The portable COPD-6 device has been validated as a screening tool for airflow obstruction through the quantification of the FEV1/FEV6 ratio. To date, however, the impact of body mass index (BMI) on its ability to predict airflow obstruction has not been evaluated. The aim of the study was to assess the predictive ability of COPD-6 to detect airflow obstruction based on the patient's BMI.
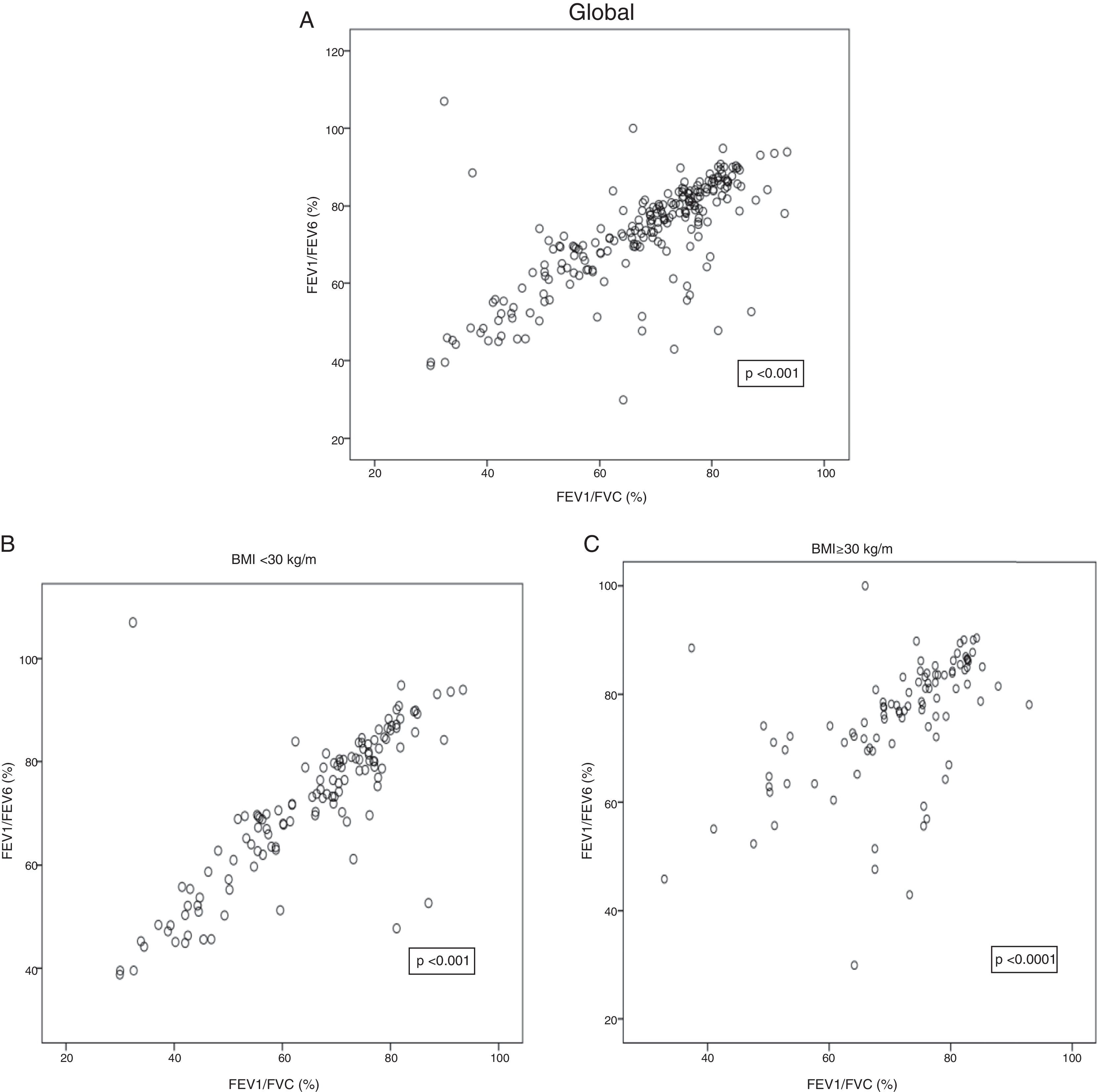
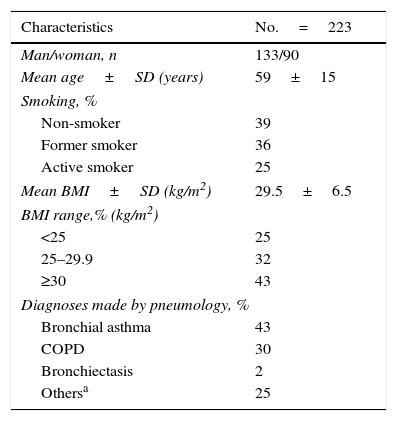
Material and methodA prospective and open cohort study in which 223 subjects who underwent conventional spirometry and COPD-6 were included. The area under the curve ROC (AUC) of FEV1/FEV6 was analyzed in the detection of obstruction for all patients in addition to BMI (BMI<30kg/m2 and BMI≥30kg/m2). Sensitivity and specificity, negative and positive predictive value as well as likelihood ratio were calculated to determine the cut-off point of COPD-6 FEV1/FEV6 ratio with greater predictive capacity.
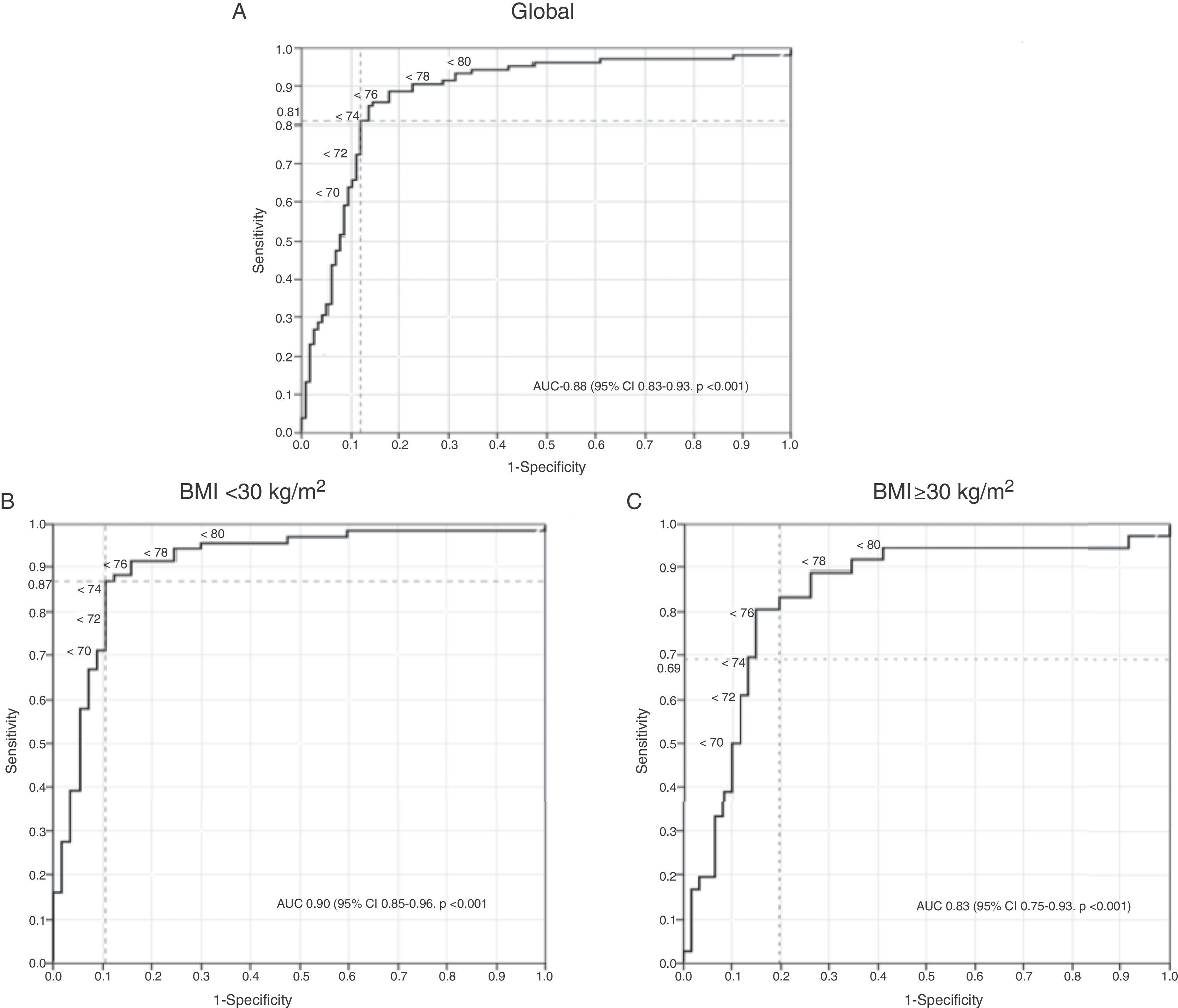
ResultsThe COPD-6 allows ruling out airflow obstruction with AUC of the estimated ROC curve of 88% (95% CI 83–93). The cut-off point FEV1/FEV6 of 0.74–0.76 shows the best predictive capacity. However, this capacity is altered according to BMI with an increase in false positives in subjects with BMI≥30kg/m2 when using the same cut-off point for the whole sample.
ConclusionThe choice of cut-off point FEV1/FEV6 for the detection of obstruction should be adjusted to the patient's BMI.
El dispositivo portátil COPD-6 se ha validado como herramienta de cribado de obstrucción al flujo aéreo a través del cociente FEV1/FEV6. Sin embargo, hasta la fecha no se ha evaluado el impacto del índice de masa corporal (IMC) sobre su capacidad para predecir dicha obstrucción. El objetivo del estudio ha sido valorar la capacidad predictiva del COPD-6 para detectar obstrucción al flujo aéreo en función del IMC del paciente.
Material y métodoEstudio observacional transversal realizado bajo los criterios de la práctica clínica habitual. Se incluyeron 223 sujetos a los que se les realizó espirometría convencional y COPD-6. Se analizó el area under the curve (AUC, «área bajo la curva») ROC del FEV1/FEV6 en la detección de obstrucción para el total de los pacientes y en función del IMC (IMC<30kg/m2 e IMC≥30kg/m2). Se calcularon la sensibilidad y la especificidad, los valores predictivos negativo y positivo, así como la razón de verosimilitud para determinar el punto de corte del cociente FEV1/FEV6 del COPD-6 con mayor capacidad predictiva.
ResultadosEl COPD-6 permite descartar obstrucción al flujo aéreo con AUC de la curva ROC estimada de 88% (IC 95% 83-93). El punto de corte FEV1/FEV6 de 0,74-0,76 muestra la mejor capacidad predictiva. Sin embargo, dicha capacidad se ve alterada en función del IMC, con un incremento de falsos positivos en sujetos con IMC≥30kg/m2 al utilizar un mismo punto de corte para toda la muestra.
ConclusiónLa elección del punto de corte del cociente FEV1/FEV6 para la detección de obstrucción debe adaptarse al IMC del paciente.