To analyse factors related to mortality and influence of antibiotic treatment on outcome in patients with nosocomial infection due to multidrug and carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (MDR-C AB).
Patients and methodsObservational and prospective study of a cohort of adult patients with MDR-C AB infection. Data collection from clinical records was done according to a standard protocol (January 2007 through June 2008). Patients with MDR-C AB infection were identified by review of results of microbiology cultures from the hospital microbiology laboratory. Epidemiological and clinical variables and predictors of mortality were analysed.
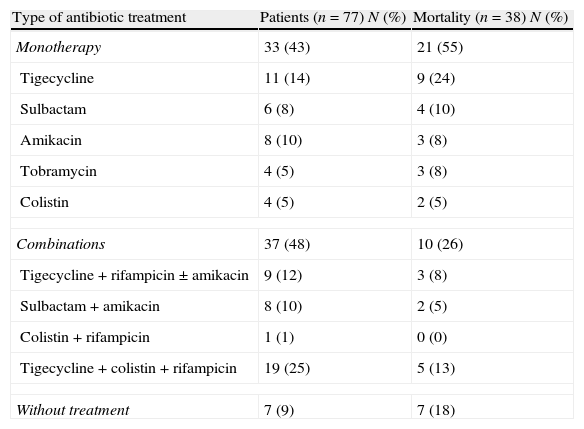
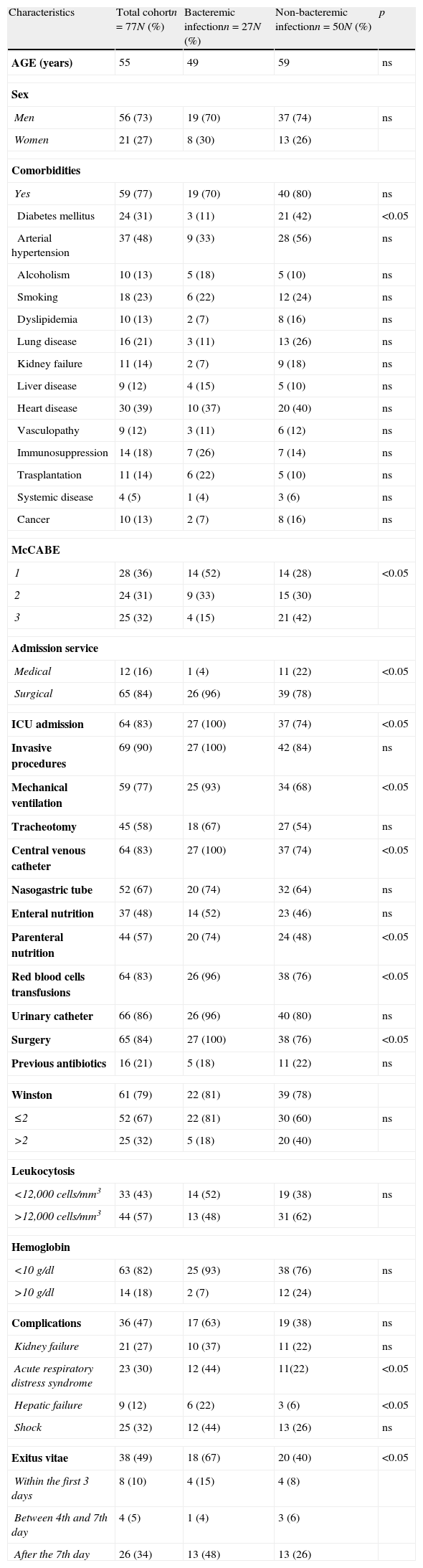
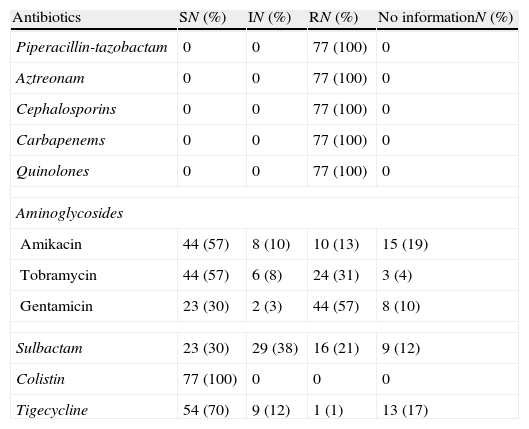
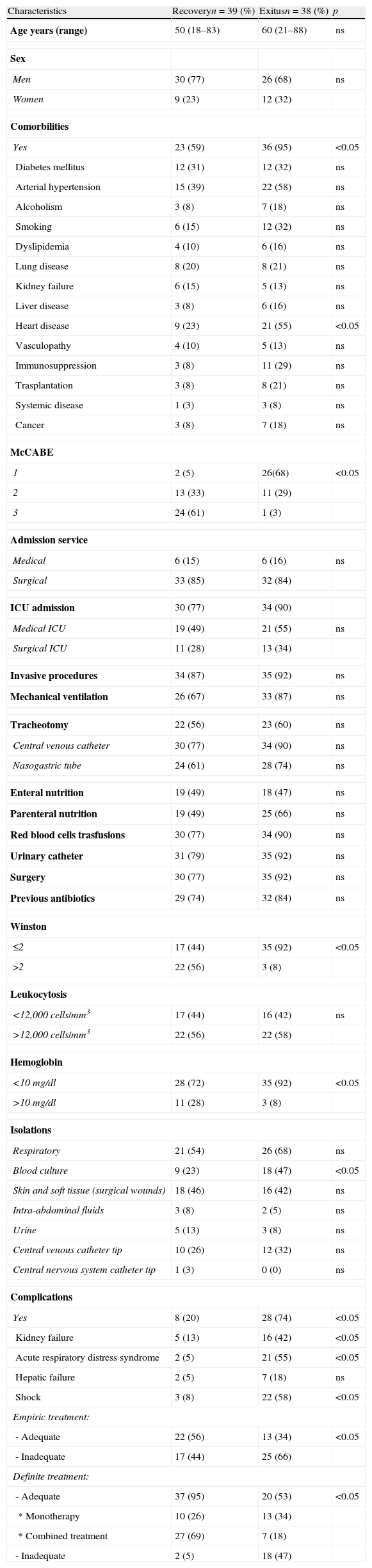
Results24 out of 101 cases were considered colonizations and 77 infections (27 bacteraemia); global mortality in infected patients was 49% (18 cases with bacteraemia and 20 with no bacteraemia). In the multivariate analysis, including the 77 cases of infection, the prognosis factors associated with mortality were age (OR 1.09; 95% CI 1.02–1.2), McCabe 1 (OR 33.98; 95% CI 4.33–266.85), bacteraemia (OR 9.89; 95% CI 1.13–86.13), inadequate empiric treatment (OR 16.7; 95% CI 2.15–129.79), and inadequate definitive treatment (OR 26.29; 95% CI 1.45–478.19). In the multivariate analysis including the 57 cases of infection with adequate definitive treatment, the prognosis factors associated with mortality were McCabe 1 (OR 24.08; 95% CI 3.67–157.96) and monotherapy versus combined treatment (OR 7.11; 95% CI 1.63–30.99).
ConclusionsOur cohort of patients with MDR-C AB infection is characterised by a very high mortality (49%); the severity of patients and inadequate treatment or monotherapy are statistically associated with mortality.
Analizar los factores asociados a mortalidad y la influencia del tratamiento antibiótico en la evolución de los pacientes con infección por Acinetobacter baumannii multiresistente y resistente a carbapenem (ABMDR-C).
Pacientes y métodosEstudio observacional y prospectivo de una cohorte de pacientes adultos con infección por ABMDR-C (Enero 2007 a junio 2008). Los casos de infección se identificaron a partir de los resultados de los cultivos microbiológicos. Analizamos las variables epidemiológicas y clínicas asociadas a mortalidad.
ResultadosVeinticuatro de los 101 aislamientos de ABMDR-C se consideraron colonizaciones y 77 fueron definidos como infecciones (27 bacteriemias); la mortalidad global de los casos de infección fue del 49% (18 pacientes con bacteriemia y 20 sin bacteriemia). En el análisis multivariado que incluía a los 77 pacientes con infección, los factores predictores de mortalidad fueron: edad (OR 1,09; IC95% 1,02-1,2), McCabe 1 (OR 33,98; IC95% 4,33-266,85), bacteriemia (OR 9,89; IC95% 1,13-86,13), tratamiento empírico inadecuado (OR 16,7; IC95% 2,15-129,79), tratamiento definitivo inadecuado(OR 26,29; IC95% 1,45-478,19). En el análisis multivariado que incluía los 57 pacientes que recibieron tratamiento definitivo adecuado, los factores predictores de mortalidad fueron McCabe 1 (OR 24,08; IC95% 3,67-157,96) y tratamiento en monoterapia versus combinaciones (OR 7,11; IC95% 1,63-30,99).
ConclusionesEn nuestra cohorte de pacientes con infección por ABMDR-C la mortalidad es elevada (49%); los pacientes graves y el tratamiento antibiótico inadecuado o el tratamiento definitivo adecuado en monoterapia se asocian de forma estadísticamente significativa a mayor mortalidad.