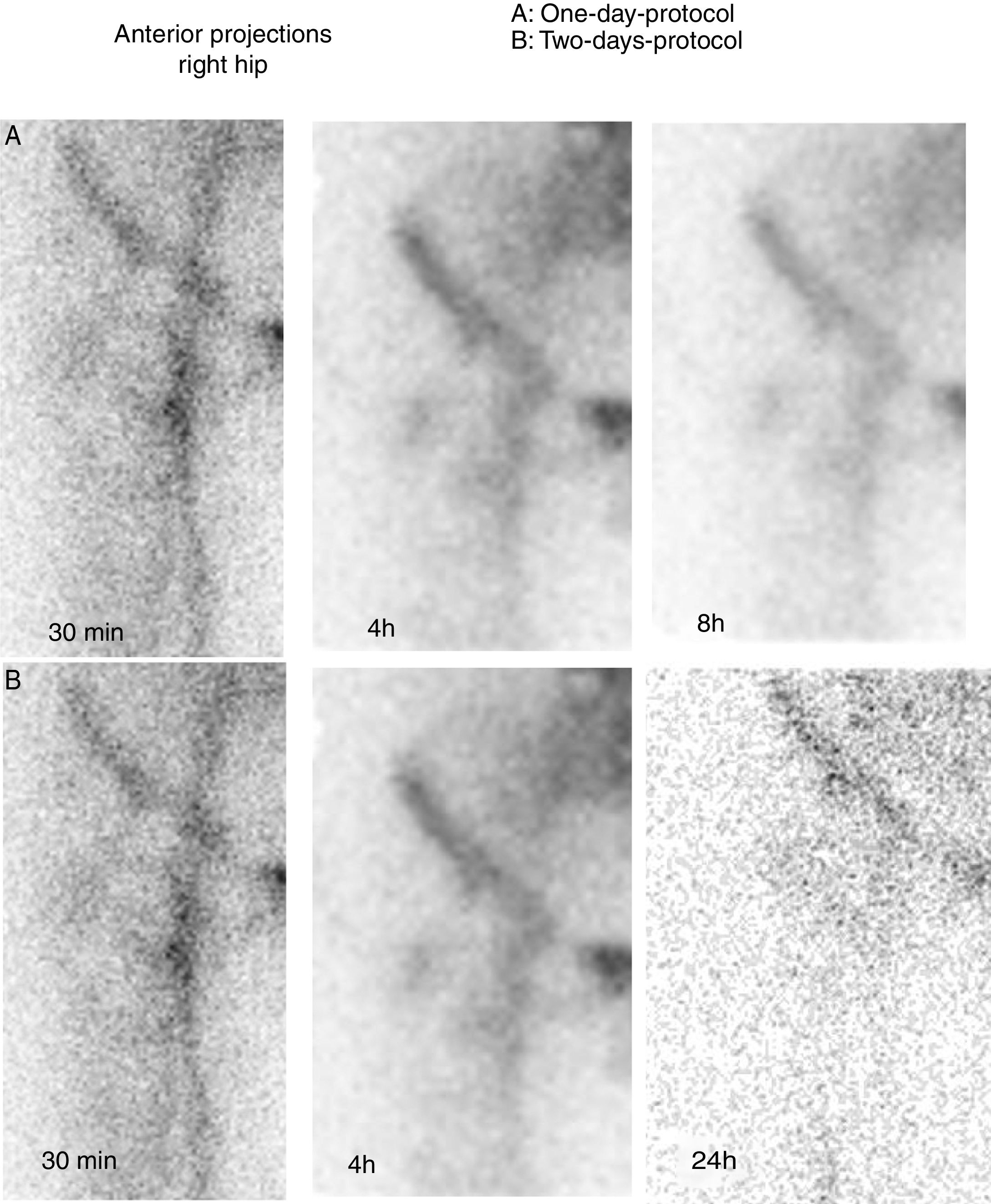
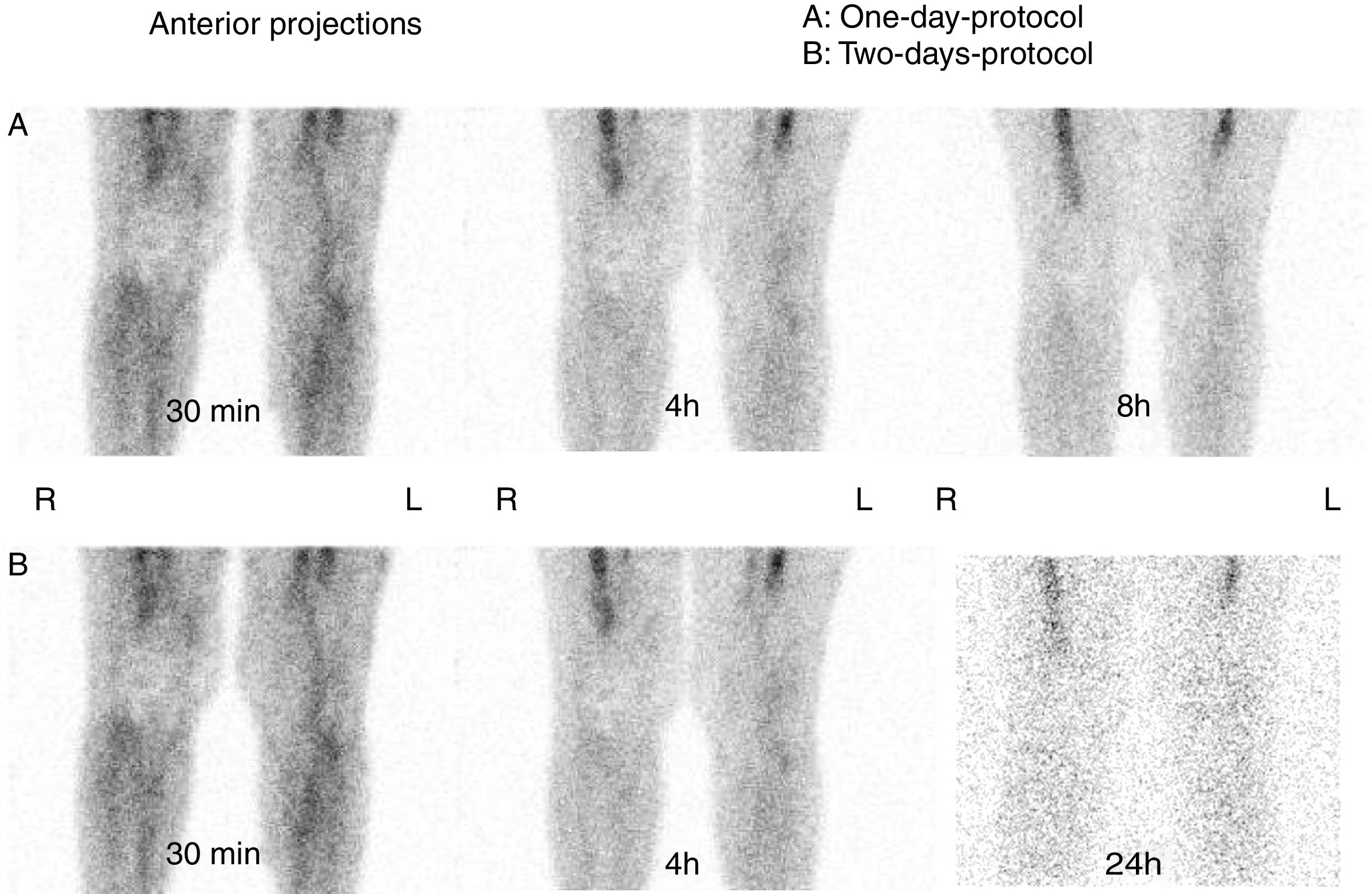
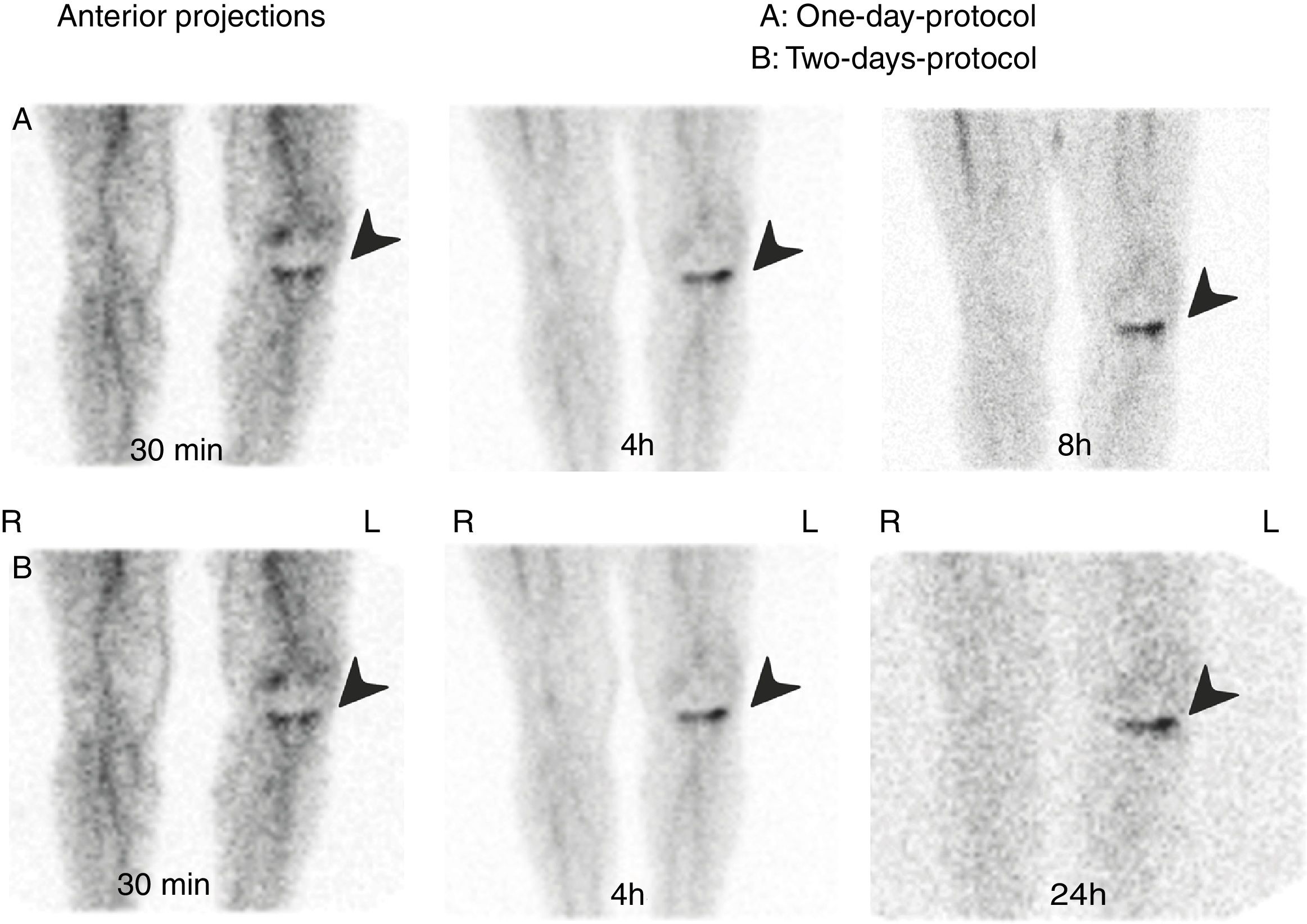
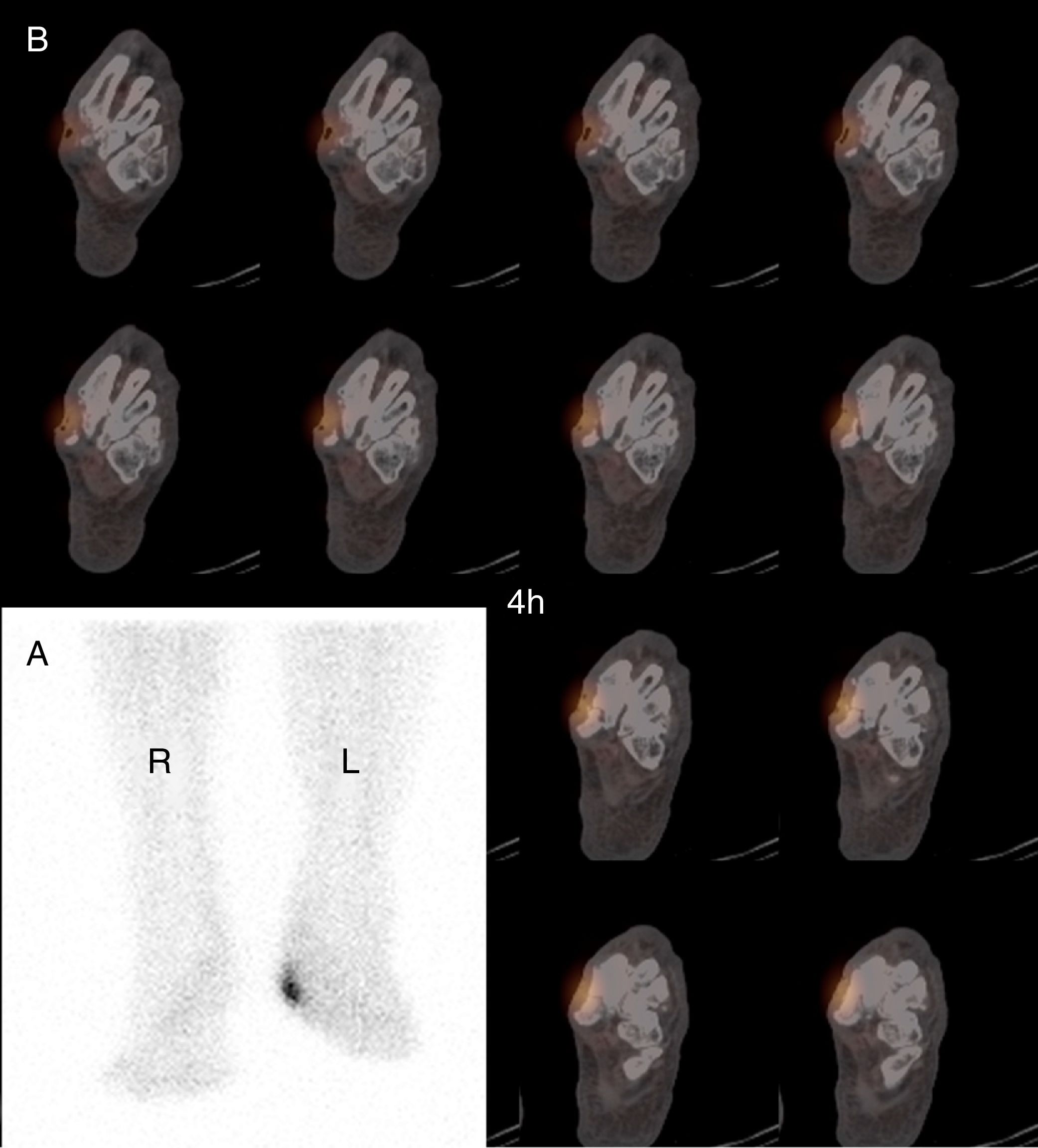
It is difficult to determine osteoarticular infection and differentiate inflammation from infection with laboratory and imaging procedures (CT, MRI, US).
Labelled white-blood-cell scintigraphy (WBCS) is the nuclear medicine test of choice but it takes two days, sometimes finds it difficult to differentiate soft tissue from bone infection and therefore causes interobserver variability, which decreases its specificity.
ObjectiveTo demonstrate the usefulness of the one-day protocol with time decay-corrected acquisition in WBCS to diagnose osteoarticular infection and to reduce interobserver variability. The role of SPECT/CT in WBCS in locating the infected focus was also evaluated.
Methods110 patients with suspected osteoarticular infection were studied prospectively. Planar images were obtained with time decay-corrected acquisition at 30min, 4h, 8h and 24h.
WBCS planar images were grouped in two protocols:
One-day protocol: experts evaluated 30min, 4h and 8h images. Two-day protocol: experts evaluated 30min, 4h and 24h images. Both protocols were classified as:
- •
Negative: absence of leukocyte migration.
- •
Positive: uptake persisted or increased over time.
- •
Aseptic inflammation: uptake decreased over time.
SPECT/CT was performed in 72 patients.
Kappa index was calculated to evaluate interobserver variability.
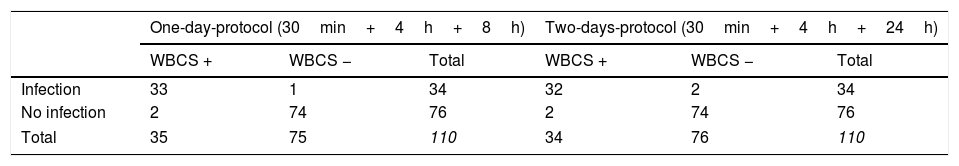
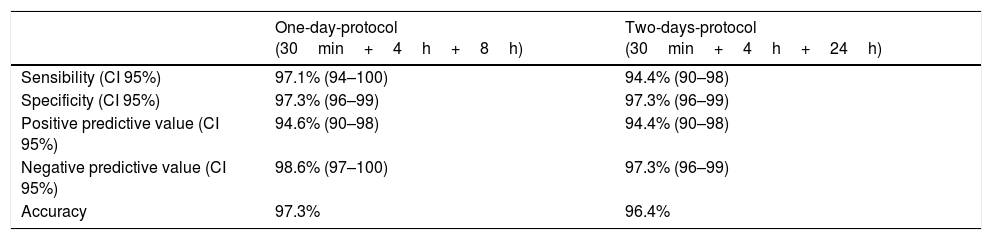
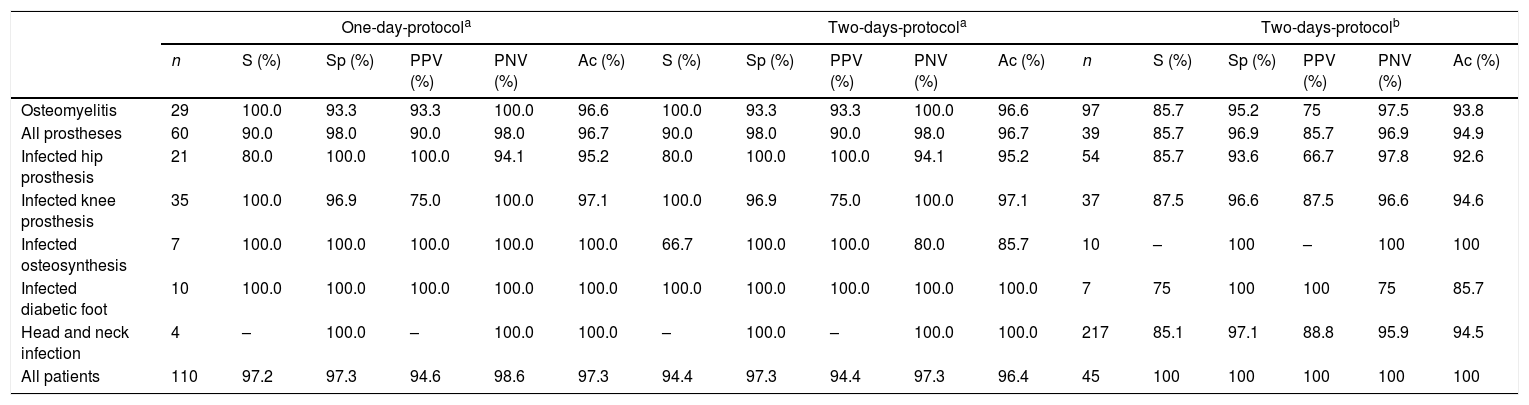
ResultsInfection was confirmed in 34 cases. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and diagnostic accuracy were 97.1%; 97.4%; 94.3%; 98.7% and 97.3% for the one-day protocol and 94.1%; 97.4%; 94.1%; 97.4% and 96.4% for two-days-protocol.
SPECT/CT contributed to diagnosis in 45/50 patients with planar WBCS positive. Kappa index: 0.8 for one-day protocol and 0.79 for two-day protocol, respectively.
ConclusionOne-day protocol with time decay-corrected acquisition WBCS and SPECT/CT enables early and accurate diagnosis of osteoarticular infection.
Resulta difícil determinar la infección osteoarticular y diferenciar entre inflamación e infección mediante procedimientos de laboratorio e imagen (TC, RM, US).
La gammagrafía con leucocitos marcados (GLM) constituye la prueba de medicina nuclear de elección, pero su duración es de dos días, y a veces es difícil diferenciar entre tejido blando e infección, por lo que se produce una variabilidad interobservador que hace disminuir su especificidad.
ObjetivoDemostrar la utilidad del protocolo de un día de GLM con corrección por decaimiento del tiempo de adquisición para diagnosticar la infección osteoarticular y reducir la variabilidad interobservador. También se evaluó la función de SPECT/TC en GLM en la localización del foco de infección.
MétodosSe estudiaron prospectivamente 110 pacientes con sospecha de infección osteoarticular. Se obtuvieron imágenes planares con corrección por decaimiento del tiempo de adquisición a 30min, 4h, 8h y 24h.
Las imágenes planares de GLM se agruparon en dos protocolos:
Protocolo de un día: los expertos evaluaron imágenes de 30min, 4h y 8h. Protocolo de dos días: los expertos evaluaron imágenes de 30min, 4h y 24h. Ambos protocolos fueron clasificados como:
- •
Negativos: ausencia de migración leucocitaria.
- •
Positivos: persistencia o incremento de la captación con el tiempo.
- •
Inflamación aséptica: disminución de la captación con el tiempo.
La SPECT/TC se realizó en 72 pacientes.
Se calculó el índice Kappa para evaluar la variabilidad interobservador.
ResultadosSe confirmó infección en 34 casos. Los valores de sensibilidad, especificidad, valor predictivo positivo, valor predictivo negativo y precisión diagnóstica fueron del 97,1%, 97,4%, 94,3%, 98,7% y 97,3% para el Protocolo de un día, y del 94,1%, 97,4%, 94,1%, 97,4% y 96,4% para el protocolo de dos días, respectivamente.
SPECT/TC contribuyó al diagnóstico en 45 de 50 pacientes con GLM planar positiva. Índice Kappa: 0,8 para el Protocolo de un día y 0,79 para el Protocolo de dos días.
ConclusiónEl Protocolo de un día de GLM con corrección por decaimiento del tiempo de adquisición y SPECT/TC permite el diagnóstico precoz y preciso de la infección osteoarticular.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)