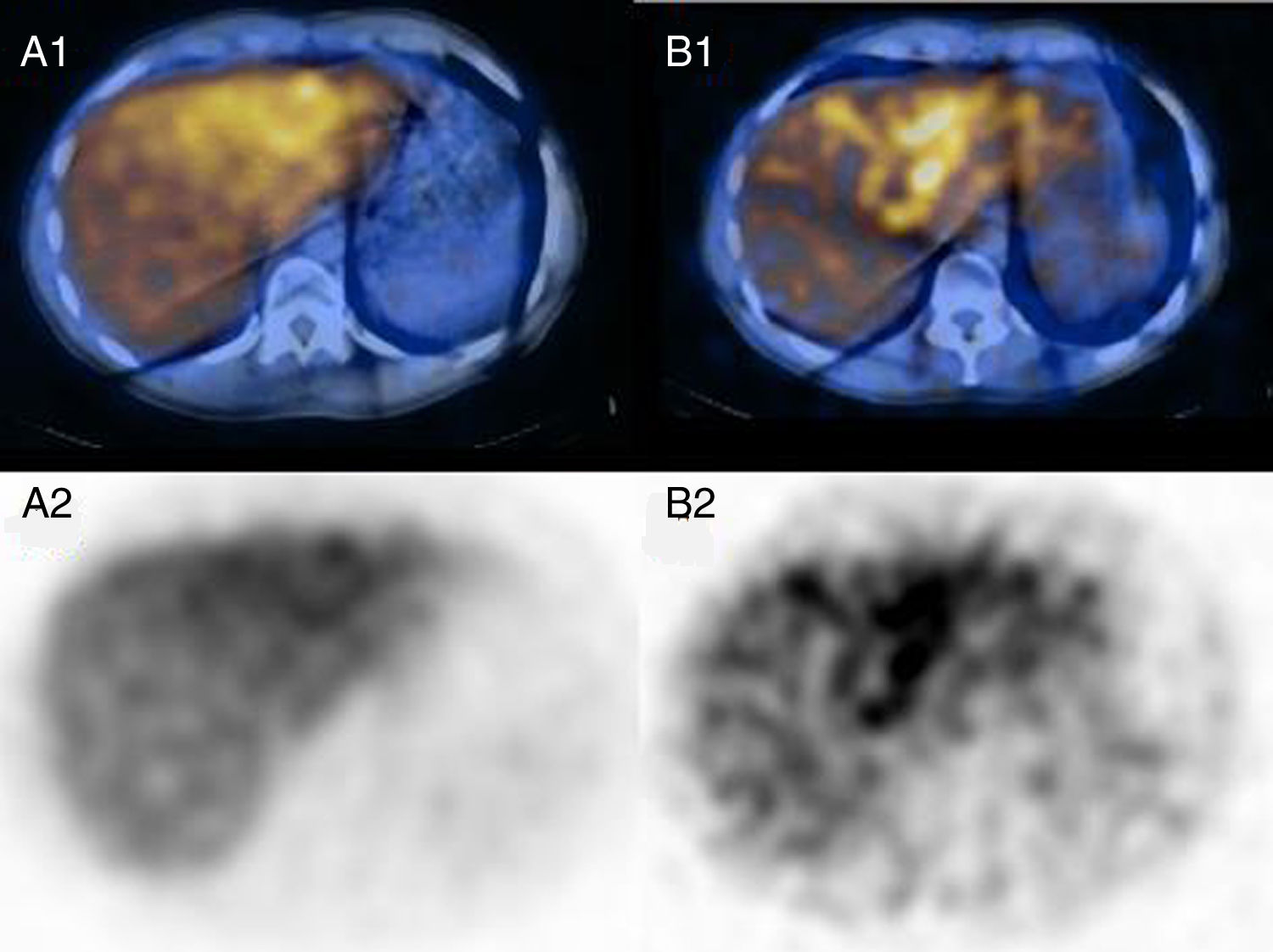
After radiopharmaceutical injection, a heightened 123I-MIBG concentration is frequently observed in the left hepatic lobe compared to the right one, but the reason of this finding remains unknown. Our aim was to retrospectively analyze the different 123I-MIBG uptake pattern between the two hepatic lobes and correlate our results with some epidemiological/clinical features.
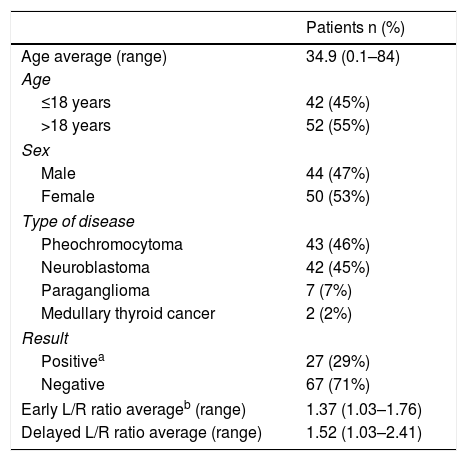
MethodsNinety-four 123I-MIBG scintigraphies from 71 patients were selected. Regions of interest were drawn in the right and left lobes using transverse tomographic sections and left to right activity ratios (L/R ratio) were calculated at 6 and 24h after radiotracer administration.
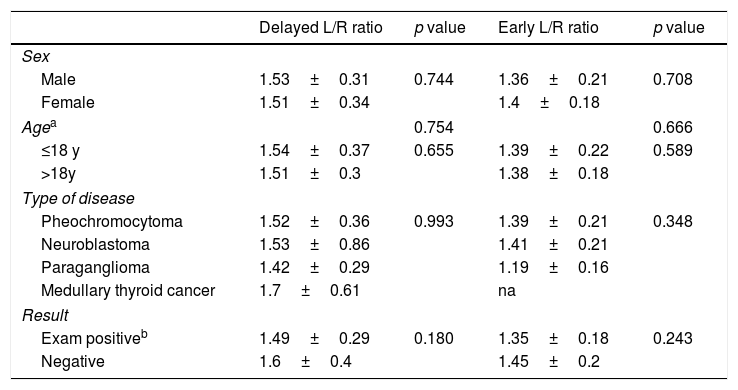
ResultsTwenty-seven examinations were positive for hypermetabolic lesions while the remaining 67 were negative. In all cases mean early and delayed L/R ratios were greater than 1.00; average early L/R ratio was 1.37 and delayed L/R ratio 1.52. The delayed L/R ratio was significantly higher than the early one. There was no difference in the L/R ratios with regard to age, gender, primary disease and result of scintigraphy.
Conclusions123I-MIBG uptake was higher in left hepatic lobe compared to right and this ratio did not correlate with any epidemiological or clinical feature. The reason of this metabolic is not yet explained and some biomolecular hypotheses could be tested in 3D dynamic in vitro models.
Después de la inyección del radiofármaco se observa con frecuencia una concentración incrementada de 123I-MIBG en el lóbulo hepático izquierdo en comparación con el derecho, pero la razón de este hallazgo sigue siendo desconocida. Nuestro objetivo fue analizar retrospectivamente el patrón de absorción de 123I-MIBG entre los dos lóbulos hepáticos y correlacionar nuestros resultados con algunas características epidemiológicas/clínicas.
Material y métodosSe seleccionaron noventa y cuatro gammagrafías 123I-MIBG de 71 pacientes. Las regiones de interés se dibujaron en los lóbulos derecho e izquierdo utilizando secciones tomográficas transversales y se calcularon relaciones de actividad de izquierda a derecha (relación I/D) a las 6 y 24 horas de la administración del radiofármaco.
ResultadosVeintisiete exámenes fueron positivos para lesiones hipermetabólicas, mientras que los 67 restantes fueron negativos. En todos los casos, las relaciones medias de I/D temprana y tardía fueron superiores a 1; la relación I/D temprana media fue de 1,37 y la relación I/D tardía de 1,52. La relación I/D tardía fue significativamente mayor que la precoz. No hubo diferencias en la relación I/D con respecto a la edad, sexo, enfermedad primaria y resultado de la gammagrafía.
ConclusionesLa absorción de 123I-MIBG fue mayor en el lóbulo hepático izquierdo en comparación con el derecho y esta relación no se correlacionó con ninguna característica epidemiológica o clínica. La razón de este metabolismo todavía no se ha explicado, y algunas hipótesis biomoleculares podrían ser probadas en modelos 3D dinámicos in vitro.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)