There are no data on the incidence of admissions associated with alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS) or about its trend over time in Spain.
ObjectiveTo analyze the characteristics, incidence rates and trends over time of hospital admissions associated with AWS in Spanish public hospitals.
Material and methodAnalysis from the Spanish public hospitals minimum basic data set of hospital admissions with AWS (CIE9-MC 291.81), alcohol withdrawal delirium (CIE9-MC 291.0) and alcohol withdrawal hallucinosis (CIE9-MC 291.3), since 1999 to 2010.
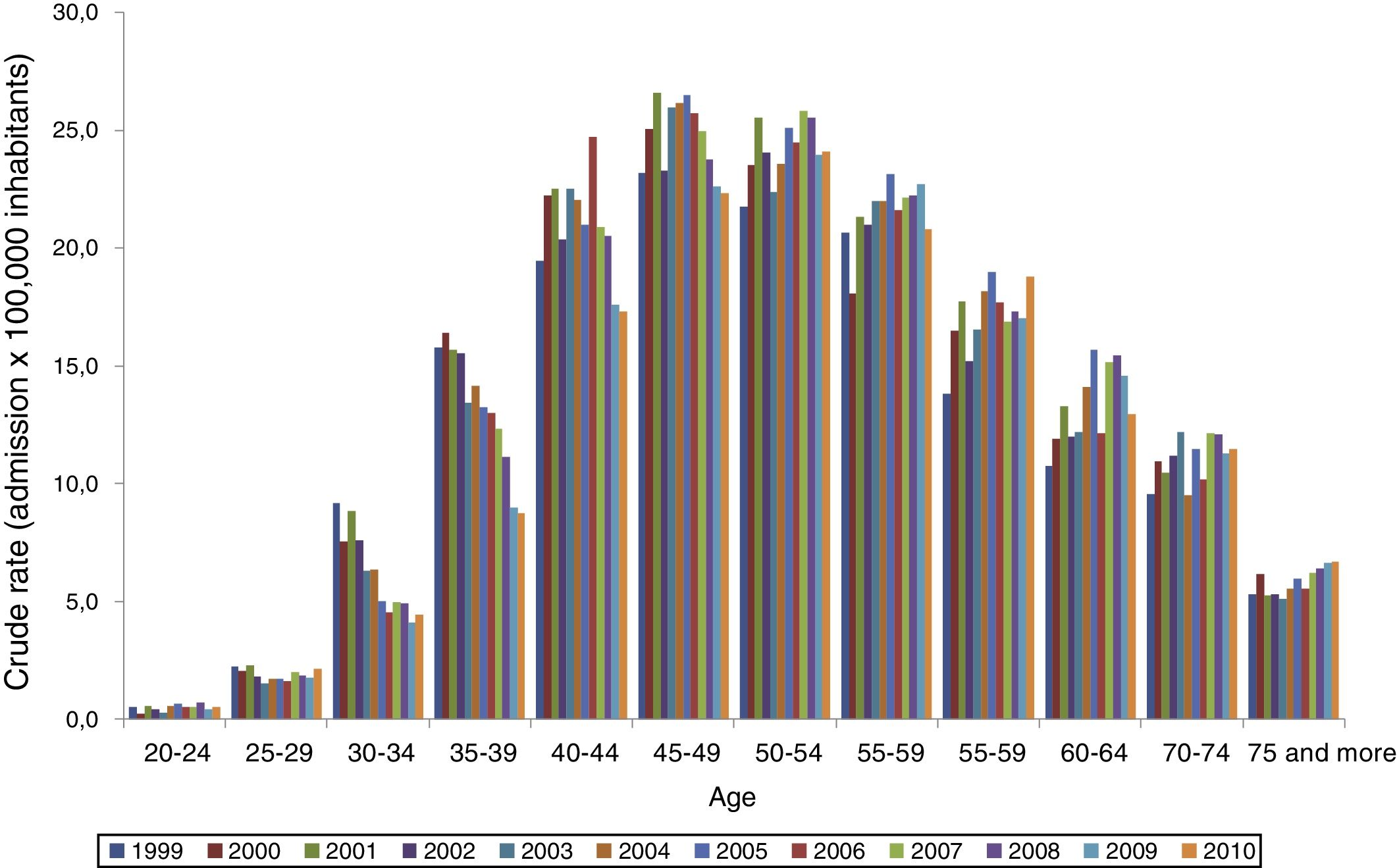
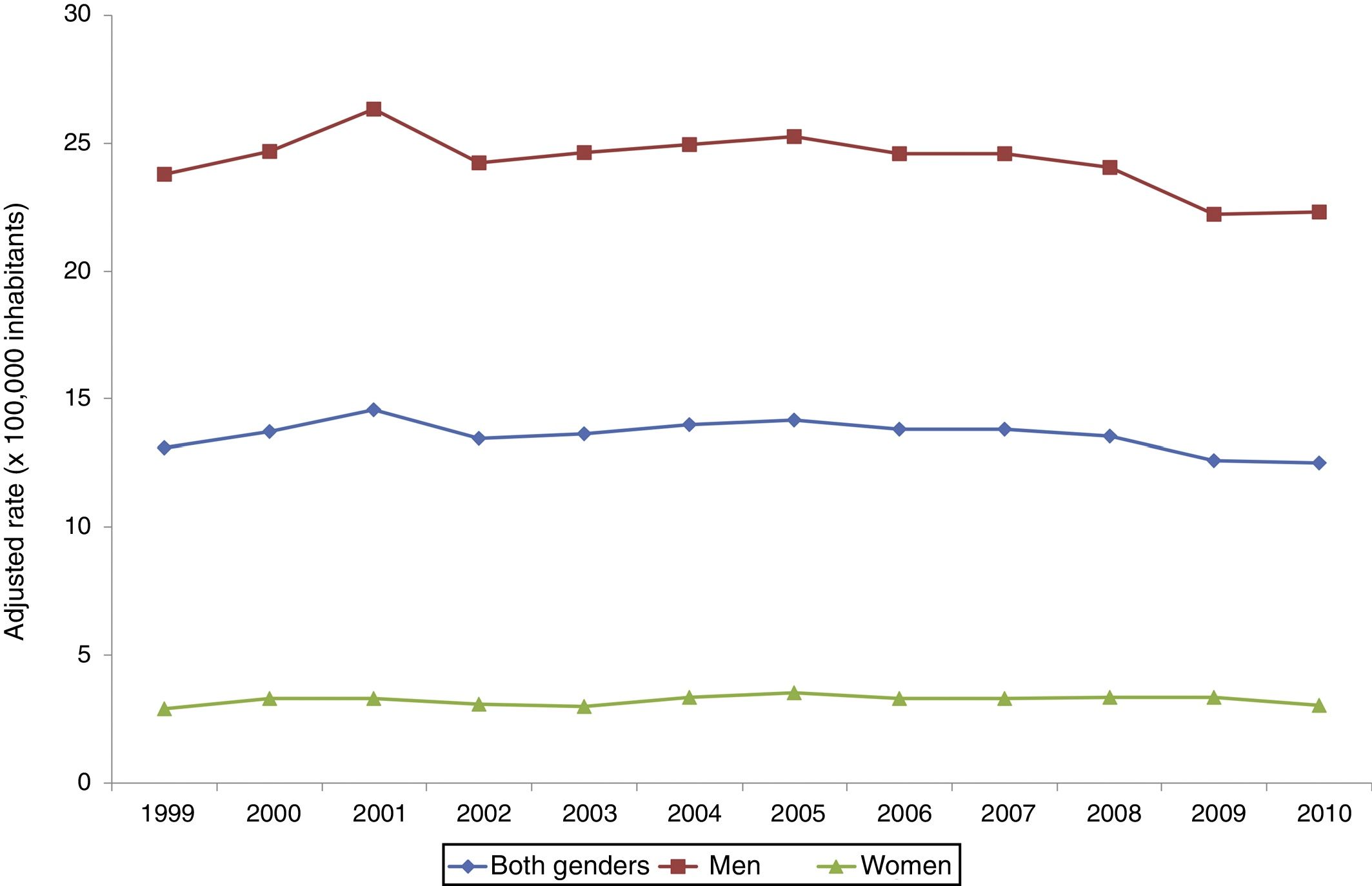
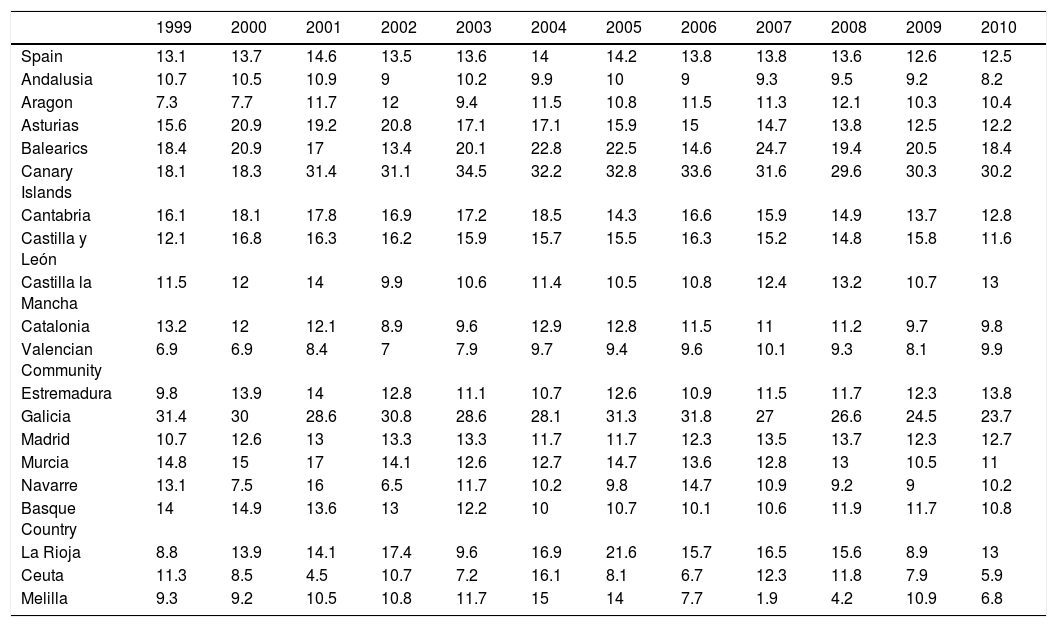
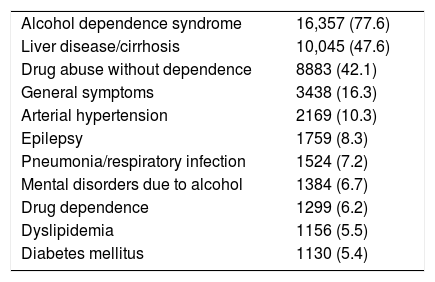
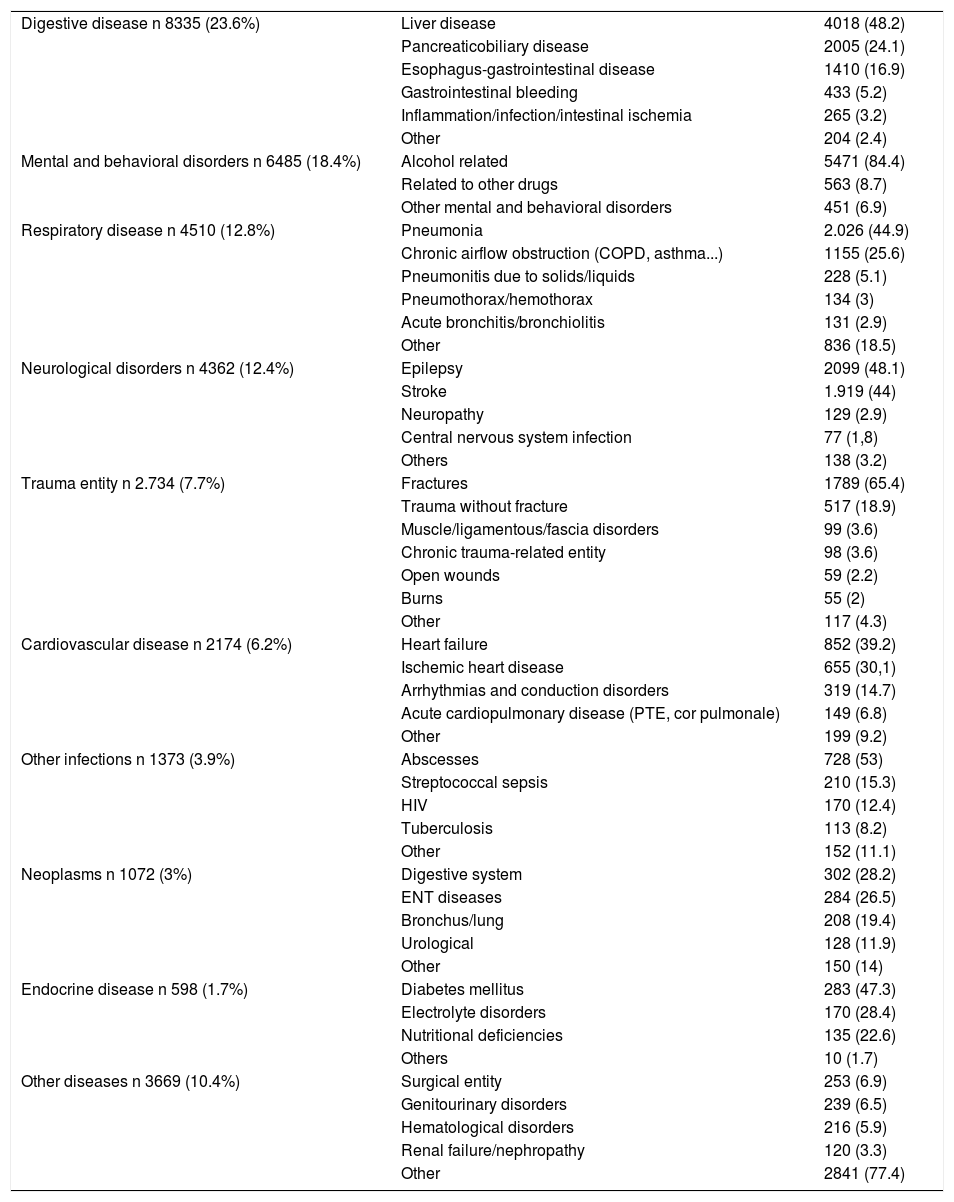
ResultsWe identified 56,395 admissions associated with AWS. Mean age was 50.9 (SD 12.5) and 88% were male. The most frequent admission department was Internal Medicine (24.9%). The mean hospital stay was 12.6 days (SD 14.4) and mortality was 4.7%; 62.6% of cases developed AWS during an admission for another reason, mostly due to alcohol-related pathologies. Secondary diagnoses in patients hospitalized for AWS were related to alcohol consumption in more than half of the cases. The incidence rate of admissions associated with AWS in Spain remained stable from 1999 to 2010, with a small decline in the last 3 years of the period. The communities with the highest incidence were the Canary Islands, the Balearic Islands and Galicia.
ConclusionsThe incidence rate of admissions associated with AWS in Spanish public hospitals in the period 1999–2010 has remained stable with slight changes. There are differences in the incidence of AWS among the different autonomous communities.
No existen datos acerca de la incidencia de ingresos asociados a síndrome de abstinencia alcohólica (SAA) ni sobre su evolución en los últimos años en España.
ObjetivosAnalizar las características, tasas de incidencia y tendencia evolutiva de los ingresos hospitalarios asociados a SAA en hospitales públicos españoles.
Material y métodoAnálisis de la base de datos del CMBD de hospitales públicos españoles de los ingresos hospitalarios con SAA (CIE9-MC 291.81), delirio por abstinencia alcohólica (CIE9-MC 291.0) o alucinosis por abstinencia alcohólica (CIE9-MC 291.3), entre los años 1999 y 2010.
ResultadosSe registraron 56.395 ingresos asociados a SAA. La edad media fue de 50,9 años (DE 12,5) y el 88% eran hombres. El servicio de ingreso más frecuente fue Medicina Interna (24,9%). La estancia media global fue de 12,6 días (DE 14,4) y la mortalidad del 4,7%. El 62,6% desarrollaron SAA durante un ingreso por otro motivo, en su mayoría por enfermedades relacionadas con el alcohol. Los diagnósticos secundarios en pacientes que ingresaron por SAA tenían relación directa o indirecta con el consumo de alcohol en más de la mitad de los casos. La tasa de incidencia de ingresos en España asociados a SAA se mantuvo estable entre 1999 y 2010, con un ligero descenso en los 3 últimos años del periodo. Las comunidades con mayor incidencia fueron Canarias, Baleares y Galicia.
ConclusionesLa incidencia de ingresos asociados a SAA en hospitales públicos españoles se ha mantenido estable con pequeñas modificaciones en el periodo 1999–2010. Existen diferencias en la incidencia de ingresos asociados a SAA entre las diferentes comunidades autónomas.