Determinar el efecto de la reserva cognitiva (RC) en el funcionamiento cognitivo de los pacientes con epilepsia del lóbulo temporal (ELT).
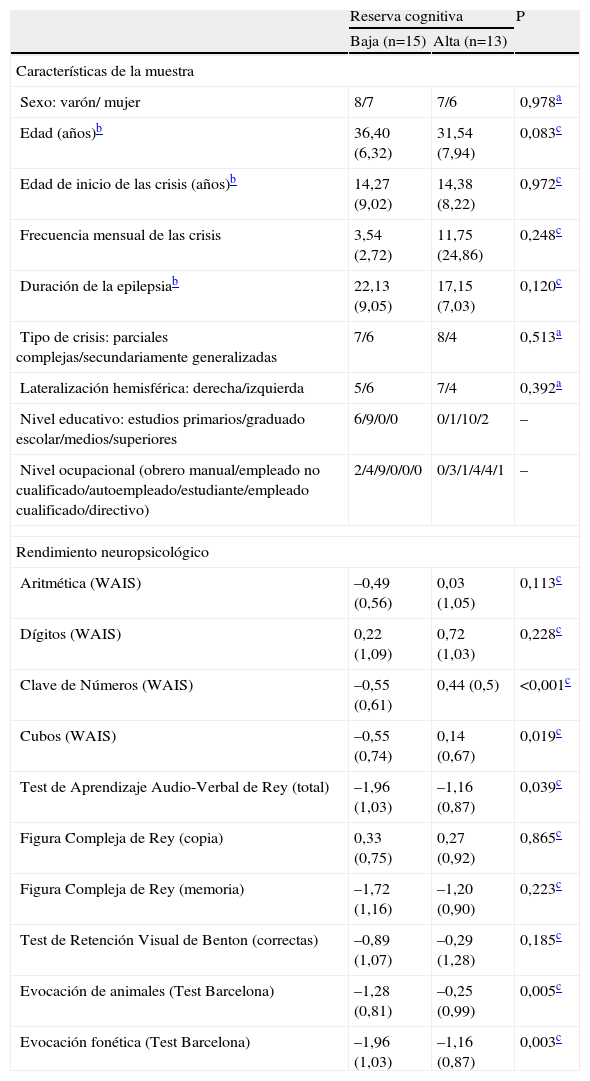
Pacientes y métodoSe evaluó con una batería neuropsicológica que incluía medidas de memoria, atención, habilidades visuoconstructivas y lenguaje a 28 pacientes con ELT admitidos en un programa de cirugía de la epilepsia. Las puntuaciones directas, ajustadas según los baremos correspondientes, se transformaron en puntuaciones normalizadas (puntuaciones z). La RC se determinó a partir del cociente intelectual premórbido, el nivel educativo y el nivel ocupacional.
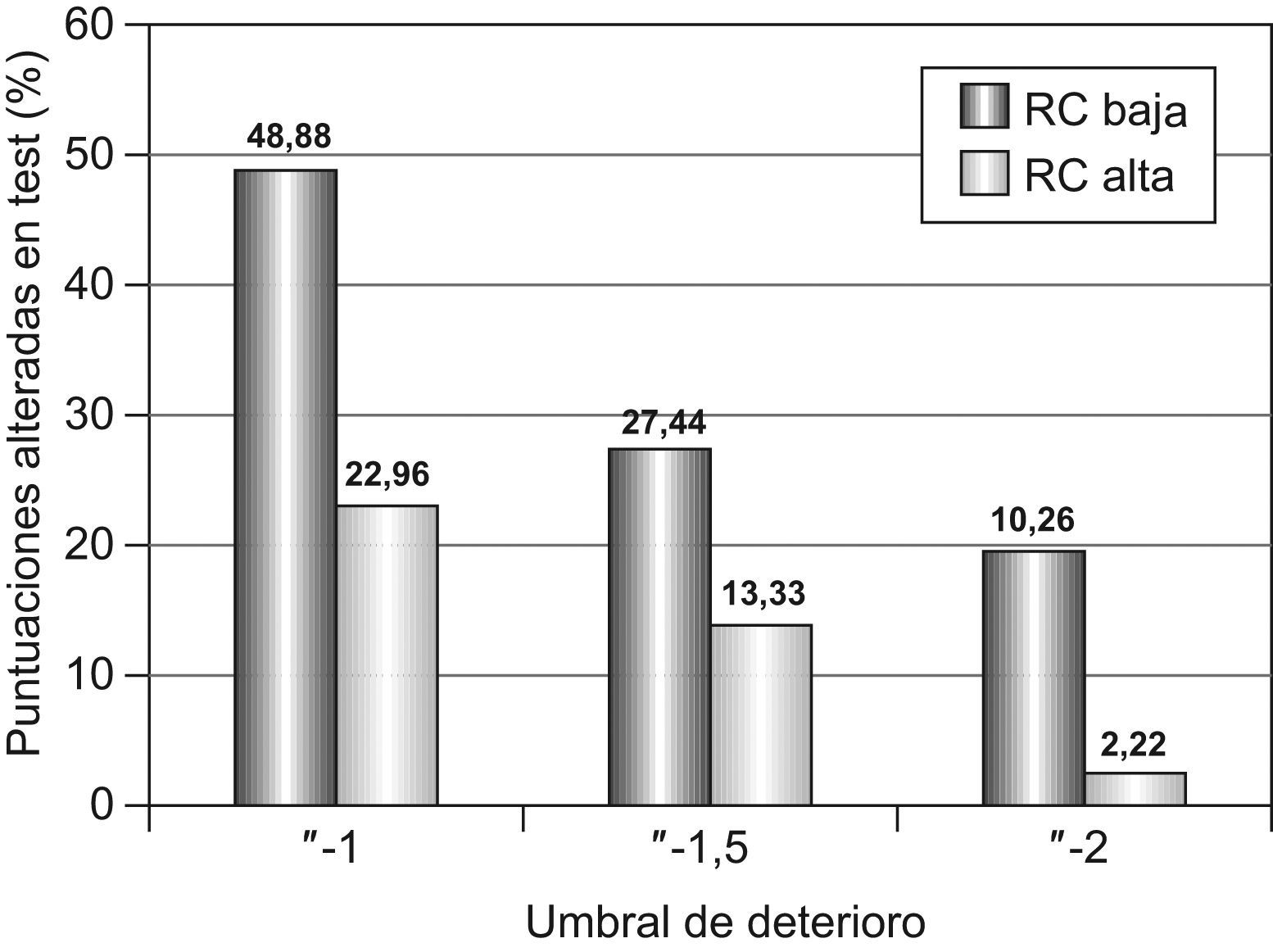
ResultadosNo se observaron diferencias significativas entre los grupos de alta y baja RC en las variables sociodemográficas y clínicas relevantes. Los pacientes con baja RC obtuvieron un rendimiento significativamente menor que los pacientes con alta RC en los test de memoria verbal (p<0,039), atención (p<0,001), visuoconstrucción (p<0,019) y fluidez fonética (p<0,003) y semántica (p<0,005).
ConclusionesLos pacientes epilépticos con baja RC muestran mayor morbilidad cognitiva que los pacientes con alta RC. Estos hallazgos indican que una mayor RC puede reducir la vulnerabilidad o retrasar la manifestación clínica del deterioro cognitivo asociado a la ELT.
Our goal was to determine the influence of the cognitive reserve (CR) on the neuropsychological performance of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE).
Patients and methodTwenty-eight patients with TLE from a program of epilepsy surgery were assessed with a neuropsychological battery that included standard clinical measures of memory, attention, visual-construction skills and language. Raw scores adjusted according normative data were transformed to z scores. CR scores were based on a combination of educational level, occupational attainment and estimated premorbid intelligence.
ResultsThere were no significance differences in socio-demographic and clinical features between the 2 groups. Epileptic patients with low CR showed significantly lower scores than patients with high CR, with regard to measures of verbal memory (p<0.039), attention (p<0.001), visual-construction skills (p<0.019), and phonetic (p<0.003) and semantic (p<0.005) fluency.
ConclusionsEpileptic patients with low CR showed greater neuropsychological morbidity than patients with high CR. These findings suggest that higher CR may decrease vulnerability or delay the clinical manifestation related to cognitive deficits following TLE.