Mediastinal lymph node involvement can be understaged in cases of lung cancer (up to 20% in stage i). Sentinel node detection is a standard technique recommended in breast cancer and melanoma action guidelines, and could also be useful in cases of lung cancer.
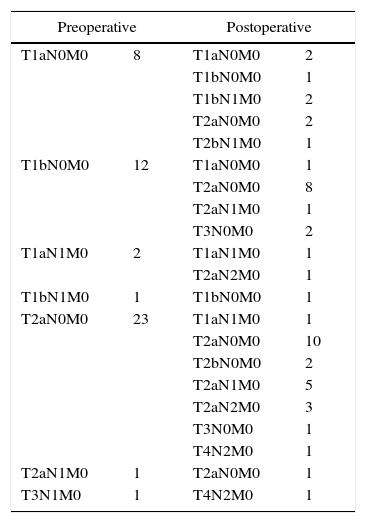
Material and methodsConsidering the detection of the sentinel node in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) as feasible, a prospective cohort study was carried out on 48 patients with resectable NSCLC, using the intraoperative injection of colloid sulphate technetium-99.
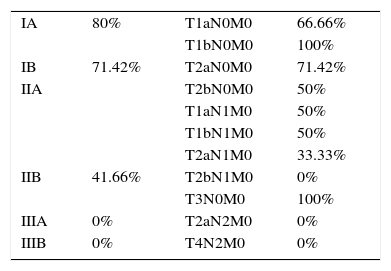
ResultsThe radioisotope migrated in all cases. The procedure's sensitivity was 88.24%, its accuracy was 95.83%, its negative predictive value was 93.94% and the false negative rate was 11.76%. No complications were associated with this technique.
ConclusionsThe detection of a sentinel node in NSCLC with the intraoperative injection of the isotope is feasible and safe, and allows for detection and sensitivity rates comparable to those of other tumor types.
En el cáncer de pulmón la afectación ganglionar mediastínica puede estar infraestadificada (hasta en el 20% de los casos en estadios i). La detección del ganglio centinela es una técnica estándar en las guías de actuación del cáncer de mama y melanoma y podría ser útil en el cáncer de pulmón.
Material y métodosCon la hipótesis de que es factible la detección del ganglio centinela en el cáncer de pulmón de células no pequeñas (CPCNP) resecable, se realizó un estudio de cohortes prospectivo en 48 pacientes con CPCNP resecables utilizando la inyección intraoperatoria de tecnecio 99 sulfato coloide.
ResultadosEl radioisótopo migró en todos los casos. La sensibilidad de la prueba es del 88,24% y la precisión del 95,83%, con un valor predictivo negativo del 93,94% y una tasa de falsos negativos del 11,76%. No existieron complicaciones relacionadas con la técnica.
ConclusionesLa detección del ganglio centinela en el CPCNP con inyección intraoperatoria de isótopos es factible y segura, y permite tasas de detección y sensibilidad superponibles a las de otros tipos de tumor.