Fundamento y objetivos: La mayoría de los pacientes con ictus llega a los servicios de urgencias fuera de la ventana terapéutica para el inicio del tratamiento trombolítico. El Código Ictus (CI) ha demostrado su eficacia para reducir los tiempos de latencia en ensayos clínicos, pero se desconoce su eficacia en la práctica clínica diaria. El objetivo fue determinar la aplicabilidad del CI en la práctica clínica diaria y su impacto en la eficacia del tratamiento trombolítico con rt-PA.
Pacientes y método: Pacientes con ictus isquémico de la arteria cerebral media (ACM) tratados con rt-PA desde junio de 2000 a diciembre de 2001, divididos en 3 períodos de 6 meses. Se valoró la influencia de la activación del CI en los tiempos de latencia, recanalización arterial y evolución neurológica precoz.
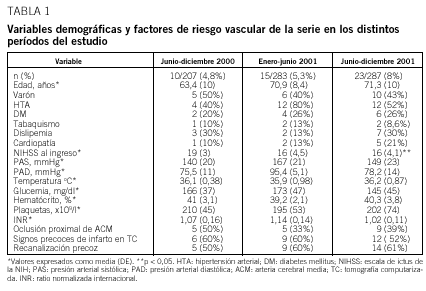
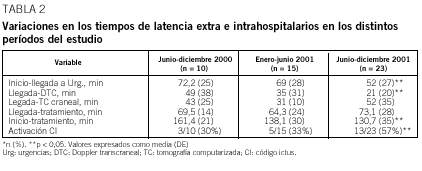
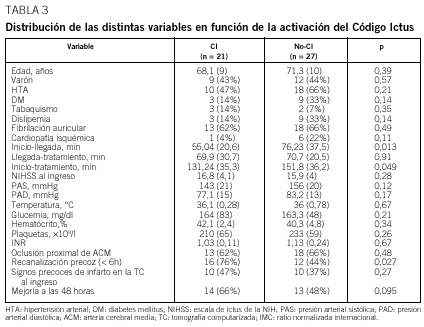
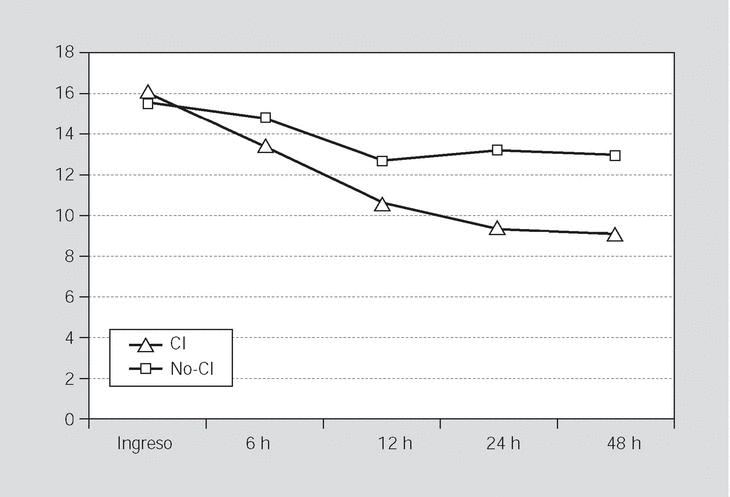
Resultados: Se estudió a 48 pacientes. Se observó un incremento significativo en el número de pacientes tratados con rt-PA en los 3 períodos (4,8; 5,3; 8,0%). Se produjo un acortamiento progresivo y significativo (p = 0,036) del retraso global en el tiempo de inicio de la fibrinólisis (de 161,4 a 130,0 min), fundamentalmente por reducción en el tiempo de llegada a urgencias (72,2 a 52,0 min; p = 0,05). La proporción de pacientes tratados con fibrinolíticos en los que se activó el CI aumentó con el tiempo (p = 0,032). La activación del CI redujo el tiempo de llegada a urgencias (p = 0,013) y el del inicio del tratamiento (p = 0,049), e incrementó el porcentaje de recanalización precoz (p = 0,027) y la probabilidad de una mejor evolución neurológica a las 48 h (p = 0,036).
Conclusiones: La activación del CI es muy útil en el tratamiento de la fase aguda del ictus: permite tratar con rt-PA i.v. a un mayor porcentaje de pacientes y de forma más precoz, lo que se traduce en una mejor evolución clínica de estos pacientes.
Background and objectives: Most stroke patients arrive to emergency rooms too late, many times beyond the therapeutic window for thrombolysis. The activation of a Stroke Code (SC) has proven to be effective in decreasing the latency time for starting therapy in clinical trials. However, its usefulness in routine clinical practice is uncertain. The aim of this study was to determine the feasibility of applying an SC in the daily clinical practice and to evaluate its impact on the efficacy of t-PA thrombolytic treatment.
Patients an method: We included middle-cerebral artery stroke patients treated with IV t-PA from June 2000 to December 2001 who were categorized into three periods of 6 months each. The influence of SC activation on the latency time, arterial recanalization and early neurological recovery was evaluated.
Results: Forty-eight patients were prospectively studied. A significant increase in the number of t-PA treated patients was observed in the three periods (4.8%, 5.3% and 8%). A significant progressive decrease (p = 0.036) in the overall delay to start t-PA was observed (from 161.4 to 130 minutes). The proportion of t-PA treated patients in whome SC was activated increased gradually (p = 0.032). SC activation reduced time from symptom onset to hospital arrival (p = 0.013) as well as the "door-to-needle" time (p = 0.049). The rate of early recanalization (p = 0.027) and neurological recovery (p = 0.036) at 48 hours was significantly higher in patients in whom SC was activated than in those in whom SC was not.
Conclusions: SC activation is very useful in the management of acute stroke, increasing the rate of t-PA treated patients and improving the clinical outcome.