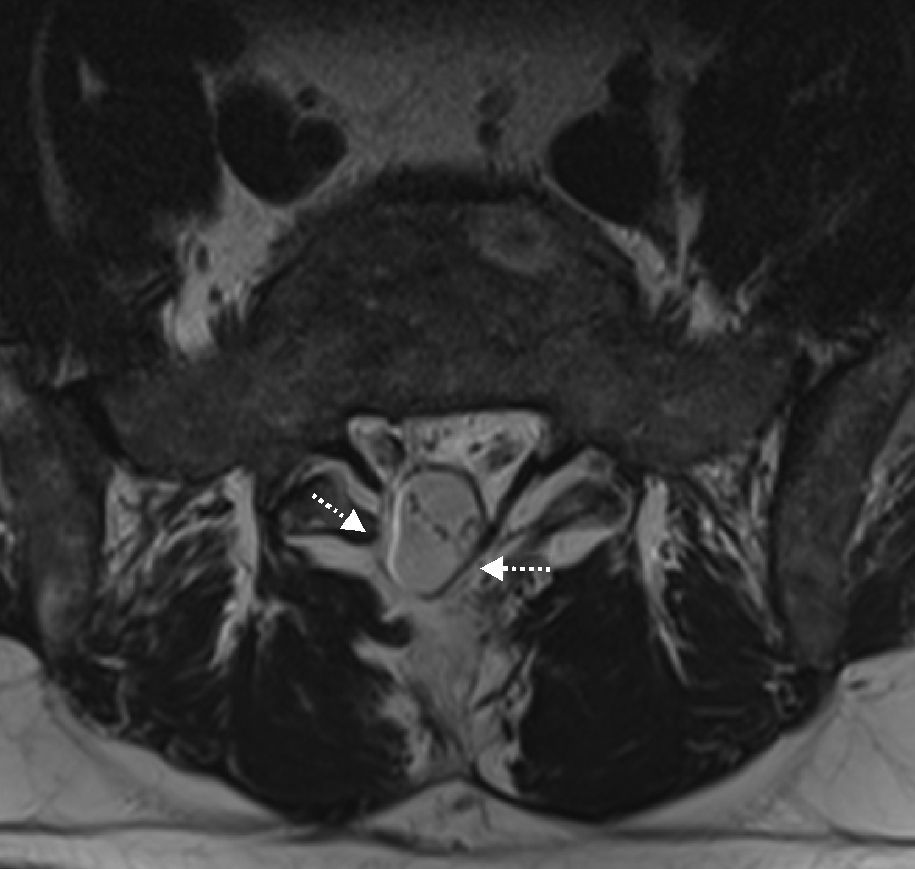
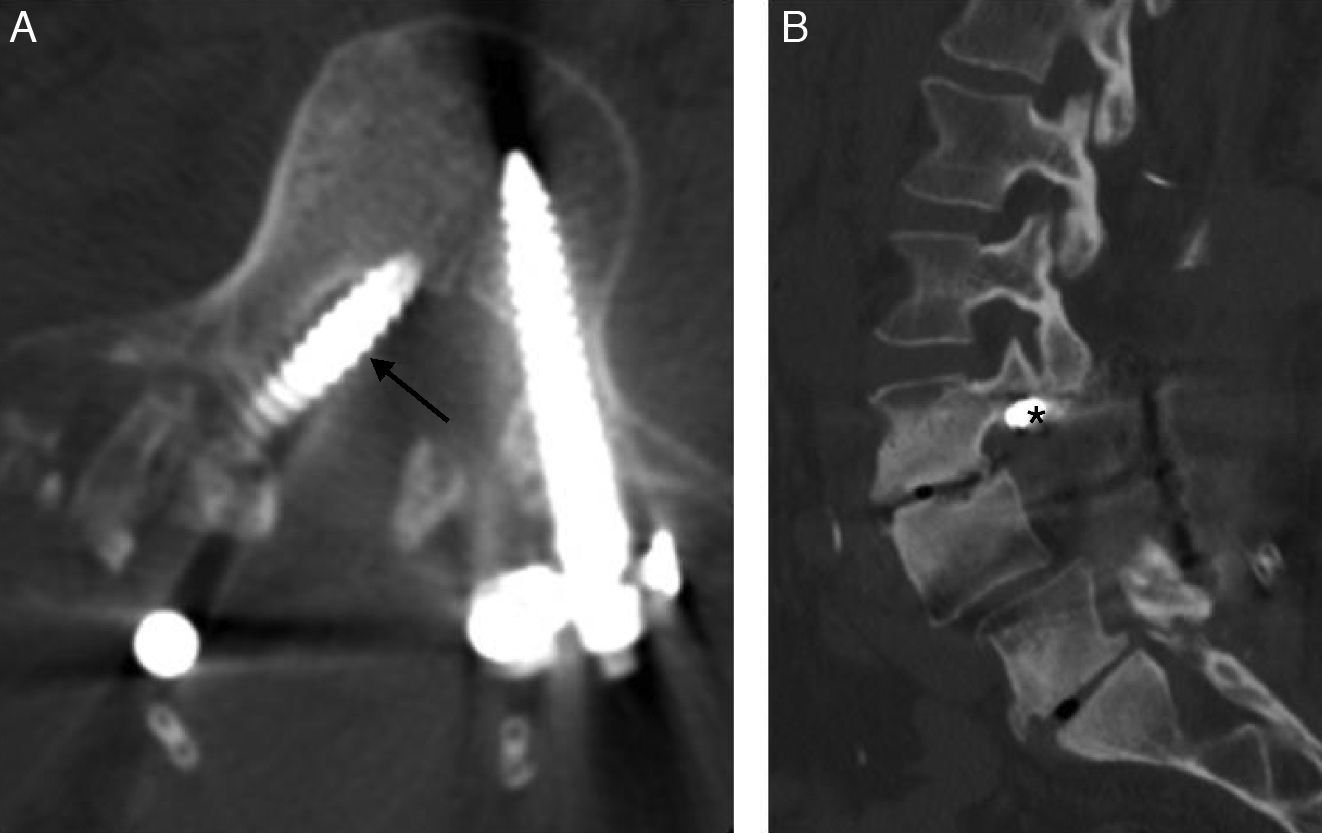
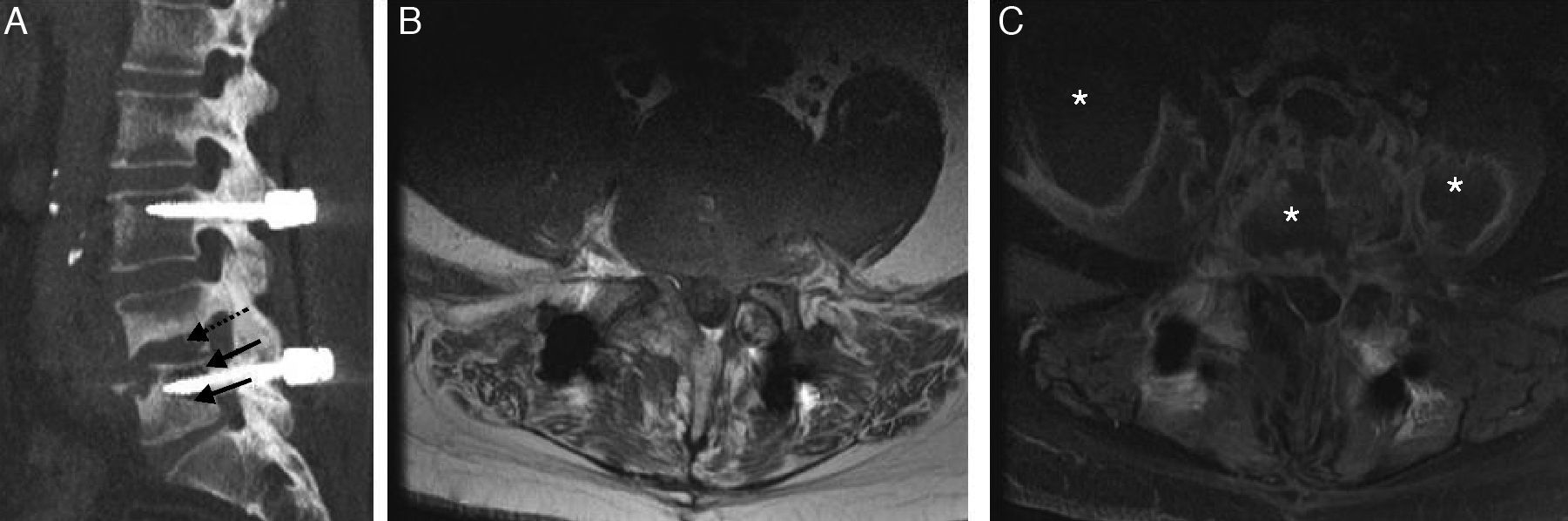
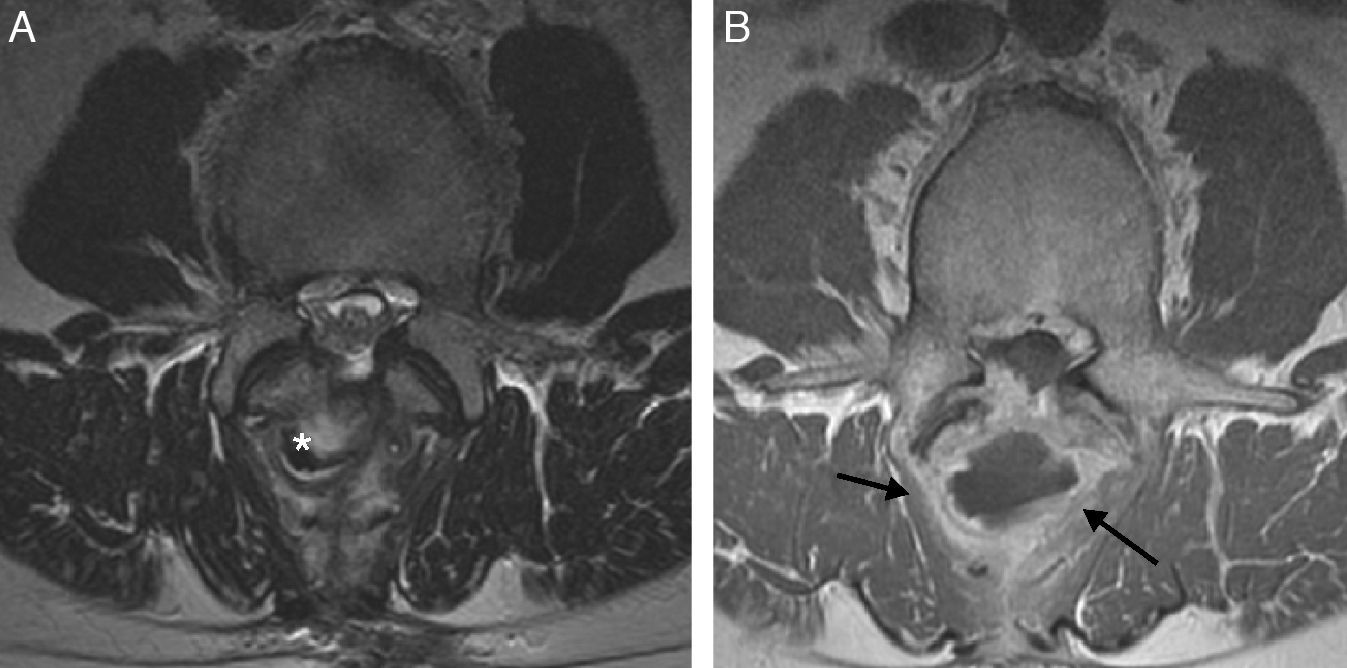
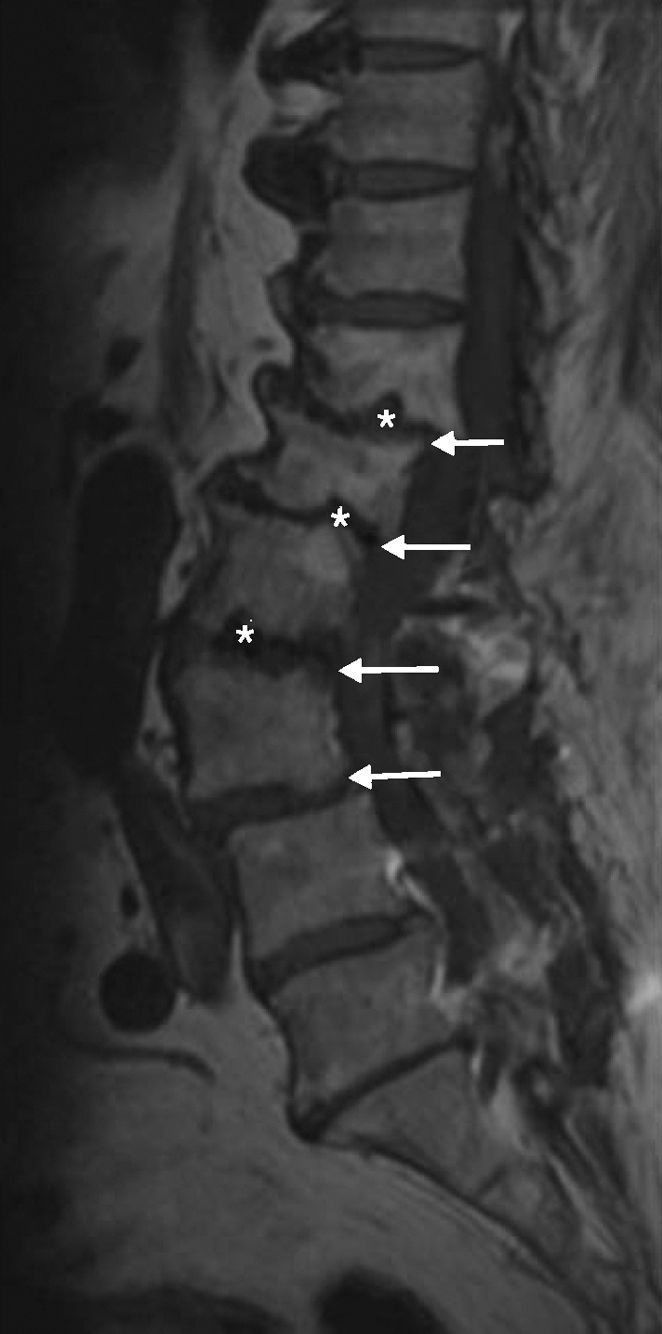
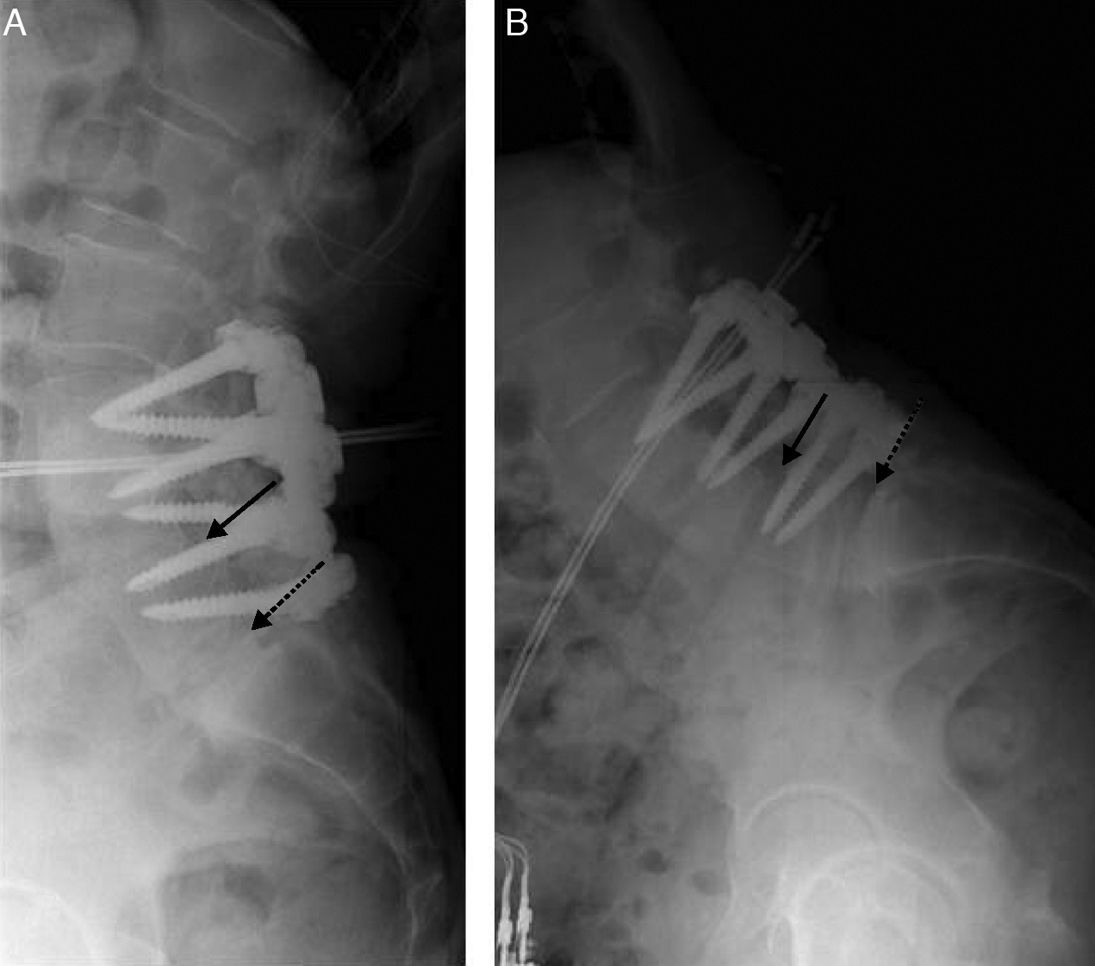
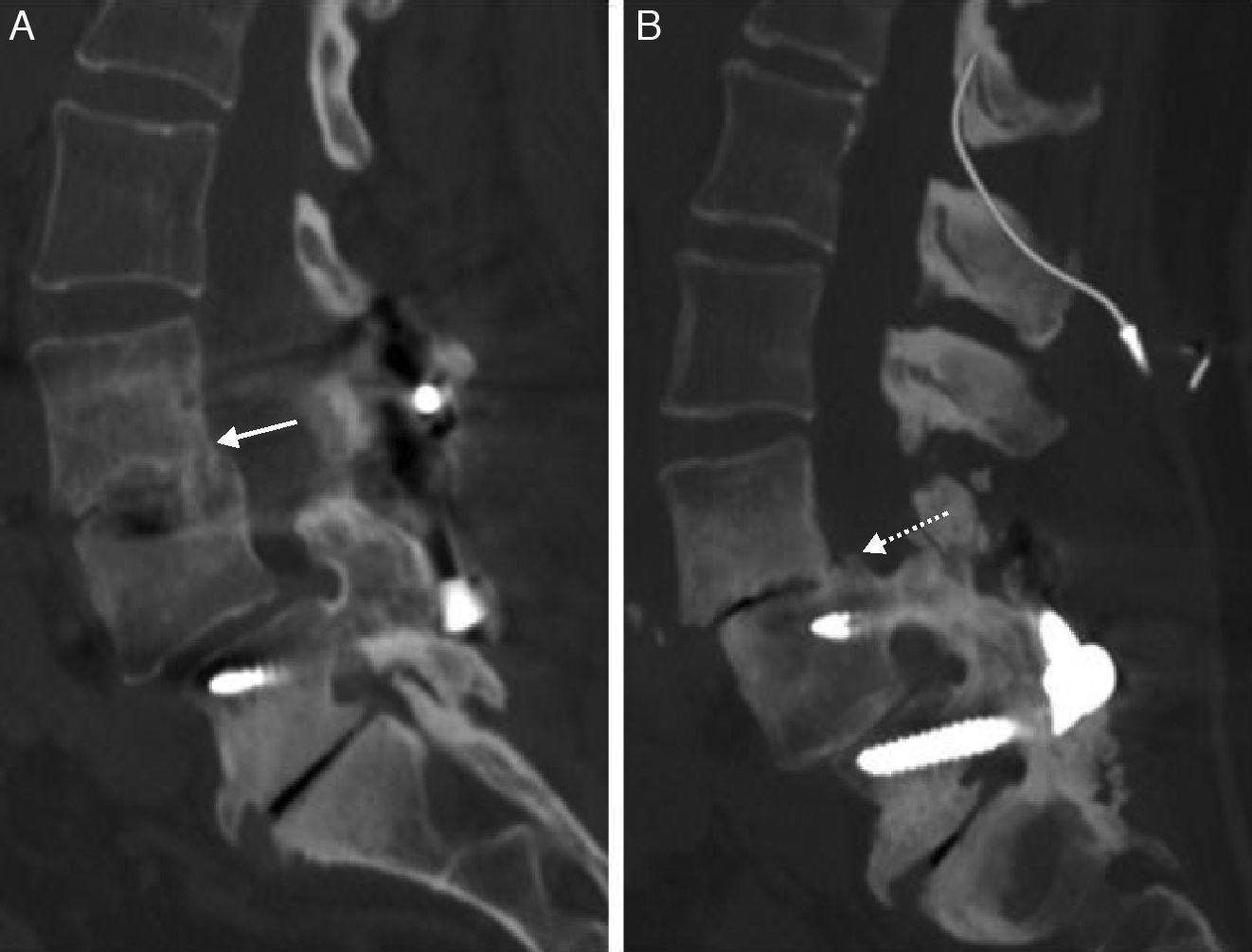
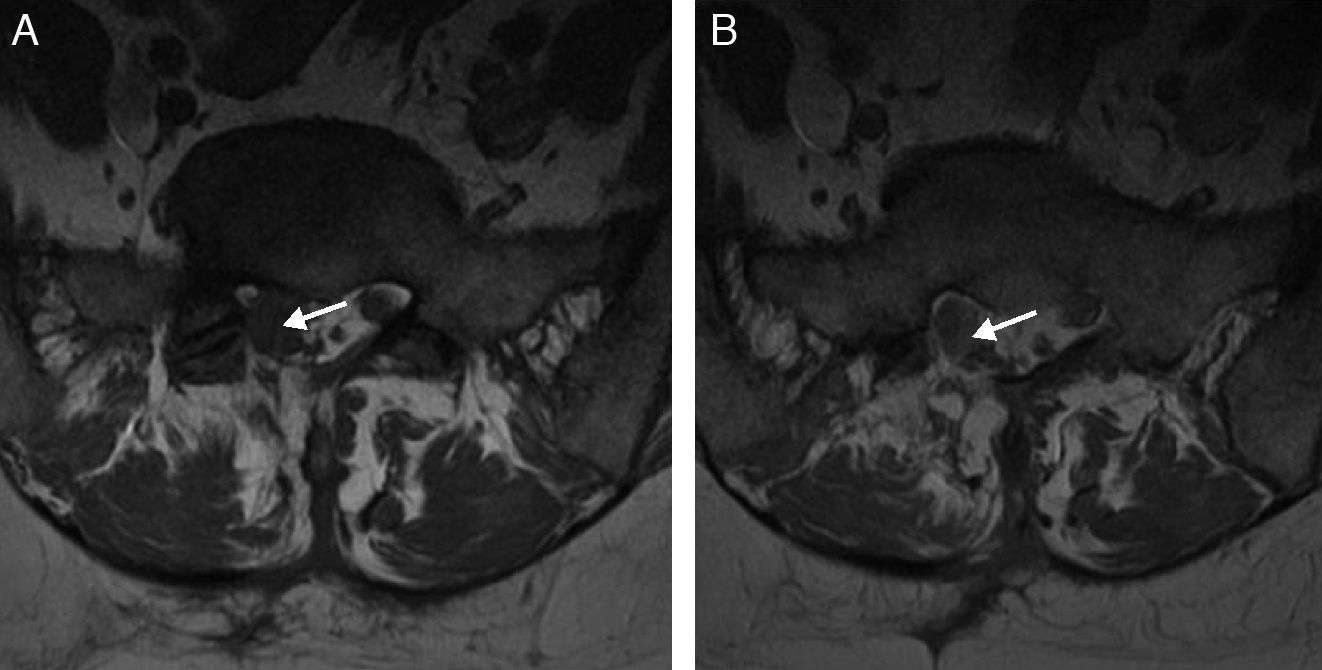
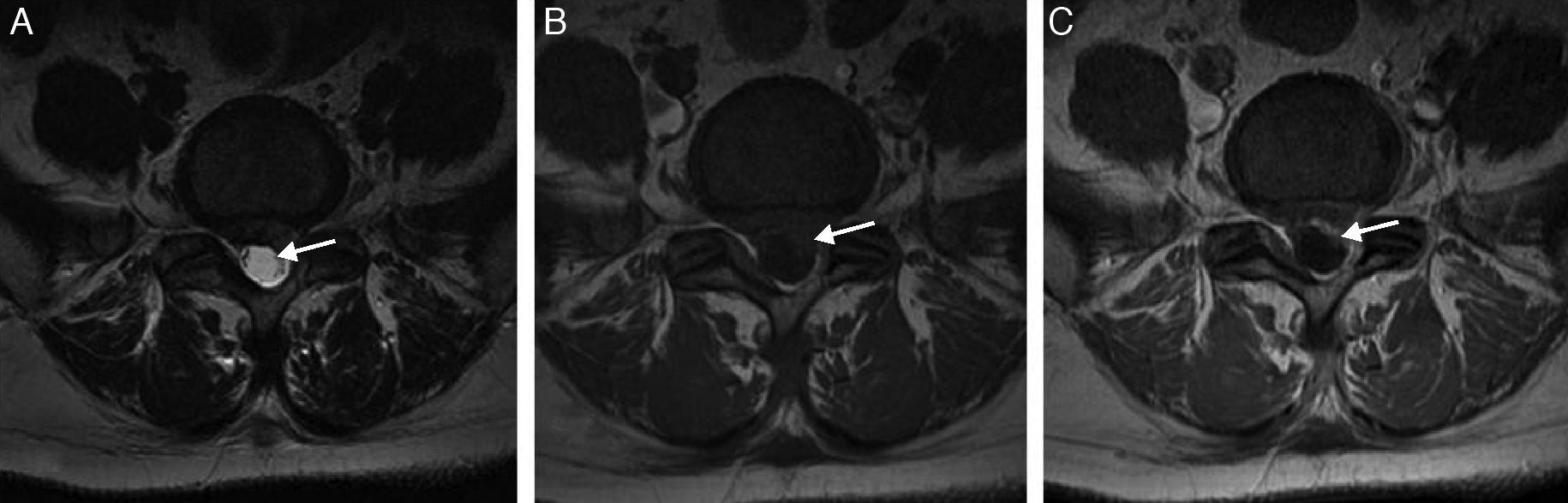
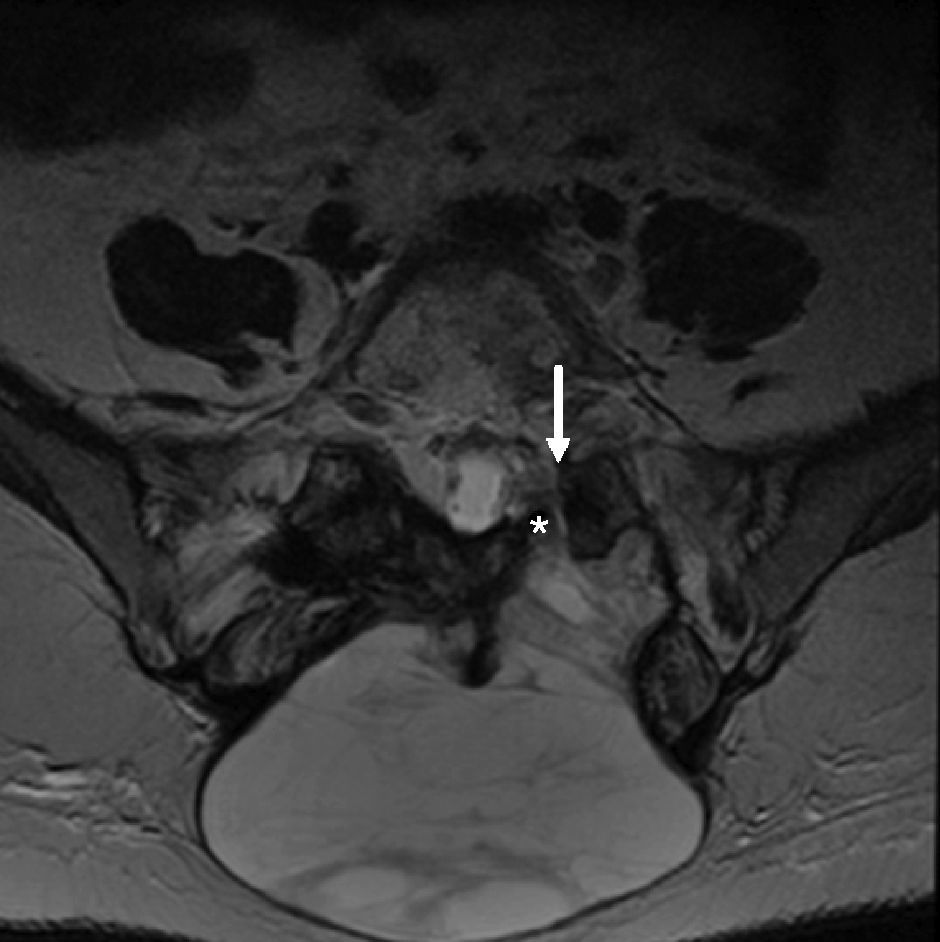
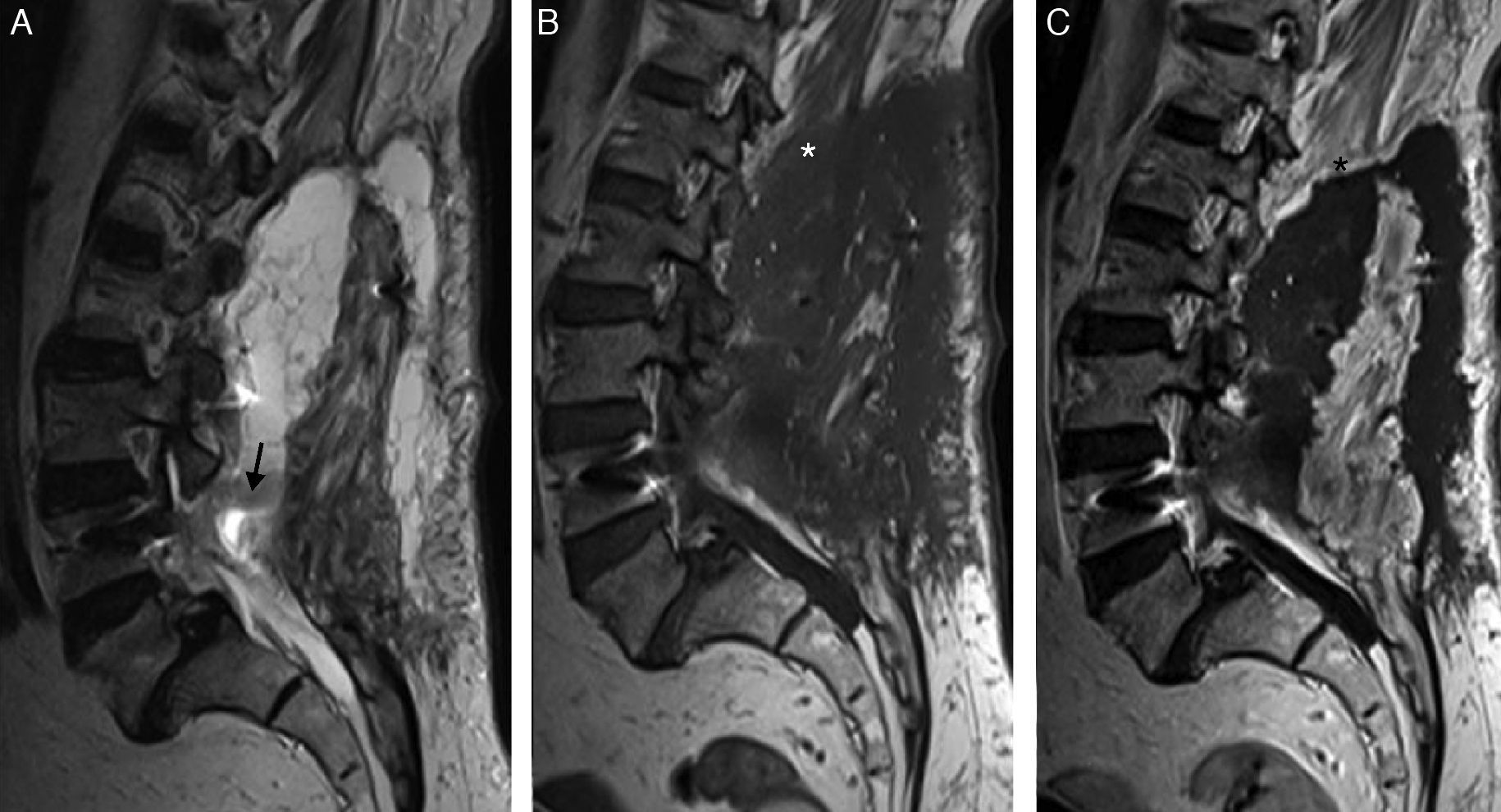
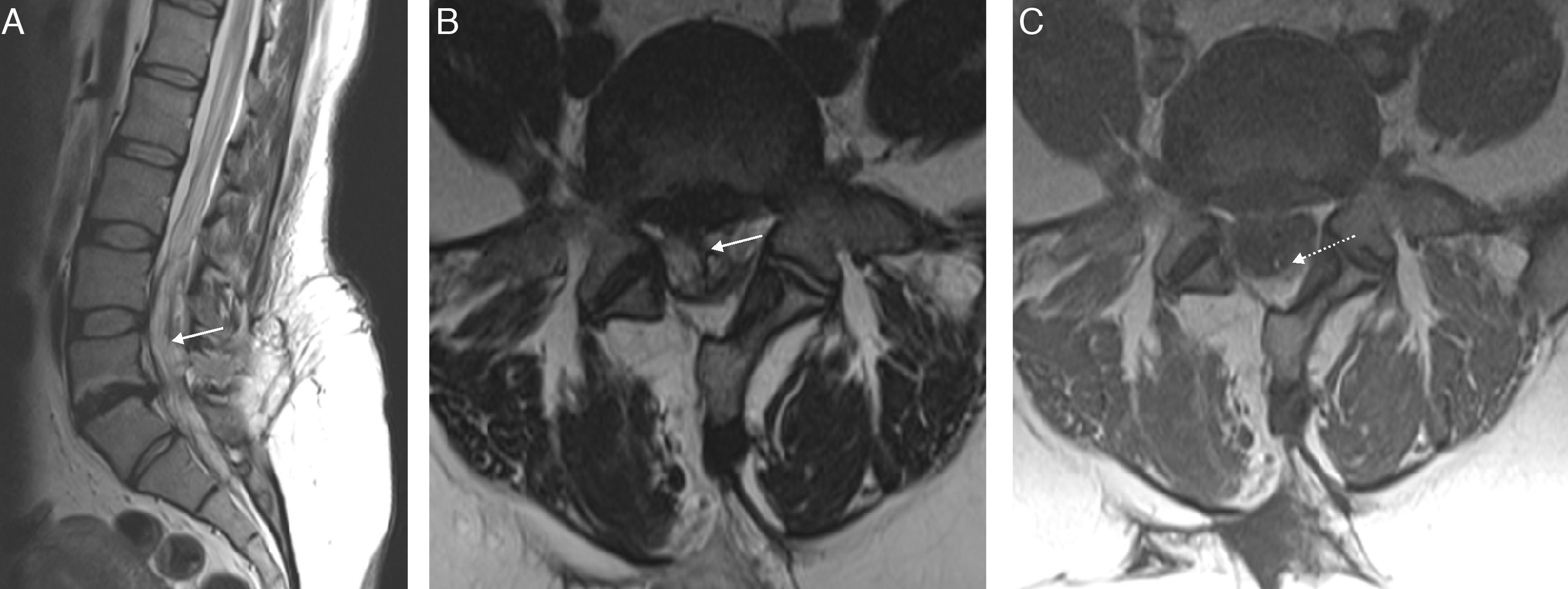
Given the prevalence of low back pain, surgical interventions on the lumbar spine are becoming more common. Among the many surgical procedures available for these interventions, the most common are laminectomy and discectomy. In 10–40% of patients who undergo surgical interventions on the lumbar spine, low back pain is not completely alleviated or it recurs, and these cases fall into the category of “failed back surgery syndrome”. This syndrome can have many different causes and multiple factors are often involved. It is important not to confuse the normal postoperative findings with those specific to failed back surgery syndrome. Deciding which imaging technique to use will depend on the type of surgical intervention, whether metallic orthopedic material was used, and the clinical suspicion. It is essential to know the advantages and limitations of the available imaging techniques to ensure the optimal evaluation of these patients, especially after interventions carried out with instrumentation to minimize the artifacts due to these materials.
Dada la gran prevalencia del dolor lumbar, la cirugía de columna es una intervención cada vez más frecuente. Existen múltiples procedimientos quirúrgicos disponibles, siendo la laminectomía y discectomía las intervenciones más frecuentes. En un 10-40% de los pacientes intervenidos, el dolor lumbar que ocasionó la intervención puede recurrir o no solucionarse completamente, incluyéndose dentro del síndrome de cirugía fallida de columna. Hay múltiples causas que pueden ocasionar este síndrome, siendo frecuentemente de etiología multifactorial y no deben confundirse con los hallazgos normales en columnas postoperadas. La decisión de la técnica de imagen a realizar dependerá del tipo de cirugía, la utilización de material ortopédico metálico y la sospecha clínica. El conocimiento de las ventajas y limitaciones de las distintas técnicas de imagen disponibles es esencial para la óptima valoración de estos pacientes, especialmente tras cirugías con instrumentación donde serán necesarios ajustes técnicos para minimizar el artefacto producido por estos materiales.