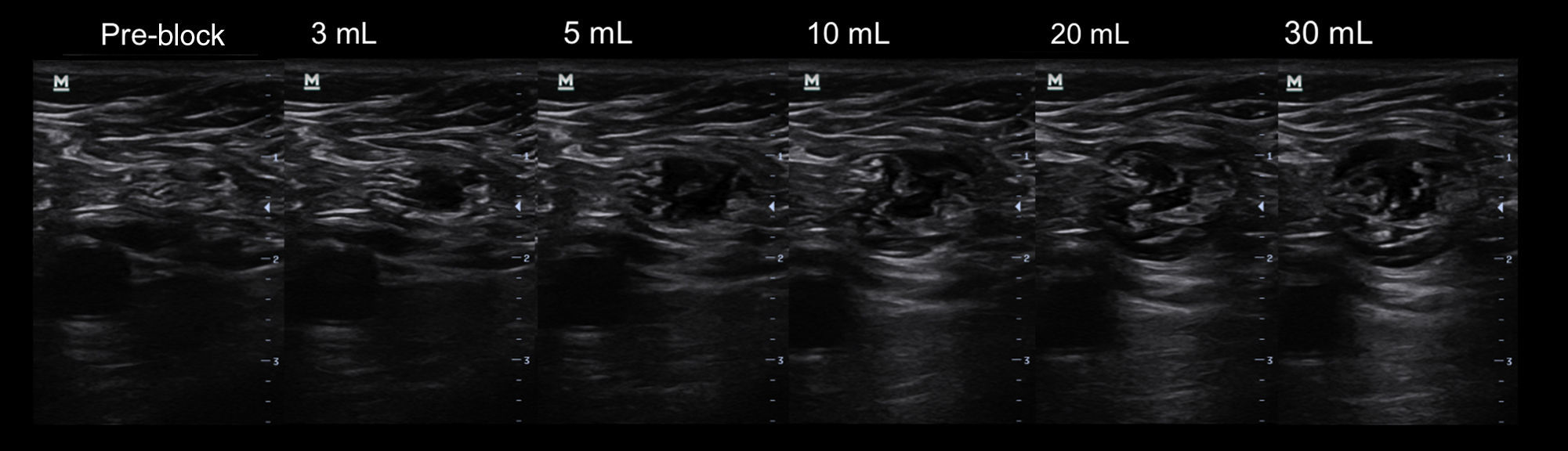
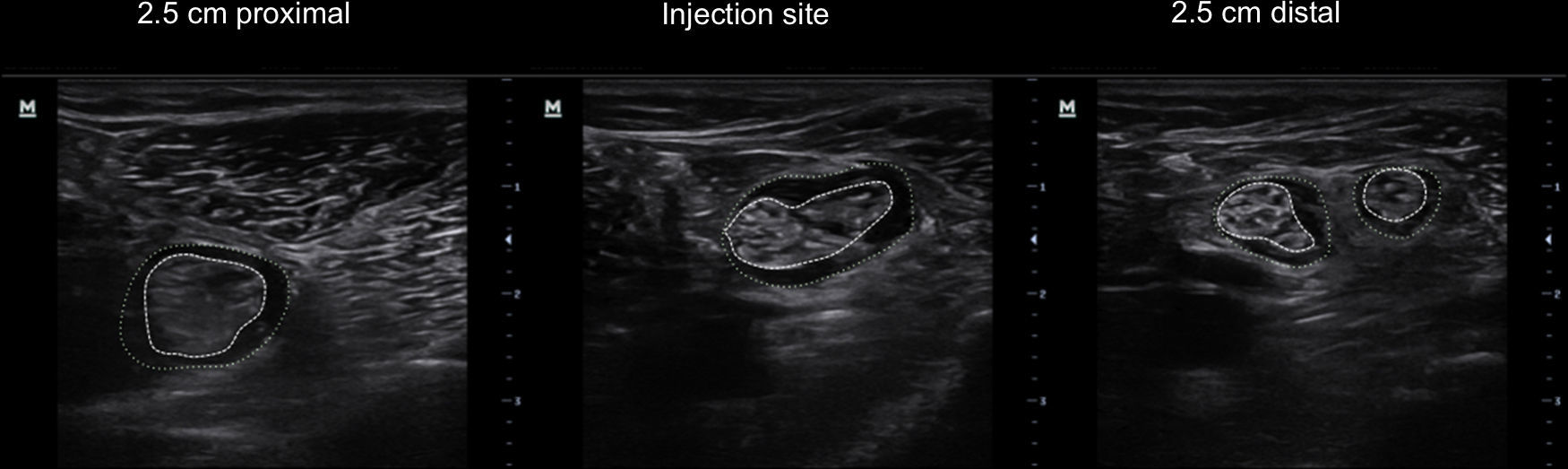
Local anaesthetic injection between the tibial and commmon peroneal nerves within connective tissue sheath results in a predictable diffusion and allows for a reduction in the volume needed to achieve a consistent sciatic popliteal block. Using 3D ultrasound volumetric acquisition, we quantified the visible volume in contact with the nerve along a 5cm segment.
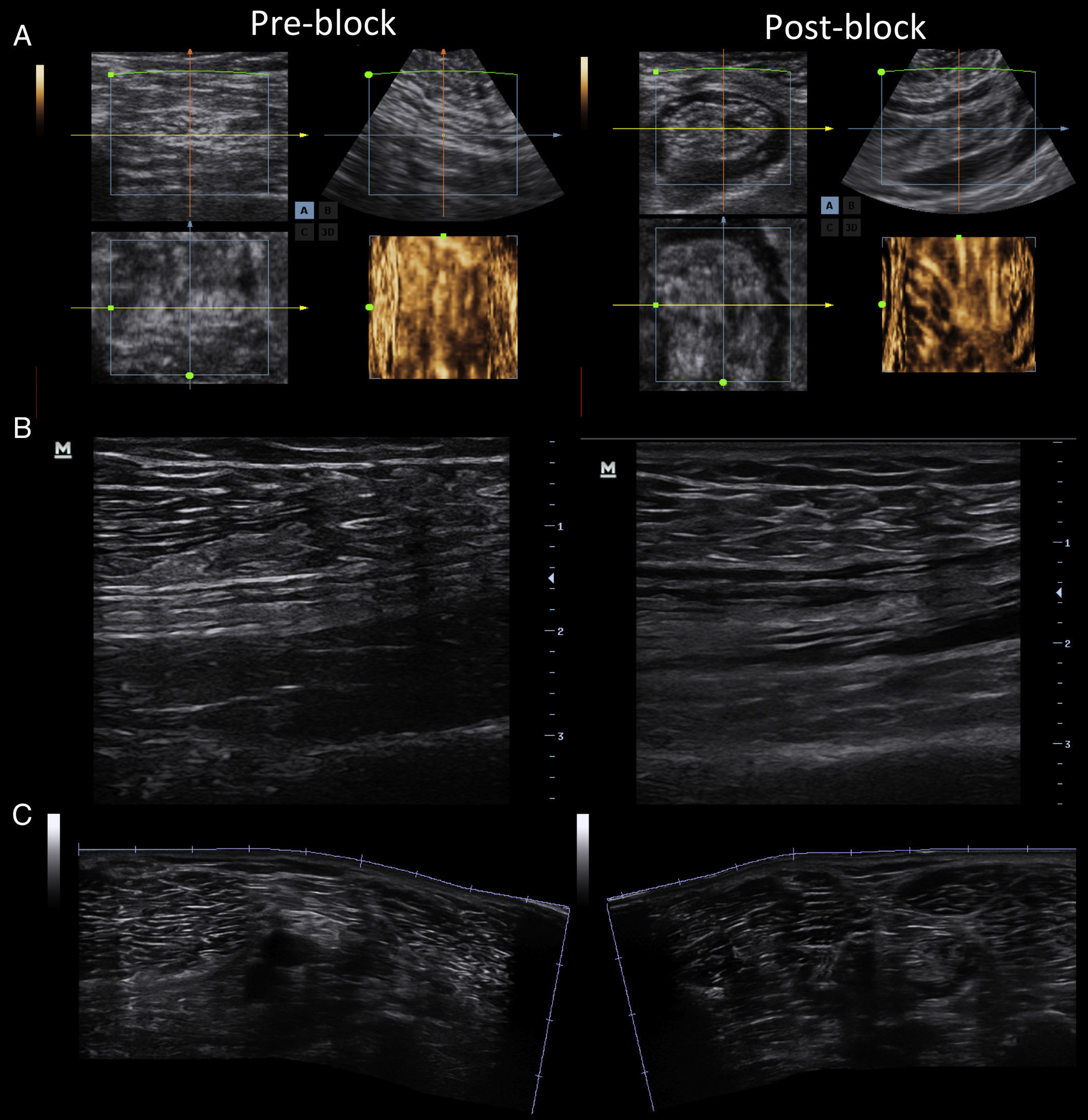
MethodsWe included 20 consecutive patients scheduled for bunion surgery. Ultrasound guided popliteal block was performed using a posterior, out of plane approach at the level of división of the sciatic nerve. Thirty mL of mepivacaine 1.5% and levobupivacaine 0.5% were slowly injected while assessing the injection pressure and the diffusion of the local anaesthetic. Volumetric acquisition was performed before and after the block to quantify the volume of the sciatic nerve and the volume of the surrounding hypoechoic halo contained inside the connective tissue in a 5cm segment.
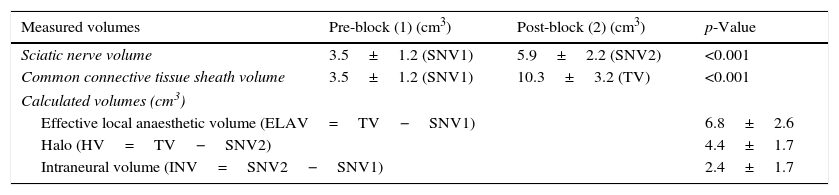
ResultsAll blocks were successful within 20min after the injection. The total estimated volume contained inside the common connective tissue sheath was 6.8±2.6cm3. Of this, the volume of the halo surrounding the nerve was 4.4±1.7cm3 and the volume inside the sciatic nerve was 2.4±1.7cm3.
ConclusionsThe volume of local anaesthetic in close contact with the sciatic nerve can be estimated by volumetric acquisition. Our results suggest that the effective volume of local anaesthetic needed for a successful sciatic popliteal block could be reduced to less than 7mL.
La administración del anestésico local en el tejido conectivo que une los componentes tibial y peroneo del nervio ciático a nivel de su división en el hueco poplíteo produce una distribución muy eficiente de anestésico para conseguir un bloqueo efectivo. Mediante ecografía en 3dimensiones podemos cuantificar este volumen de contacto en una longitud determinada del nervio.
MétodosSe incluyó a 20 pacientes consecutivos programados para cirugía de hallux valgus. En todos los casos se realizó un bloqueo poplíteo ecoguiado en la división del nervio ciático, en abordaje «fuera de plano» con el paciente en decúbito prono. Se administraron 30ml de anestésico local y se evaluó su difusión. Se realizó una adquisición volumétrica del nervio ciático antes e inmediatamente después de finalizar la inyección del fármaco para cuantificar el volumen del nervio ciático y el volumen contenido en el interior del tejido conectivo que envuelve ambos componentes del nervio ciático; todo ello en un segmento de 5cm de nervio.
ResultadosTodos los bloqueos fueron efectivos a los 20min. El volumen de anestésico local contenido en el interior del tejido conectivo fue de 6,8±2,6cm3. De este volumen, 4,4±1,7cm3 se situaban en el halo que envolvía los componentes del nervio y 2,4±1,7cm3 se ubicaban en el interior del nervio ciático o sus componentes.
ConclusionesEl volumen en contacto con el nervio ciático puede ser estimado mediante la adquisición volumétrica. Nuestros resultados indican que el volumen para el bloqueo efectivo del nervio ciático a nivel poplíteo quizás se podrá reducir de forma significativa en un futuro.