Stroke is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in adults and implies high social and health costs. Best Practice Guidelines (BPG) are useful tools for improving patient health outcomes and quality of care.
AimTo evaluate the results of BPG implementation in the care of hospitalised stroke patients.
MethodPre-post quasi-experimental study. Sample: 18 years old or older with a stroke diagnosis admitted to Albacete General Hospital. Duration or Timeline: Baseline measurement (T0; December 2014); Implementation start (T1; October–December 2015); Consolidation (T2; January–December 2016). Variables: Independent; implementation of the guideline “Stroke assessment across the continuum of care”.
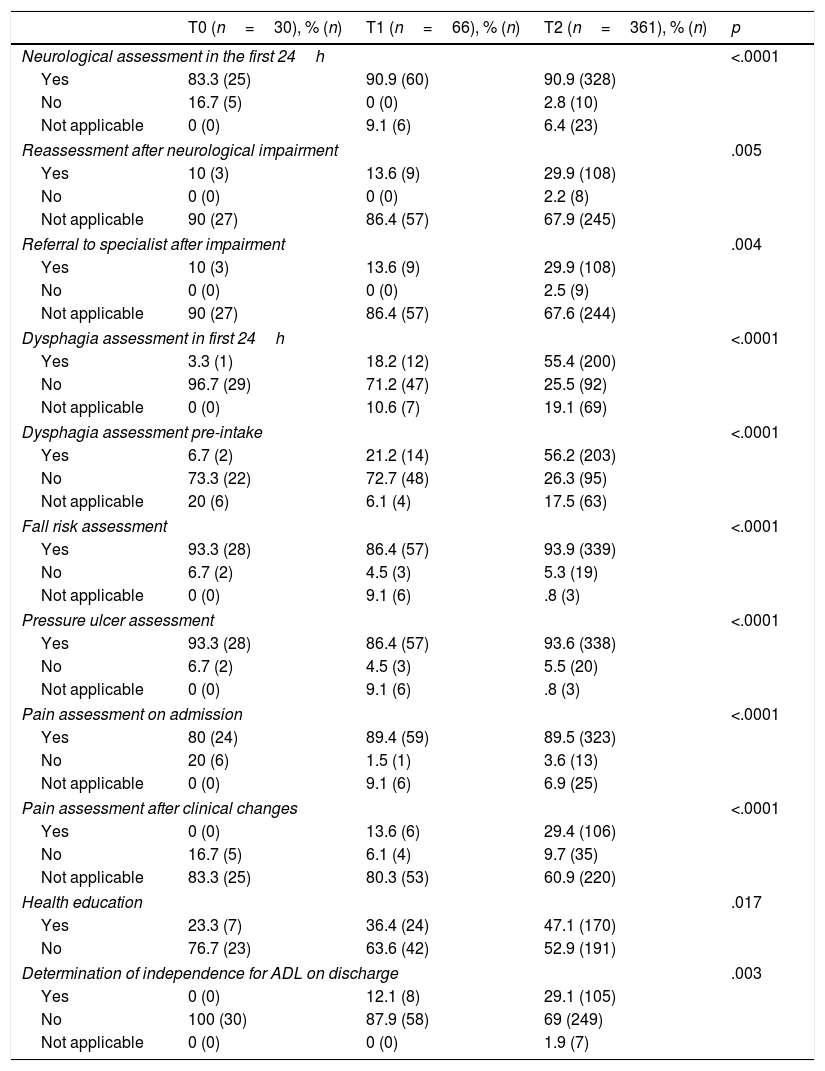
Results(i) Implementation process: neurological assessment, dysphagia, fall risk, pain detection, pressure ulcer development risk (PUD), health education. (ii) Patient results: Aspiration pneumonia, falls, independence for basic activities of daily life (ADL), PUD, pain.
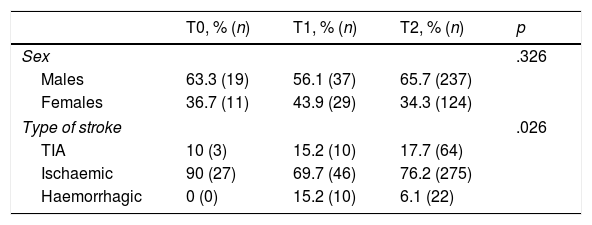
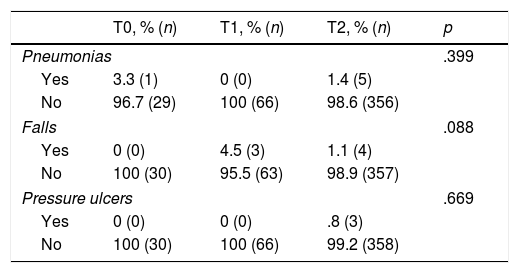
Results457 patients (30 T0, 66 T1, 361 T2). 64.1% men, mean age 68.8years; ischaemic stroke 76.1%, 16.8% transient ischaemic attack (TIA), and 7% haemorrhagic. There were no statistically significant differences in age, sex and independence for ADL between periods, but there were regarding types of stroke diagnoses. There were significant improvements in all process variables per period. The patient results were: 6 pneumonias, 3 PUD and 7 falls; 54.5% patients had ADL independence at discharge.
ConclusionsThere were good implementation results of all recommendations, detecting possibilities of improvement in dysphagia assessment and independence assessment at discharge, providing healthcare education and filling of records.
El ictus es una causa importante de morbimortalidad en adultos y supone un elevado coste sociosanitario. Las Guías de Buena Práctica Clínica (GBP) son herramientas útiles para mejorar los resultados en salud de los pacientes y la calidad de los cuidados.
ObjetivoEvaluar los resultados de implantación de una GBP para la atención de pacientes con ictus hospitalizados.
MétodoEstudio cuasi-experimental pre-post. Mayores de 18 años ingresados en el Complejo Hospitalario Universitario de Albacete con diagnóstico de ictus. Periodos: Medición basal (T0; diciembre 2014); Inicio implantación (T1; octubre-diciembre 2015); Consolidación (T2; enero-diciembre 2016). Variables: Independiente: Implantación de la guía «Valoración del ictus mediante atención continuada». Variables de resultado: a)Proceso implantación: Valoración neurológica, disfagia, riesgo caídas, detección dolor, riesgo lesión por presión (LPP), educación sanitaria. b)Sobre el paciente: Neumonía por aspiración, caídas, independencia para actividades básicas de la vida diaria (ABVD), LPP, dolor.
ResultadosUn total de 457 pacientes (30 T0; 66 T1; 361 T2); 64,1% hombres, edad media 68,8años; ictus isquémicos 76,1%, 16,8% AIT y 7% hemorrágicos. No existieron diferencias estadísticamente significativas en edad, sexo e independencia para las ABVD entre periodos, sí respecto al tipo de ictus. En todas las variables de proceso se produjeron mejoras significativas por periodos. Como resultados en pacientes se produjeron 6 neumonías, 3 LPP y 7 caídas; un 54,5% eran independientes para las ABVD al alta.
ConclusionesExisten buenos niveles de implantación de todas las recomendaciones, detectando posibilidades de mejora en valoración de disfagia e independencia al alta, proporcionar educación sanitaria y sobre la cumplimentación de registros.
Article
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEDENE, (https://sedene.com/revista-de-sedene/ ) y autentifíquese.