Journal Information
Vol. 118. Issue 1.
Pages 10-12 (January 2002)
Vol. 118. Issue 1.
Pages 10-12 (January 2002)
Indicaciones y rendimiento diagnóstico de la punción lumbar en urgencias
Indications and diagnosis efficiency of lumbar puncture in the Emergency Department
Visits
4559
This item has received
Article information
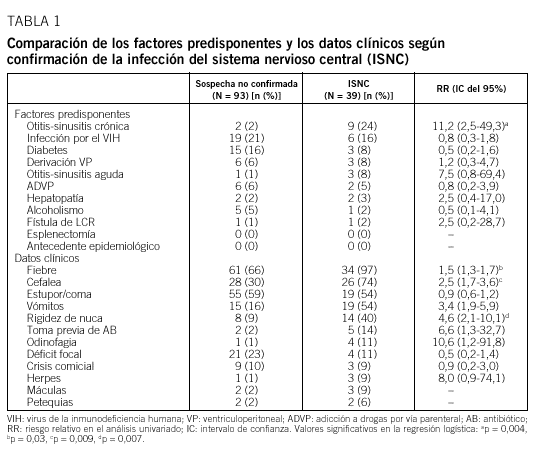
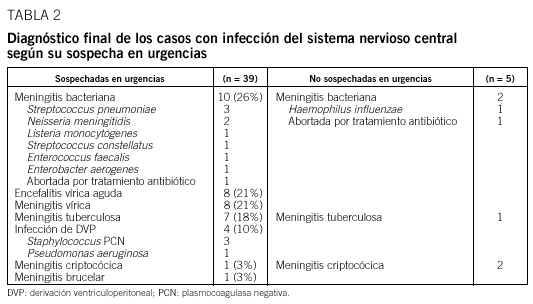
Fundamento: Conocer la frecuencia con que se realiza la punción lumbar (PL) en urgencias y sus indicaciones, así como su rendimiento diagnóstico en la sospecha de infección del sistema nervioso central (ISNC). Pacientes y Método: Se analizaron las punciones practicadas durante dos años en un servicio de urgencias, comparando las características clínicas de los casos en que la PL confirmó o no la sospecha de infección. Se revisaron los casos de ISNC no sospechados en urgencias. Resultados: En el 0,4% de las urgencias médicas se practicó un PL. En el 76% la indicación fue sospecha de ISNC, de las cuales se confirmaron el 30%. Fiebre, cefalea, rigidez de nuca y antecedentes de otitis o sinusitis crónica fueron las variables asociadas a ISNC. Un 11% de las ISNC no se sospecharon en urgencias, y de ellas el 80% tenían el antecedente de infección por el VIH. Conclusiones: La PL se realiza frecuentemente en urgencias, fundamentalmente por sospecha de ISNC, que se confirma en un tercio de los casos. La ISNC no sospechada en urgencias corresponde mayoritariamente a meningitis subagudas en pacientes con infección por el VIH.
Palabras clave:
Urgencias
Punción lumbar
Infección del sistema nervioso central
Background: To know the frequency, indications and diagnosis efficiency of lumbar puncture (LP) in the Emergency Department (ED) when suspecting a central nervous system (CNS) infection. Patients and method: We analyzed all the LP performed over a 2-year period in the ED. We compared the clinical characteristics of patients with and without CNS infection. We also reviewed all the cases of CNS infection diagnosed in the hospital in the same period. Results: A LP was performed in 0.4% of emergencies. In 76% of cases, it was performed because of CNS infection suspicion, which was confirmed in 30% of cases. Fever, headache, nuchal rigidity and chronical otitis were all clinical variables associated with CNS infection. An 80% of CNS infections that were not diagnosed in the ED corresponded to HIV-infected patients. Conclusions: Lumbar puncture is frequently performed in the ED, mostly for suspicion of CNS infection, which is eventually confirmed in one third of cases. CNS infection cases which have not been suspected in the ED usually correspond to a subacute meningitis in a HIV-infected patient.
Keywords:
Emergency
Lumbar punction
Central nervous system infections
These are the options to access the full texts of the publication Medicina Clínica
Subscriber
Subscribe
Purchase
Contact
Phone for subscriptions and reporting of errors
From Monday to Friday from 9 a.m. to 6 p.m. (GMT + 1) except for the months of July and August which will be from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m.
Calls from Spain
932 415 960
Calls from outside Spain
+34 932 415 960
E-mail