The aim of our study was to identify the rate of diabetic patients treated for hypothyroidism and compare them with a group without type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Patients and methodsWe reviewed the computerized clinical records of 5161 patients. We identified diabetic patients treated with l-thyroxine. We compared the prevalence of PH with those patients under treatment with levothyroxine without T2DM. We excluded patients with a thyroid neoplasia, thyroid surgery, panhypopituitarism, or surgical complications of multinodular goiter or a thyroid nodule. Subclinical hypothyroidism was not considered.
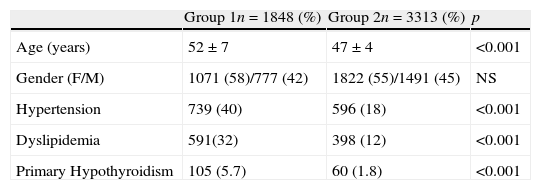
ResultsWe included 1848 adult patients with T2DM in the study group, 58% women and 42% men. For the control group, we included 3313 non-diabetic patients, 55% women and 45% men. The mean age in the study group was 52±7 years, and 47±4 years in the control group (p<.001). The rate of hypothyroidism in the study group was 5.7%, and in the control group 1.8% (odds ratio of 3.45; 95% confidence interval 2.51–4.79) (p<.001).
ConclusionA strong association between T2DM and hypothyroidism was found. We recommend a thyroid profile in all patients with T2DM, similar to the recommendation in type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Nuestro objetivo fue determinar la proporción de pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2(DM2) con hipotiroidismo primario (HP) y compararlos con un grupo sin diabetes.
Pacientes y métodosSe revisó una base electrónica que incluyó 5.161 pacientes. Se identificaron los pacientes con DM2 tratados con levotiroxina. Se comparó con la prevalencia de HP en aquellos pacientes sin DM2. Se excluyeron enfermos con neoplasia o cirugía de tiroides, panhipopituitarismo o complicaciones quirúrgicas de bocio multinodular o nódulo tiroideo.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 1.848 pacientes adultos con DM2 en el grupo de estudio, 58% mujeres y 42% hombres. Para el grupo control se revisaron 3.313 individuos, 55% mujeres y 45% hombres. La edad media del grupo de estudio fue de 52±7 años, y 47±4 años en el grupo control (p<0,001). La tasa de hipotiroidismo en el grupo de estudio fue de 5,7% (n=105) y en el grupo control 1,8% (n=60) (odds ratio 3,45; intervalo de confianza del 95% 2,51-4,79) (p<0,001).
ConclusiónExiste una asociación significativa entre HP y DM2. Recomendamos el perfil tiroideo en todos los pacientes con DM2, similar a lo sugerido en la diabetes mellitus tipo 1.